Supports Helm v3 operations for package management in Kubernetes, enabling installation, upgrades, and uninstallation of Helm charts through natural language commands.
Provides comprehensive access to Kubernetes functionality including resource management, deployment scaling, pod operations, security configuration, diagnostics, and monitoring through natural language.
Allows installation of the MCP tool directly from PyPI, with support for version-specific installations and development versions.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Kubectl MCP Toollist all pods in the default namespace"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Installation
Quick Start with npx (Recommended - Zero Install)
Or install with pip (Python)
Related MCP server: MCP Toolkit
📑 Table of Contents
What Can You Do?
Simply ask your AI assistant in natural language:
💬 "Why is my pod crashing?"
Instant crash diagnosis with logs, events, and resource analysis
Root cause identification with actionable recommendations
💬 "Deploy a Redis cluster with 3 replicas"
Creates deployment with best practices
Configures services, persistent storage, and health checks
💬 "Show me which pods are wasting resources"
AI-powered cost optimization analysis
Resource recommendations with potential savings
💬 "Which services can't reach the database?"
Network connectivity diagnostics with DNS resolution
Service chain tracing from ingress to pods
💬 "Audit security across all namespaces"
RBAC permission analysis
Secret security scanning and pod security policies
💬 "Show me the cluster dashboard"
Interactive HTML dashboards with live metrics
Visual timeline of events and resource usage
253 powerful tools | 8 workflow prompts | 8 data resources | Works with all major AI assistants
Why kubectl-mcp-server?
🚀 Stop context-switching - Manage Kubernetes directly from your AI assistant conversations
