<!--
~ Copyright (c) 2024- Datalayer, Inc.
~
~ BSD 3-Clause License
-->
[](https://datalayer.io)
[](https://github.com/sponsors/datalayer)
<div align="center">
<!-- omit in toc -->
# 🪐🔧 Jupyter MCP Server
**An [MCP](https://modelcontextprotocol.io) server developed for AI to connect and manage Jupyter Notebooks in real-time**
*Developed by [Datalayer](https://github.com/datalayer)*
[](https://pypi.org/project/jupyter-mcp-server)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/jupyter-mcp-server)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause)
</div>
> [!NOTE]
> **We Need Your Feedback!**
>
> We're actively developing support for **JupyterHub** and **Google Colab** deployments. If you're using or planning to use Jupyter MCP Server with these platforms, we'd love to hear from you!
>
> - 🏢 **JupyterHub users**: Share your deployment setup and requirements
> - 🌐 **Google Colab users**: Help us understand your use cases and workflows
>
> Join the conversation in our [Community page](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/community) - your feedback will help us prioritize features and ensure these integrations work seamlessly for your needs.
## 📖 Table of Contents
- [Key Features](#-key-features)
- [MCP Overview](#-mcp-overview)
- [Getting Started](#-getting-started)
- [Best Practices](#-best-practices)
