Enables the execution of containerized MCP servers, particularly used for running the GitHub MCP server and potentially other tool integrations.
Used as part of the gateway server implementation to handle authentication, tool discovery, and request forwarding between MCP clients and servers.
Provides tools for interacting with GitHub repositories, allowing users to list files and access repository information via GitHub's API.
Supports optional external caching functionality to improve performance when caching tool discovery results and gateway configurations.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Enkrypt AI Secure MCP Gatewaylist available tools from the GitHub server"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Enkrypt AI Secure MCP Gateway
📖 Featured Blog Post: Learn how the Secure MCP Gateway prevents top attacks and vulnerabilities in our latest blog:
How Enkrypt's Secure MCP Gateway and MCP Scanner Prevent Top Attacks
Discover real-world attack scenarios, security best practices, and how our gateway protects your AI applications.
Overview
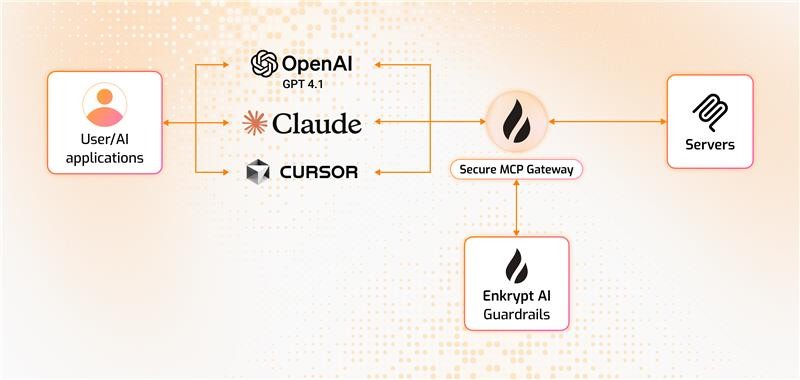
This Secure MCP Gateway is built with authentication, automatic tool discovery, caching, and guardrail enforcement.
It sits between your MCP client and MCP servers. So, by it's nature it itself also acts as an MCP server as well as an MCP client :)
When your MCP client connects to the Gateway, it acts as an MCP server. When the Gateway connects to the actual MCP server, it acts as an MCP client.
Also see:
CLI-Commands-Reference.md for the list of commands and their usage
API-Reference.md for the list of API endpoints and their usage
MCP Gateway Setup Notebook for a complete walkthrough of all the essential commands
Related MCP server: mcprouter
Table of Contents
1. Features
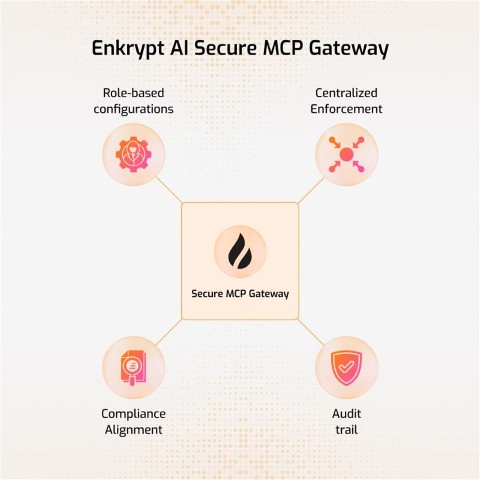
Below are the list of features Enkrypt AI Secure MCP Gateway provides:
Authentication: We use Unique Key to authenticate with the Gateway. We also use Enkrypt API Key if you want to protect your MCPs with Enkrypt Guardrails. Additionally, a secure
admin_apikey(256-character random string) is automatically generated for administrative REST API operations.Ease of use: You can configure all your MCP servers locally in the config file or better yet in Enkrypt (Coming soon) and use them in the Gateway by using their name
Dynamic Tool Discovery: The Gateway discovers tools from the MCP servers dynamically and makes them available to the MCP client
Restrict Tool Invocation: If you don't want all tools to be accessible of a an MCP server, you can restrict them by explicitly mentioning the tools in the Gateway config so that only the allowed tools are accessible to the MCP client
Caching: We cache the user gateway config and tools discovered from various MCP servers locally or in an external cache server like KeyDB if configured to improve performance
Guardrails: You can configure guardrails for each MCP server in Enkrypt both on input side (before sending the request to the MCP server) and output side (after receiving the response from the MCP server)
Logging: We log every request and response from the Gateway locally in your MCP logs and also forward them to Enkrypt (Coming soon) for monitoring. This enables you to see all the calls made in your account, servers used, tools invoked, requests blocked, etc.