🧠 AI-powered diagnostics - Get intelligent troubleshooting, not just raw data
💰 Built-in cost optimization - Identify waste and get actionable savings recommendations
🔒 Enterprise-ready - OAuth 2.1 auth, RBAC validation, non-destructive mode, secret masking
⚡ Zero learning curve - Natural language instead of memorizing kubectl commands
🌐 Universal compatibility - Works with Claude, Cursor, Windsurf, Copilot, and 15+ other AI tools
📊 Visual insights - Interactive dashboards and browser automation for web-based tools
☸️ Production-grade - Deploy in-cluster with kMCP, 216 passing tests, active maintenance
From debugging crashed pods to optimizing cluster costs, kubectl-mcp-server is your AI-powered DevOps companion.
Live Demos
Claude Desktop
Cursor AI
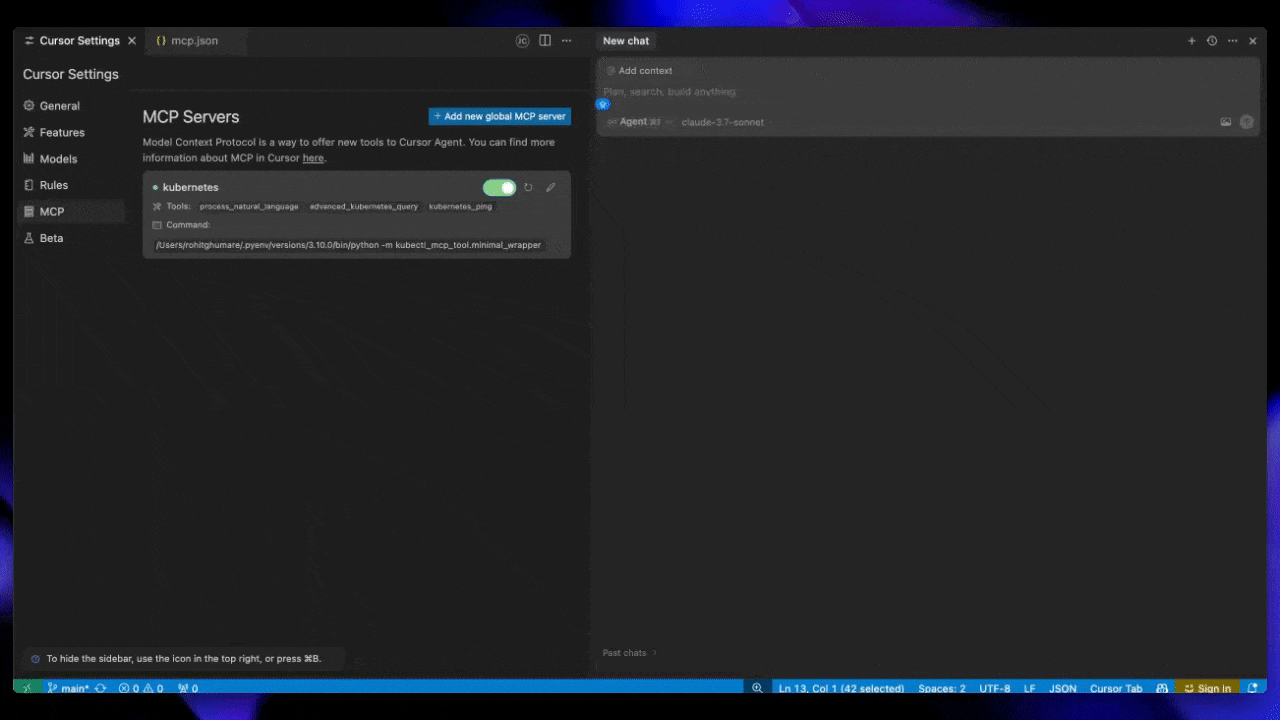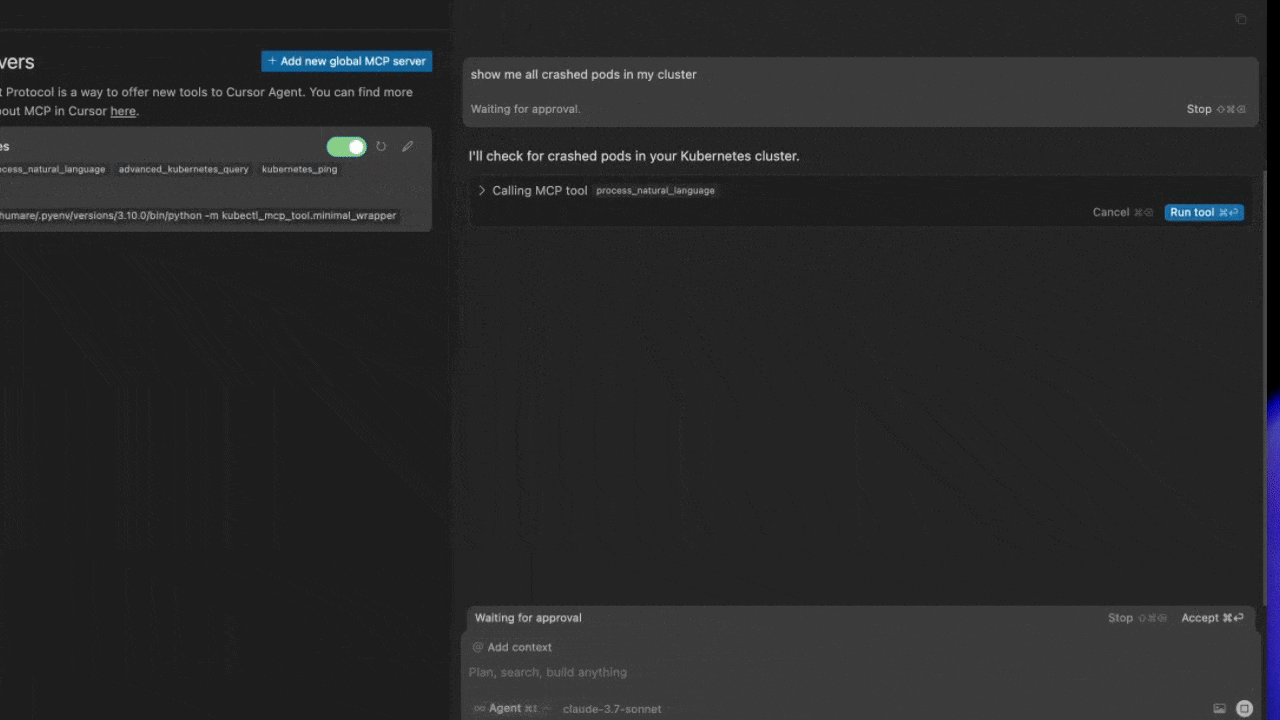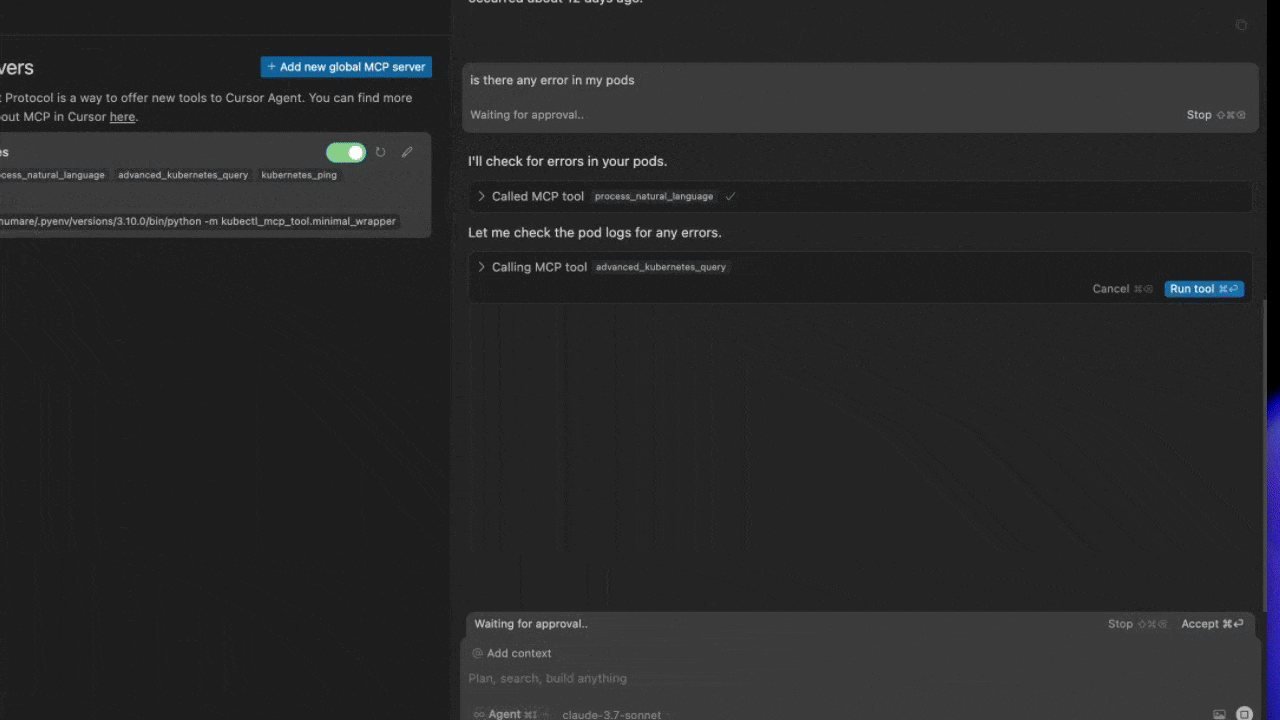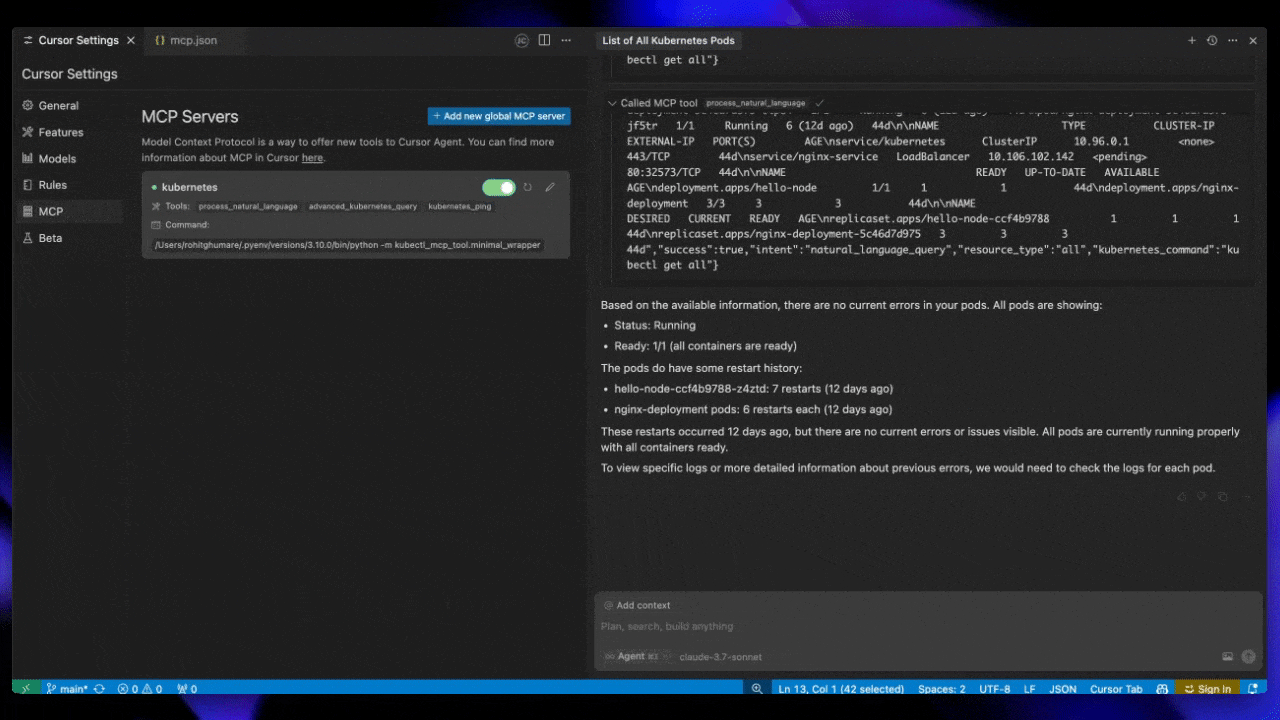
Windsurf
Installation
Quick Start with npx (Recommended - Zero Install)
Or install with pip (Python)
Install from GitHub Release
Prerequisites
Python 3.9+ (for pip installation)
Node.js 14+ (for npx installation)
kubectl installed and configured
Access to a Kubernetes cluster
Docker
Getting Started
1. Test the Server (Optional)
Before integrating with your AI assistant, verify the installation:
2. Connect to Your AI Assistant
Choose your favorite AI assistant and add the configuration:
Quick Setup with Your AI Assistant
Claude Desktop
Add to ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json:
Cursor AI
Add to ~/.cursor/mcp.json:
Windsurf
Add to ~/.config/windsurf/mcp.json:
Using Python Instead of npx
More integrations: GitHub Copilot, Goose, Gemini CLI, Roo Code, and 15+ other clients —> see full configuration guide below.
3. Restart Your AI Assistant
After adding the configuration, restart your AI assistant (GitHub Copilot, Claude Code,Claude Desktop, Cursor, etc.) to load the MCP server.