- [Contributing](#-contributing)
- [Resources](#-resources)
## 🚀 Key Features
- ⚡ **Real-time control:** Instantly view notebook changes as they happen.
- 🔁 **Smart execution:** Automatically adjusts when a cell run fails thanks to cell output feedback.
- 🧠 **Context-aware:** Understands the entire notebook context for more relevant interactions.
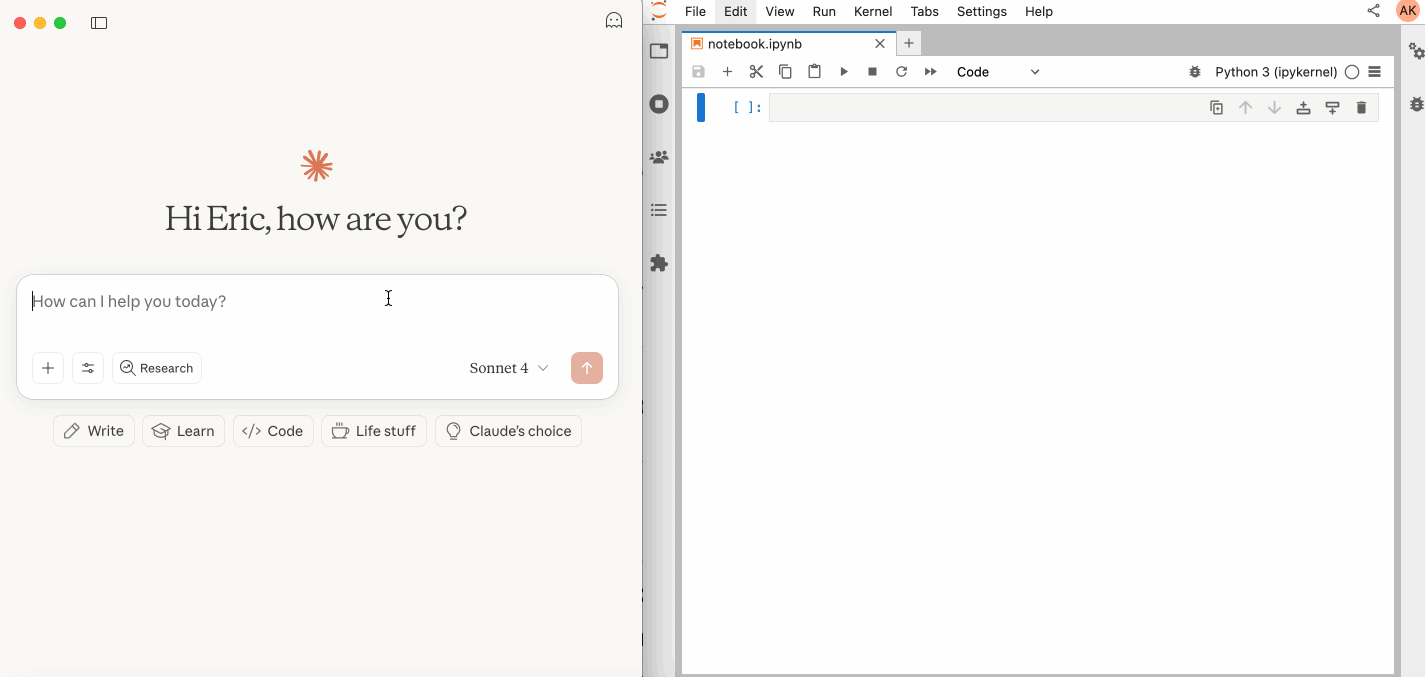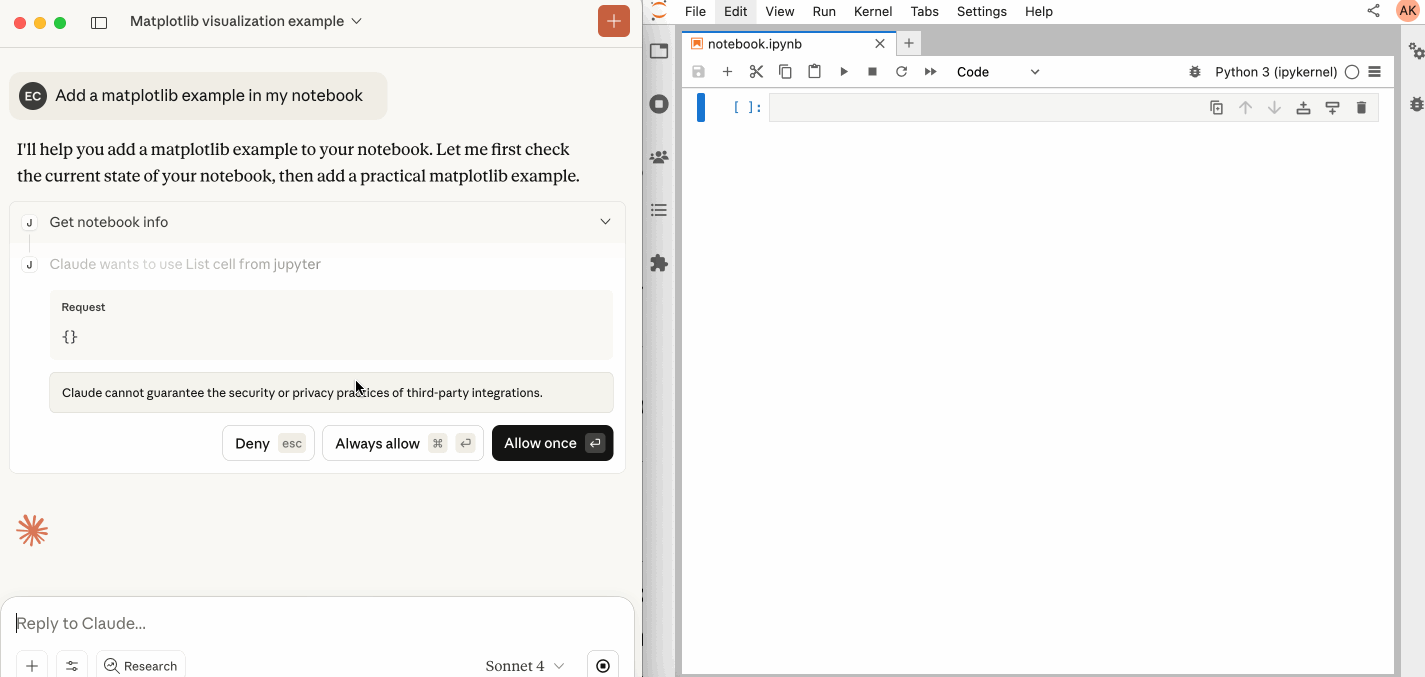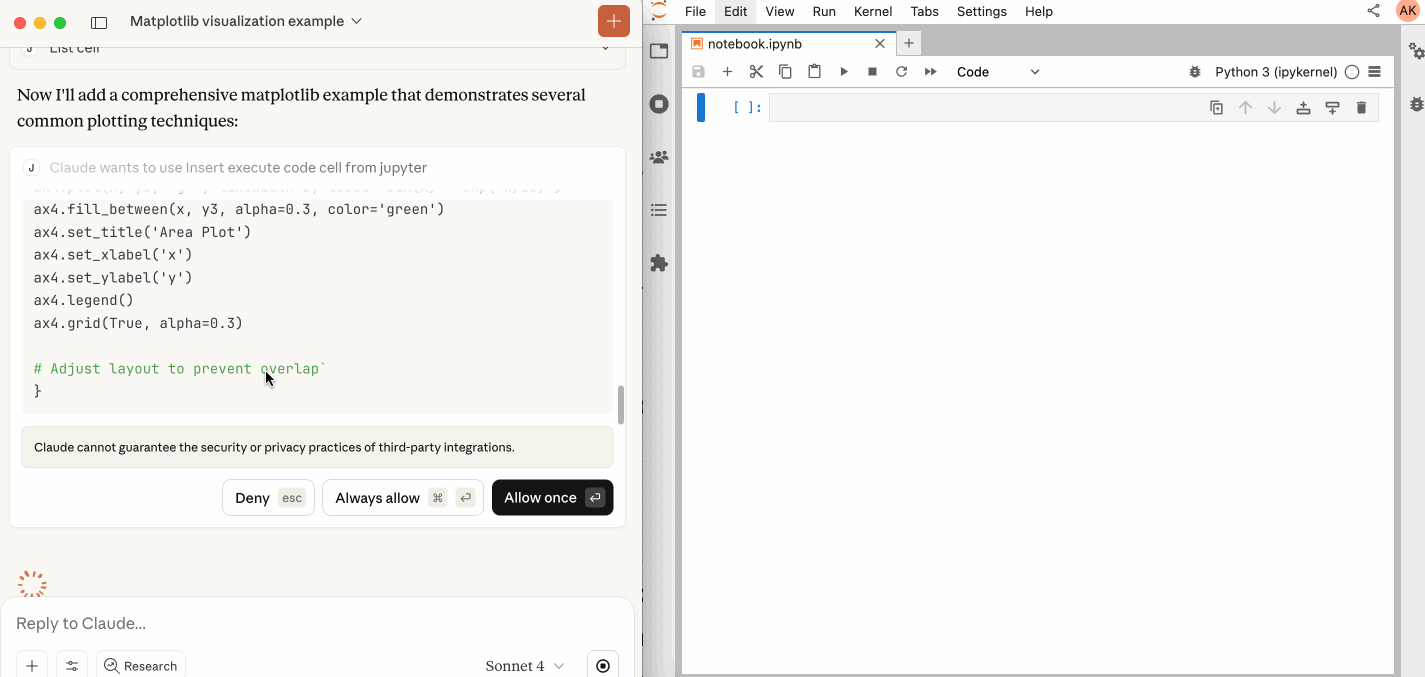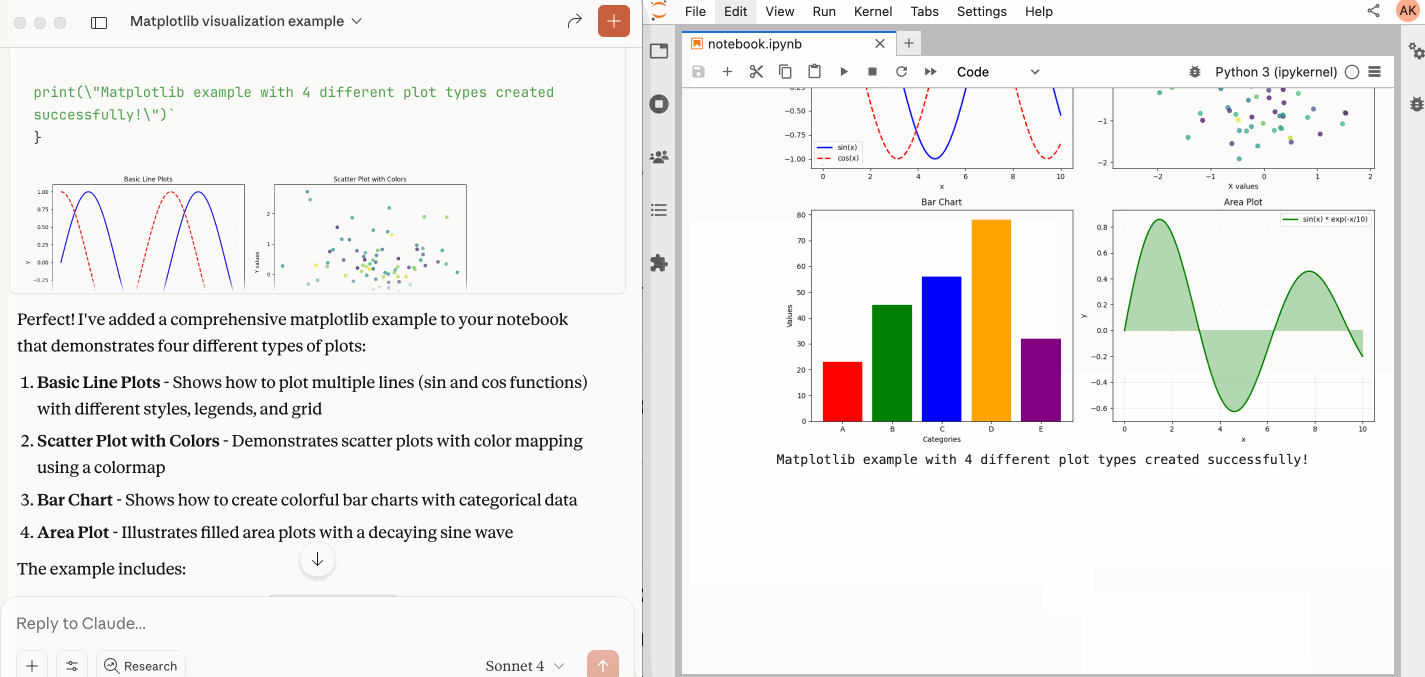
- 📊 **Multimodal support:** Support different output types, including images, plots, and text.
- 📚 **Multi-notebook support:** Seamlessly switch between multiple notebooks.
- 🎨 **JupyterLab integration:** Enhanced UI integration like automatic notebook opening.
- 🤝 **MCP-compatible:** Works with any MCP client, such as Claude Desktop, Cursor, Windsurf, and more.
Compatible with any Jupyter deployment (local, JupyterHub, ...) and with [Datalayer](https://datalayer.ai) hosted Notebooks.
## 🔧 MCP Overview
### 🔧 Tools Overview
The server provides a rich set of tools for interacting with Jupyter notebooks, categorized as follows.
For more details on each tool, their parameters, and return values, please refer to the [official Tools documentation](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/tools).