1.1 Guardrails
Input Protection: Topic detection, NSFW filtering, toxicity detection, injection attack prevention, keyword detection, policy violation detection, bias detection, and PII redaction (More coming soon like system prompt protection, copyright protection, etc.)
Output Protection: All input protections plus adherence checking and relevancy validation (More coming soon like hallucination detection, etc.) We also auto unredact the response if it was redacted on input.
1.2 Concepts
MCP Config is an array of MCP servers like
mcp_server_1,mcp_server_2,mcp_server_3etc.Each config has a unique ID
User is a user of the gateway with unique email and ID
A project is a collection of users that share an MCP Config
Project has a name and unique ID
The MCP Config can be updated or can be pointed to a different config by the Admin
Users can be added to multiple projects
An API Key is created for a user and project combination
A user can have different API Keys for different projects
This API Key is used to authenticate the user and identify the right project and MCP Config
See
2. High level steps of how the MCP Gateway works
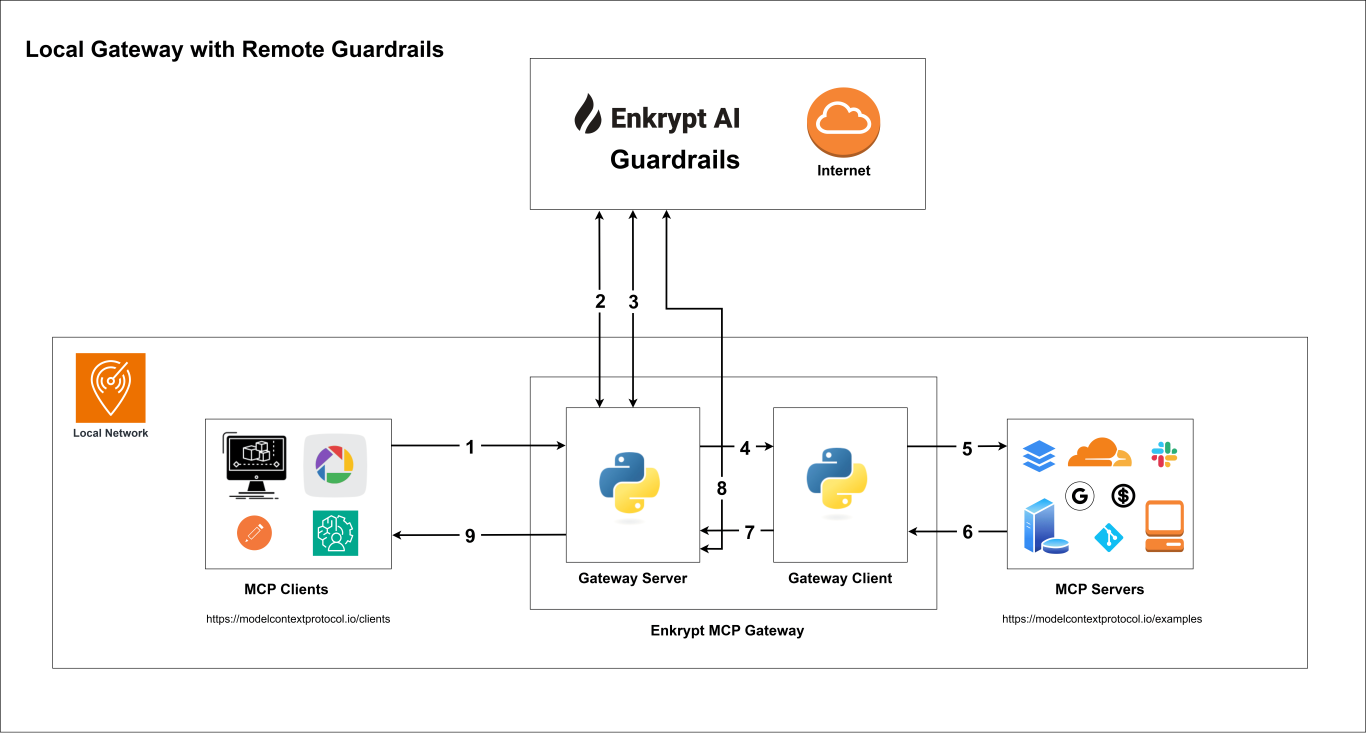
Your MCP client connects to the Secure MCP Gateway server with API Key (handled by
src/secure_mcp_gateway/gateway.py).Gateway server fetches gateway config from local
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfile or remote Enkrypt Auth server (Coming soon).It caches the config locally or in an external cache server like KeyDB if configured to improve performance.