4. Try These Commands
Start a conversation with your AI assistant and try these:
Troubleshooting:
Deployments:
Cost & Optimization:
Security:
Helm:
Multi-Cluster:
MCP Client Compatibility
Works seamlessly with all MCP-compatible AI assistants:
Client | Status | Client | Status |
Claude Desktop | ✅ Native | Claude Code | ✅ Native |
Cursor | ✅ Native | Windsurf | ✅ Native |
GitHub Copilot | ✅ Native | OpenAI Codex | ✅ Native |
Gemini CLI | ✅ Native | Goose | ✅ Native |
Roo Code | ✅ Native | Kilo Code | ✅ Native |
Amp | ✅ Native | Trae | ✅ Native |
OpenCode | ✅ Native | Kiro CLI | ✅ Native |
Antigravity | ✅ Native | Clawdbot | ✅ Native |
Droid (Factory) | ✅ Native | Any MCP Client | ✅ Compatible |
All Supported AI Assistants
Claude Code
Add to ~/.config/claude-code/mcp.json:
GitHub Copilot (VS Code)
Add to VS Code settings.json:
Goose
Add to ~/.config/goose/config.yaml:
Gemini CLI
Add to ~/.gemini/settings.json:
Roo Code / Kilo Code
Add to ~/.config/roo-code/mcp.json or ~/.config/kilo-code/mcp.json:
Complete Feature Set
253 MCP Tools for Complete Kubernetes Management
Category | Tools |
Pods |
|
Deployments |
|
Workloads |
|
Services & Networking |
|
Storage |
|
Config |
|
Cluster |
|
RBAC & Security |
|
CRDs |
|
Helm Releases |
|
Helm Charts |
|
Helm Repos |
|
Helm Operations |
|
Helm Development |
|
Context |
|
Diagnostics |
|
Operations |
|
Autoscaling |
|
Cost Optimization |
|
Advanced |
|
UI Dashboards |
|
GitOps (Flux/Argo) |
|
Cert-Manager |
|
Policy (Kyverno/Gatekeeper) |
|
Backup (Velero) |
|
KEDA Autoscaling |
|
Cilium/Hubble |
|
Argo Rollouts/Flagger |
|
Cluster API |
|
KubeVirt VMs |
|
Istio/Kiali |
|
vCluster (vind) |
|
kind (K8s in Docker) |
|
MCP Resources
Access Kubernetes data as browsable resources:
Resource URI | Description |
| List all available kubectl contexts |
| Get current active context |
| Get current namespace |
| List all namespaces |
| Get cluster information |
| Get detailed node information |
| Get Kubernetes version |
| List available API resources |
| Get deployment YAML |
| Get service YAML |
| Get pod YAML |
| Get ConfigMap YAML |
| Get secret YAML (data masked) |
| Get ingress YAML |
MCP Prompts
Pre-built workflow prompts for common Kubernetes operations:
Prompt | Description |
| Comprehensive troubleshooting guide for pods/deployments |
| Step-by-step deployment workflow |
| Security scanning and RBAC analysis workflow |
| Resource optimization and cost analysis workflow |
| Backup and recovery planning workflow |
| Network debugging for services and connectivity |
| Scaling guide with HPA/VPA best practices |
| Kubernetes cluster upgrade planning |
Key Capabilities
🤖 253 Powerful Tools - Complete Kubernetes management from pods to security
🎯 8 AI Workflow Prompts - Pre-built workflows for common operations
📊 8 MCP Resources - Browsable Kubernetes data exposure
🎨 6 Interactive Dashboards - HTML UI tools for visual cluster management
🌐 26 Browser Tools - Web automation with cloud provider support
🔄 107 Ecosystem Tools - GitOps, Cert-Manager, Policy, Backup, KEDA, Cilium, Rollouts, CAPI, KubeVirt, Istio, vCluster
⚡ Multi-Transport - stdio, SSE, HTTP, streamable-http
🔐 Security First - Non-destructive mode, secret masking, RBAC validation
🏥 Advanced Diagnostics - AI-powered troubleshooting and cost optimization
☸️ Multi-Cluster - Target any cluster via context parameter in every tool
🎡 Full Helm v3 - Complete chart lifecycle management
🔧 Powerful CLI - Shell-friendly tool discovery and direct calling
🐳 Cloud Native - Deploy in-cluster with kMCP or kagent
Using the CLI
The built-in CLI lets you explore and test tools without an AI assistant:
CLI Features
Structured errors: Actionable error messages with suggestions
Colorized output: Human-readable with JSON mode for scripting (
--json)NO_COLOR support: Respects
NO_COLORenvironment variableStdin support: Pipe JSON arguments to commands
Advanced Configuration
Transport Modes
The server supports multiple transport protocols:
Transport Options:
--transport: Choose fromstdio,sse,http,streamable-http(default:stdio)--host: Bind address (default:0.0.0.0)--port: Port for network transports (default:8000)--non-destructive: Enable read-only mode (blocks delete, apply, create operations)
Environment Variables
Core Settings:
Variable | Description | Default |
| Path to kubeconfig file |
|
| Enable verbose logging |
|
| Log file path | None (stdout) |
Authentication (Enterprise):
Variable | Description | Default |
| Enable OAuth 2.1 authentication |
|
| OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server URL | - |
| JWKS endpoint URL | Auto-derived |
| Expected token audience |
|
| Required OAuth scopes |
|
Browser Automation (Optional):
Variable | Description | Default |
| Enable browser automation tools |
|
| Cloud provider (browserbase/browseruse) | None |
| Persistent profile path | None |
| Remote CDP WebSocket URL | None |
| Proxy server URL | None |
Optional: Interactive Dashboards (6 UI Tools)
Get beautiful HTML dashboards for visual cluster management.