#### Server Management Tools
| Name | Description |
| :--------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `list_files` | List files and directories in the Jupyter server's file system. |
| `list_kernels` | List all available and running kernel sessions on the Jupyter server. |
| `connect_to_jupyter` | Connect to a Jupyter server dynamically without restarting the MCP server. *Not available when running as Jupyter extension. Useful for switching servers dynamically or avoiding hardcoded configuration.* [Read more](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/reference/tools/#3-connect_to_jupyter) |
#### Multi-Notebook Management Tools
| Name | Description |
| :----------------- | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `use_notebook` | Connect to a notebook file, create a new one, or switch between notebooks. |
| `list_notebooks` | List all notebooks available on the Jupyter server and their status |
| `restart_notebook` | Restart the kernel for a specific managed notebook. |
| `unuse_notebook` | Disconnect from a specific notebook and release its resources. |
| `read_notebook` | Read notebook cells source content with brief or detailed format options. |
#### Cell Operations and Execution Tools
| Name | Description |
| :------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `read_cell` | Read the full content (Metadata, Source and Outputs) of a single cell. |
| `insert_cell` | Insert a new code or markdown cell at a specified position. |
| `delete_cell` | Delete a cell at a specified index. |
| `overwrite_cell_source` | Overwrite the source code of an existing cell. |
| `execute_cell` | Execute a cell with timeout, supports multimodal output including images. |
| `insert_execute_code_cell` | Insert a new code cell and execute it in one step. |
| `execute_code` | Execute code directly in the kernel, supports magic commands and shell commands. |
#### JupyterLab Integration
*Available only when JupyterLab mode is enabled. It is enabled by default.*
When running in JupyterLab mode, Jupyter MCP Server integrates with [jupyter-mcp-tools](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-mcp-tools) to expose additional JupyterLab commands as MCP tools. By default, the following tools are enabled:
| Name | Description |
| :---------------------------- | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `notebook_run-all-cells` | Execute all cells in the current notebook sequentially |
| `notebook_get-selected-cell` | Get information about the currently selected cell |
<details>
<summary><strong>📚 Learn how to customize additional tools</strong></summary>
You can now customize which tools from `jupyter-mcp-tools` are available using the `allowed_jupyter_mcp_tools` configuration parameter. This allows you to enable additional notebook operations, console commands, file management tools, and more.
```bash
# Example: Enable additional tools via command-line
jupyter lab --port 4040 --IdentityProvider.token MY_TOKEN --JupyterMCPServerExtensionApp.allowed_jupyter_mcp_tools="notebook_run-all-cells,notebook_get-selected-cell,notebook_append-execute,console_create"
```
For the complete list of available tools and detailed configuration instructions, please refer to the [Additional Tools documentation](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/reference/tools-additional).
</details>
### 📝 Prompt Overview
The server also supports [prompt feature](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/server/prompts) of MCP, providing a easy way for user to interact with Jupyter notebooks.
| Name | Description |
| :------------- | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `jupyter-cite` | Cite specific cells from specified notebook (like `@` in Coding IDE or CLI) |
For more details on each prompt, their input parameters, and return content, please refer to the [official Prompt documentation](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/reference/prompts).
## 🏁 Getting Started
For comprehensive setup instructions—including `Streamable HTTP` transport, running as a Jupyter Server extension and advanced configuration—check out [our documentation](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/). Or, get started quickly with `JupyterLab` and `STDIO` transport here below.
### 1. Set Up Your Environment
```bash
pip install jupyterlab==4.4.1 jupyter-collaboration==4.0.2 jupyter-mcp-tools>=0.1.4 ipykernel
pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt
pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17
```
> [!TIP]
> To confirm your environment is correctly configured:
> 1. Open a notebook in JupyterLab
> 2. Type some content in any cell (code or markdown)
> 3. Observe the tab indicator: you should see an "×" appear next to the notebook name, indicating unsaved changes
> 4. Wait a few seconds—the "×" should automatically change to a "●" without manually saving
>
> This automatic saving behavior confirms that the real-time collaboration features are working properly, which is essential for MCP server integration.
### 2. Start JupyterLab
```bash
# Start JupyterLab on port 8888, allowing access from any IP and setting a token
jupyter lab --port 8888 --IdentityProvider.token MY_TOKEN --ip 0.0.0.0
```
> [!NOTE]
> If you are running notebooks through JupyterHub instead of JupyterLab as above, refer to our [JupyterHub setup guide](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech//providers/jupyterhub-streamable-http/).
### 3. Configure Your Preferred MCP Client
Next, configure your MCP client to connect to the server. We offer two primary methods—choose the one that best fits your needs:
- **📦 Using `uvx` (Recommended for Quick Start):** A lightweight and fast method using `uv`. Ideal for local development and first-time users.
- **🐳 Using `Docker` (Recommended for Production):** A containerized approach that ensures a consistent and isolated environment, perfect for production or complex setups.