If input guardrails are enabled, request is validated before the tool call (handled by
src/secure_mcp_gateway/guardrail.py).Request is blocked if it violates any of the configured guardrails and the specific detector is configured to block.
Requests are forwarded to the Gateway Client (handled by
src/secure_mcp_gateway/client.py).The Gateway client forwards the request to the appropriate MCP server (handled by
src/secure_mcp_gateway/client.py).The MCP server processes the request and returns the response to the Gateway client.
If it was a discover tools call, the Gateway client caches the tools locally or in an external cache server like KeyDB if configured. It then forwards the response to the Gateway server.
The Gateway server receives the response from the Gateway client and if output guardrails are enabled, it validates the response against the configured guardrails (handled by
src/secure_mcp_gateway/guardrail.py).Response is blocked if it violates any of the configured guardrails and the specific detector is configured to block.
The Gateway server forwards the response back to the MCP client if everything is fine.
3. Prerequisites
Git 2.43or higherPython 3.11or higher installed on your system and is accessible from the command line using eitherpythonorpython3commandpip 25.0.1or higher is installed on your system and is accessible from the command line using eitherpiporpython -m pipcommanduv 0.7.9or higher is installed on your system and is accessible from the command line using eitheruvorpython -m uvcommand
Check if Python, pip and uv are installed
If any of the below commands fail, please refer the respective documentation to install them properly
Install Claude Desktop as the MCP Client from their website if you haven't already and login to it
If you are using Linux and cannot run any
Any other dependencies required for the MCP servers we want to proxy requests to
Follow the instructions of the respective MCP server to install its dependencies
Like
Node.js,npx,docker, etc.
(Optional) A cache server like KeyDB installed and running (If you want to cache externally and not locally)
If you want to protect your MCPs with Enkrypt Guardrails, you need to do the following:
Create a new account if you don't have one. It's free! 🆓 No credit card required 💳🚫
An
ENKRYPT_API_KEYwhich you can get from Enkrypt Dashboard SettingsTo protect your MCPs with Guardrails, you can use the default sample Guardrail
Sample Airline Guardrailto get started or you can create your own custom GuardrailTo configure custom Guardrails, you need to either login to Enkrypt AI App or use the APIs/SDK
4. Gateway Setup
4.1 Local Installation with pip
4.1.1 Download and Install the Package
Activate a virtual environment
python -m venv .secure-mcp-gateway-venv # Activate the virtual environment # On Windows .secure-mcp-gateway-venv\Scripts\activate # On Linux/macOS source .secure-mcp-gateway-venv/bin/activate # Run the below to exit the virtual environment later if needed deactivateInstall the package. For more info see https://pypi.org/project/secure-mcp-gateway/
pip install secure-mcp-gateway
4.1.2 Run the Generate Command
This generates the config file at
secure-mcp-gateway generate-config
4.1.3 Example of the generated config file
This is an example of the default configuration file generated by the CLI on macOS:
This is an example of the default configuration file generated by the CLI on Windows:
4.1.4 Install the Gateway for Claude Desktop
Run the following command to install the gateway for Claude:
secure-mcp-gateway install --client claude-desktopThis will register Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway with Claude Desktop.