Installation:
6 Dashboard Tools:
📊
show_pods_dashboard_ui- Real-time pod status table📝
show_pod_logs_ui- Interactive log viewer with search🎯
show_cluster_overview_ui- Complete cluster dashboard⚡
show_events_timeline_ui- Events timeline with filtering📄
show_resource_yaml_ui- YAML viewer with syntax highlighting📸
render_k8s_dashboard_screenshot- Export dashboards as PNG
Features:
🎨 Dark theme optimized for terminals (Catppuccin)
🔄 Graceful fallback to JSON for incompatible clients
🖼️ Screenshot rendering for universal compatibility
🚀 Zero external dependencies
Works With: Goose, LibreChat, Nanobot (full HTML UI) | Claude Desktop, Cursor, others (JSON + screenshots)
Optional: Browser Automation (26 Tools)
Automate web-based Kubernetes operations with agent-browser integration.
Quick Setup:
What You Can Do:
🌐 Test deployed apps via Ingress URLs
📸 Screenshot Grafana, ArgoCD, or any K8s dashboard
☁️ Automate cloud console operations (EKS, GKE, AKS)
🏥 Health check web applications
📄 Export monitoring dashboards as PDF
🔐 Test authentication flows with persistent sessions
26 Available Tools: browser_open, browser_screenshot, browser_click, browser_fill, browser_test_ingress, browser_screenshot_grafana, browser_health_check, and 19 more
Advanced Features:
Cloud providers: Browserbase, Browser Use
Persistent browser profiles
Remote CDP connections
Session management
Optional: kubectl-mcp-app (8 Interactive UI Dashboards)
A standalone npm package that provides beautiful, interactive UI dashboards for Kubernetes management using the MCP ext-apps SDK.
Installation:
Claude Desktop Configuration:
8 Interactive UI Tools:
Tool | Description |
| Interactive pod viewer with filtering, sorting, status indicators |
| Real-time log viewer with syntax highlighting and search |
| Deployment dashboard with rollout status, scaling, rollback |
| Helm release manager with upgrade/rollback actions |
| Cluster overview with node health and resource metrics |
| Cost analyzer with waste detection and recommendations |
| Events timeline with type filtering and grouping |
| Network topology graph showing Services/Pods/Ingress |
Features:
🎨 Dark/light theme support
📊 Real-time data visualization
🖱️ Interactive actions (scale, restart, delete)
🔗 Seamless integration with kubectl-mcp-server
More Info: See kubectl-mcp-app/README.md for full documentation.
Enterprise: OAuth 2.1 Authentication
Secure your MCP server with OAuth 2.1 authentication (RFC 9728).
Supported Identity Providers: Okta, Auth0, Keycloak, Microsoft Entra ID, Google OAuth, and any OIDC-compliant provider.
Use Case: Multi-tenant environments, compliance requirements, audit logging.