<details>
<summary><b>📦 Using uvx (Quick Start)</b></summary>
First, install `uv`:
```bash
pip install uv
uv --version
# should be 0.6.14 or higher
```
See more details on [uv installation](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/).
Then, configure your client:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["jupyter-mcp-server@latest"],
"env": {
"JUPYTER_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"JUPYTER_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}
```
</details>
<details>
<summary><b>🐳 Using Docker (Production)</b></summary>
**On macOS and Windows:**
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run", "-i", "--rm",
"-e", "JUPYTER_URL",
"-e", "JUPYTER_TOKEN",
"-e", "ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT",
"datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest"
],
"env": {
"JUPYTER_URL": "http://host.docker.internal:8888",
"JUPYTER_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}
```
**On Linux:**
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run", "-i", "--rm",
"-e", "JUPYTER_URL",
"-e", "JUPYTER_TOKEN",
"-e", "ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT",
"--network=host",
"datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest"
],
"env": {
"JUPYTER_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"JUPYTER_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}
```
</details>
> [!TIP]
>
> 1. **Port Configuration**: Ensure the `port` in your Jupyter URLs matches the one used in the `jupyter lab` command. For simplified config, set this in `JUPYTER_URL`.
> 1. **Server Separation**: Use `JUPYTER_URL` when both services are on the same server, or set individual variables for advanced deployments. The different URL variables exist because some deployments separate notebook storage (`DOCUMENT_URL`) from kernel execution (`RUNTIME_URL`).
> 1. **Authentication**: In most cases, document and runtime services use the same authentication token. Use `JUPYTER_TOKEN` for simplified config or set `DOCUMENT_TOKEN` and `RUNTIME_TOKEN` individually for different credentials.
> 1. **Notebook Path**: The `DOCUMENT_ID` parameter specifies the path to the notebook the MCP client default to connect. It should be relative to the directory where JupyterLab was started. If you omit `DOCUMENT_ID`, the MCP client can automatically list all available notebooks on the Jupyter server, allowing you to select one interactively via your prompts.
> 1. **Image Output**: Set `ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT` to `false` if your LLM does not support mutimodel understanding.
For detailed instructions on configuring various MCP clients—including [Claude Desktop](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/clients/claude_desktop), [VS Code](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/clients/vscode), [Cursor](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/clients/cursor), [Cline](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/clients/cline), and [Windsurf](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/clients/windsurf) — see the [Clients documentation](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/clients).
## ✅ Best Practices
- Interact with LLMs that supports multimodal input (like Gemini 2.5 Pro) to fully utilize advanced multimodal understanding capabilities.
- Use a MCP client that supports returning image data and can parse it (like Cursor, Gemini CLI, etc.), as some clients may not support this feature.
- Break down complex task (like the whole data science workflow) into multiple sub-tasks (like data cleaning, feature engineering, model training, model evaluation, etc.) and execute them step-by-step.
- Provide clearly structured prompts and rules (👉 Visit our [Prompt Templates](prompt/README.md) to get started)
- Provide as much context as possible (like already installed packages, field explanations for existing datasets, current working directory, detailed task requirements, etc.).
## 🤝 Contributing
We welcome contributions of all kinds! Here are some examples:
- 🐛 Bug fixes
- 📝 Improvements to existing features
- 🔧 New feature development
- 📚 Documentation improvements and prompt templates
For detailed instructions on how to get started with development and submit your contributions, please see our [**Contributing Guide**](CONTRIBUTING.md).
### Our Contributors
[](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server/graphs/contributors)
## 📚 Resources
Looking for blog posts, videos, or other materials about Jupyter MCP Server?
👉 Visit the [**Resources section**](https://jupyter-mcp-server.datalayer.tech/resources) in our documentation for more!
[](https://star-history.com/#datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server&type=Date)
______________________________________________________________________
<div align="center">
**If this project is helpful to you, please give us a ⭐️**
Made with ❤️ by [Datalayer](https://github.com/datalayer)
</div>