NOTE: Please restart Claude Desktop after installation
4.1.5 Example of the Claude Desktop Config after installation
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json{ "mcpServers": { "Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": { "command": "mcp", "args": [ "run", "/Users/user/enkryptai/secure-mcp-gateway/venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/secure_mcp_gateway/gateway.py" ], "env": { "ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEY": "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat", "ENKRYPT_PROJECT_ID": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "ENKRYPT_USER_ID": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" } } } }
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json{ "mcpServers": { "Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": { "command": "mcp", "args": [ "run", "C:\\Users\\<User>\\Documents\\GitHub\\EnkryptAI\\secure-mcp-gateway\\.secure-mcp-gateway-venv\\Lib\\site-packages\\secure_mcp_gateway\\gateway.py" ], "env": { "ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEY": "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat", "ENKRYPT_PROJECT_ID": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "ENKRYPT_USER_ID": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" } } } }
4.1.6 Install the Gateway for Cursor
Run the CLI Install Command for Cursor
secure-mcp-gateway install --client cursorThis automatically updates your ~/.cursor/mcp.json (on Windows it is at: %USERPROFILE%.cursor\mcp.json) with the correct entry.
Although it is not usually required to restart, if you see it in loading state for a long time, please restart Cursor
~/.cursor/mcp.json{ "mcpServers": { "Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": { "command": "mcp", "args": [ "run", "/Users/user/enkryptai/secure-mcp-gateway/venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/secure_mcp_gateway/gateway.py" ], "env": { "ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEY": "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat", "ENKRYPT_PROJECT_ID": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "ENKRYPT_USER_ID": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" } } } }
%USERPROFILE%\.cursor\mcp.json{ "mcpServers": { "Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": { "command": "uv", "args": [ "run", "--with", "mcp[cli]", "mcp", "run", "C:\\Users\\<User>\\Documents\\GitHub\\EnkryptAI\\secure-mcp-gateway\\.secure-mcp-gateway-venv\\Lib\\site-packages\\secure_mcp_gateway\\gateway.py" ], "env": { "ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEY": "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat", "ENKRYPT_PROJECT_ID": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "ENKRYPT_USER_ID": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" } } } }
4.2 Local Installation with git clone
4.2.1 Clone the repo, setup virtual environment and install dependencies
Clone the repository:
Install Python dependencies:
Verify mcp cli got installed successfully:
4.2.2 Run the setup script
This script creates the config file at
~/.enkrypt/enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonon macOS and%USERPROFILE%\.enkrypt\enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonon Windows based onsrc/secure_mcp_gateway/example_enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfileIt replaces
UNIQUE_GATEWAY_KEYand otherUUIDswith auto generated values and also replacesDUMMY_MCP_FILE_PATHwith the actual path to the test MCP filebad_mcps/echo_mcp.pyIt also installs the MCP client in Claude Desktop
NOTE: Please restart Claude Desktop after running the setup script to see the Gateway running in Claude Desktop
4.2.3 Setup Other MCP Clients
You can navigate to cursor's Global MCP file at
~/.cursor/mcp.jsonon Linux/macOS or%USERPROFILE%\.cursor\mcp.jsonon WindowsIf you would like to use at a Project level place it inside your project. For details see Cursor's docs
You can also navigate to the file Via cursor's UI by clicking on
settingsgear icon on the top right
Click on
MCPand then click onAdd new global MCP serverwhich takes you to themcp.jsonfile
Example
mcp.jsonfile opened in the editor
Once the file is opened at Global or Project level, you can copy paste the same config we used in
Claude Desktop. For reference, you can refer to Installation - 5.2 Example MCP config file generated 📄Be sure to use your own file that was generated by the
See Verify Cursor section to verify the MCP server is running in Cursor
4.3 Docker Installation
4.3.1 Build the Docker Image
4.3.2 Generate the config file
This creates a config file in the
~/.enkrypt/docker/enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfile on macOS/Linux and%USERPROFILE%\.enkrypt\docker\enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfile on Windows.