Integrations & Ecosystem
Docker MCP Toolkit
Works with Docker MCP Toolkit:
agentregistry
Install from the centralized agentregistry:
Available via: PyPI (uvx), npm (npx), OCI (docker.io/rohitghumare64/kubectl-mcp-server)
agentgateway
Route to multiple MCP servers through agentgateway:
Connect clients to http://localhost:3000/mcp for unified access to all 253 tools.
In-Cluster Deployment
Option 1: kMCP (Recommended)
Deploy with kMCP - a control plane for MCP servers:
See kMCP quickstart for details.
Option 2: Standard Kubernetes
Deploy with kubectl/kustomize:
See deploy/ directory for all manifests and configuration options.
Option 3: kagent (AI Agent Framework)
Integrate with kagent - a CNCF Kubernetes-native AI agent framework:
Your AI agents now have access to all 253 Kubernetes tools. See kagent quickstart.
Architecture
The MCP server implements the Model Context Protocol, translating natural language requests into kubectl operations.
Modular Structure
Agent Skills (25 Skills for AI Coding Agents)
Extend your AI coding agent with Kubernetes expertise using our Agent Skills library. Skills provide specialized knowledge and workflows that agents can load on demand.
Quick Install
Available Skills (25)
Category | Skills |
Core Resources | k8s-core, k8s-networking, k8s-storage |
Workloads | k8s-deploy, k8s-operations, k8s-helm |
Observability | k8s-diagnostics, k8s-troubleshoot, k8s-incident |
Security | k8s-security, k8s-policy, k8s-certs |
GitOps | k8s-gitops, k8s-rollouts |
Scaling | k8s-autoscaling, k8s-cost, k8s-backup |
Multi-Cluster | k8s-multicluster, k8s-capi, k8s-kubevirt, k8s-vind |
Networking | k8s-service-mesh, k8s-cilium |
Tools | k8s-browser, k8s-cli |
Convert to Other Agents
Use SkillKit to convert skills to your preferred AI agent format:
Supported agents: Claude, Cursor, Codex, Gemini CLI, GitHub Copilot, Goose, Windsurf, Roo, Amp, and more.
See kubernetes-skills/README.md for full documentation.
Multi-Cluster Support
Seamlessly manage multiple Kubernetes clusters through natural language. Every tool supports an optional context parameter to target any cluster without switching contexts.
Context Parameter (v1.15.0)
Most kubectl-backed tools accept an optional context parameter to target specific clusters.
Note: vCluster (vind) and kind tools run via their local CLIs and do not accept the context parameter.
Talk to your AI assistant:
Direct tool calls with context:
Context Management
Talk to your AI assistant:
Or use the CLI directly:
How It Works
If
contextis omitted, the tool uses your current kubectl contextIf
contextis specified, the tool targets that cluster directlyResponse includes
"context": "production"or"context": "current"for clarityWorks with all kubeconfig setups and respects
KUBECONFIGenvironment variableNo need to switch contexts for cross-cluster operations
Development & Testing
Setup Development Environment
Running Tests
Test Structure
234 tests covering: tool registration, resource exposure, prompt generation, server initialization, non-destructive mode, secret masking, error handling, transport methods, CLI commands, browser automation, and ecosystem tools.
Code Quality
Contributing
We ❤️ contributions! Whether it's bug reports, feature requests, documentation improvements, or code contributions.
Ways to contribute:
🐛 Report bugs via GitHub Issues
💡 Suggest features or improvements
📝 Improve documentation
🔧 Submit pull requests
⭐ Star the project if you find it useful!
Development setup: See Development & Testing section above.
Before submitting a PR:
Run tests:
pytest tests/ -vFormat code:
black kubectl_mcp_tool testsCheck linting:
flake8 kubectl_mcp_tool tests
Support & Community
License
MIT License - see LICENSE for details.
Links & Resources
Package Repositories:
Project:
Ecosystem:
Made with ❤️ for the Kubernetes and AI community
If kubectl-mcp-server makes your DevOps life easier, give it a ⭐ on GitHub!