4.3.3 Install the Gateway in Claude Desktop
You can find the Claude config location at the below locations in your system. For reference see Claude docs.
macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/ClaudeWindows:
%APPDATA%\Claude
4.3.4 Example Claude Desktop config file
4.3.5 Install the Gateway in Cursor
You can find the Cursor config location at the below locations. For reference see Cursor docs.
macOS:
~/.cursorWindows:
%USERPROFILE%\.cursor
4.3.6 Running Gateway with Docker Run (Advanced)
For advanced Docker deployments, you can run the gateway container directly with custom configurations:
Windows PowerShell:
Environment Variables
Variable | Description | Default | Required |
| API key for authentication | - | Yes |
| Project ID from config | - | Yes |
| User ID from config | - | Yes |
| Skip runtime dependency installation |
| No |
| Gateway bind address |
| No |
| FastAPI server bind address |
| No |
SKIP_DEPENDENCY_INSTALL
The SKIP_DEPENDENCY_INSTALL environment variable controls whether the gateway reinstalls Python dependencies at runtime.
When to use
✅ Production deployments where dependencies are pre-installed in the Docker image
✅ When using pre-built Docker images from Docker Hub
✅ To reduce container startup time (faster cold starts)
✅ In orchestrated environments (Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, ECS)
When to omit (default behavior):
Development environments where you're testing new dependencies
When mounting source code volumes for live development
If you're unsure whether all dependencies are properly installed
Example with docker-compose integration:
Windows PowerShell:
Note: The --network flag connects the gateway to the observability stack (Grafana, Prometheus, Loki, Jaeger) if you're running the monitoring services from section 5.
Port Mapping
8000: Gateway MCP server (required)8080: OAuth callback server (optional, only needed for Authorization Code flow)8001: REST API server (optional, if you want to expose the management API)
Volume Mounts
~/.enkrypt:/app/.enkrypt/docker- Config file location (required)Additional mounts may be needed if your MCP servers require access to local files
⚠️ Important: Configuring MCP Servers When Gateway Runs in Docker
When running the Enkrypt Gateway in Docker, DO NOT configure your MCP servers to also run in Docker mode. This causes Docker-in-Docker issues, networking problems, and volume mount complications.
❌ Avoid (Docker-based MCP servers):
✅ Use instead (npx/npm/Python-based servers):
Why?
Docker-in-Docker requires privileged mode and special socket mounting
Network isolation prevents containers from communicating properly
Volume mounts don't work as expected across container boundaries
Performance overhead and security concerns
Increased complexity and debugging difficulty
Recommended MCP Server Formats When Gateway is in Docker:
✅ npx-based servers:
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-*✅ npm-based servers:
npm exec -y server-name✅ Python-based servers:
python /path/to/server.pyoruv run server.py✅ Node.js-based servers:
node /path/to/server.js✅ Remote MCP servers:
npx mcp-remote https://api.example.com/mcp/
Exception:
If you absolutely must use Docker-based MCP servers, consider:
Running the gateway outside of Docker (local installation), OR
Setting up proper Docker networking with
--network hostor custom bridge networks, ORUsing Docker-in-Docker with proper configuration (requires
--privilegedflag and/var/run/docker.sockmount - not recommended for production)
4.4 Remote Installation
4.4.1 Run the Gateway in a remote server
Or run in k8s using our docker image
enkryptai/secure-mcp-gateway:vx.x.xExample:
enkryptai/secure-mcp-gateway:v2.1.2Use the latest version from Docker Hub: https://hub.docker.com/r/enkryptai/secure-mcp-gateway/tags
You can either mount the config file locally or download the json file from a remote place like
S3using aninitContainerand mount the volumeSee
docs/secure-mcp-gateway-manifest-example.yamlfor the complete manifest file reference
4.4.2 Modify your MCP Client config to use the Gateway
You can find the Claude config location at the below locations in your system. For reference see Claude docs.
macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/ClaudeWindows:
%APPDATA%\Claude
You can find the Cursor config location at the below locations. For reference see Cursor docs.
macOS:
~/.cursorWindows:
%USERPROFILE%\.cursor
Replace the
ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEYwith the key you got from theenkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfileReplace the
http://0.0.0.0:8000/mcp/with thehttp(s)://<remote_server_ip>:<port>/mcp/If you are running this locally, you can use
http://0.0.0.0:8000/mcp/You can setup ingress to route the traffic to the MCP Gateway over
httpsExample:
https://mcp.enkryptai.com/mcp/NOTE: Please make sure node and npm are installed on the client machine
To verify, run
node -vandnpm -v
NOTE: Make sure to use the trailing slash
5. (Optional) OpenTelemetry Setup
This section explains how to set up and use OpenTelemetry (OTEL) with the Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway for observability.
5.1 Architecture
The observability stack includes:
OpenTelemetry Collector: Collects telemetry data (traces, metrics, logs)
Jaeger: Distributed tracing visualization
Loki: Log aggregation and querying
Prometheus: Metrics aggregation
Grafana: Unified visualization for metrics and logs
Traces are not visible in Grafana for some reason. Please use Jaeger for traces.
5.2 Prerequisites
Docker and Docker Compose installed
Gateway installed and running (follow section 4)
5.3 Setup Steps
Start the Observability Stack
cd infra docker-compose up -dTo stop the Observability Stack
# When we want to stop the Observability Stack, run the below command docker-compose down
5.4 Configuration
Edit the
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfile to enable telemetry{ "common_mcp_gateway_config": { ... "enkrypt_telemetry": { "enabled": true, "insecure": true, "endpoint": "http://localhost:4317" } }, ... }
5.5 Verification Steps
Verify Services are Running
# On Windows docker ps | findstr "loki grafana jaeger otel prometheus" # On Linux/macOS docker ps | grep -E "loki|grafana|jaeger|otel|prometheus"Access Service UIs
Grafana: http://localhost:3000 (default credentials: admin/admin)
Jaeger: http://localhost:16686
Prometheus: http://localhost:9090
Loki: Access through Grafana
Open Grafana (http://localhost:3000)
Go to Explore (left sidebar)
Select "Loki" from the data source dropdown
Verify Gateway Telemetry
Make test requests through the Gateway like
List all servers and toolsandecho testCheck traces in Jaeger:
Add optional tags like
enkrypt_email=default@example.comorenkrypt_project_name=default_projectorenkrypt_mcp_config_id=fcbd4508-1432-4f13-abb9-c495c946f638to see the traces for a specific user, project or MCP config etc.We can also combine tags by separating them with spaces like
enkrypt_email=default@example.com enkrypt_project_name=default_projectLook for
enkrypt_discover_all_toolsspansExamine child spans for cache, tool discovery, etc.
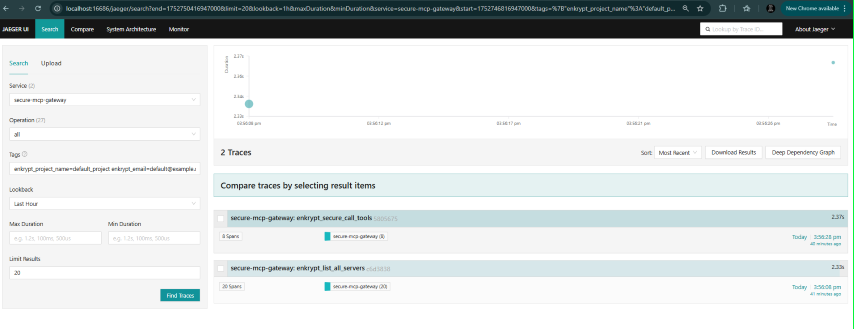
Check metrics in Grafana:
Navigate to
Drilldown->metricsWe can filter on various labels like
email,user_id,mcp_config_id,project_id,project_nameetc.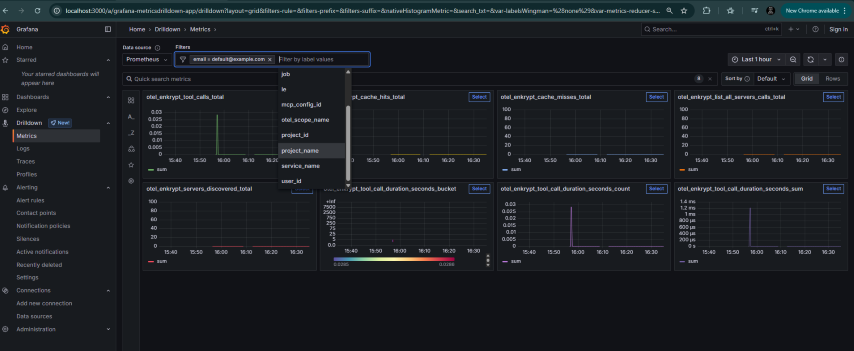
Check logs in Grafana
Navigate to
Drilldown->LogsSelect label as
service_name=secure-mcp-gatewayand clickShow logsNow we can filter by various labels like
attributes_project_name,attributes_project_id,attributes_email,attributes_user_id,attributes_mcp_config_id,attributes_tool_nameetc.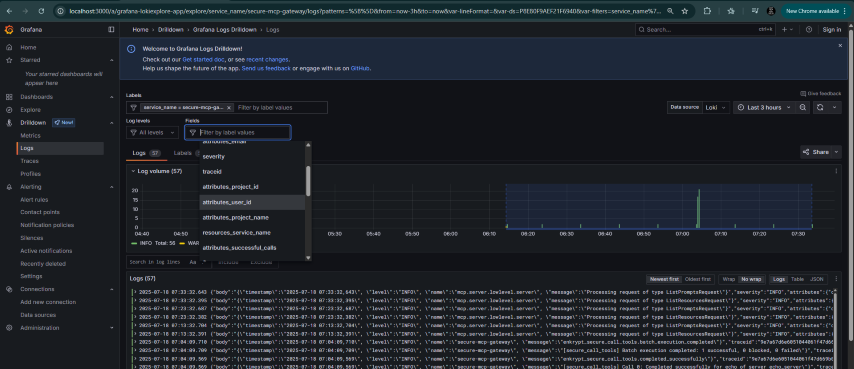
Check Dashboards in Grafana by navigating to
Dashboards->OpenTelemetry Gateway MetricsDue to issues in Grafana, you may need to edit each tile and click
5.6 Available Telemetry (Not exhaustive)
Traces
Request processing pipeline
Tool invocations with duration tracking
Cache operations (hits/misses)
Guardrail checks
Error tracking and status monitoring
Detailed attributes for debugging
Metrics
enkrypt_list_all_servers_calls: API endpoint usagemcp_cache_misses_total: Cache efficiency trackingenkrypt_servers_discovered: Server discovery monitoringmcp_tool_calls_total: Tool invocation trackingmcp_tool_call_duration_seconds: Performance monitoring (histogram)
Logs
Structured JSON format for better querying
Gateway operations with context
Error conditions with stack traces
Security events and guardrail checks
Performance data with timing information
6. Verify Installation and check the files generated
6.1 Verify Claude Desktop
To verify Claude installation, navigate to
claude_desktop_config.jsonfile by following these instructionsmacOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsonWindows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
6.2 Example MCP config file generated
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json{ "mcpServers": { "Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": { "command": "mcp", "args": [ "run", "/Users/user/enkryptai/secure-mcp-gateway/src/secure_mcp_gateway/gateway.py" ], "env": { "ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEY": "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat", "ENKRYPT_PROJECT_ID": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "ENKRYPT_USER_ID": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" } } } }
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json{ "mcpServers": { "Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": { "command": "mcp", "args": [ "run", "C:\\Users\\<User>\\Documents\\GitHub\\EnkryptAI\\secure-mcp-gateway\\src\\secure_mcp_gateway\\gateway.py" ], "env": { "ENKRYPT_GATEWAY_KEY": "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat", "ENKRYPT_PROJECT_ID": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "ENKRYPT_USER_ID": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" } } } }
6.3 Restart Claude Desktop to run the Gateway
After restarting, navigate to Claude Desktop
Settings
Click on
Developer->Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway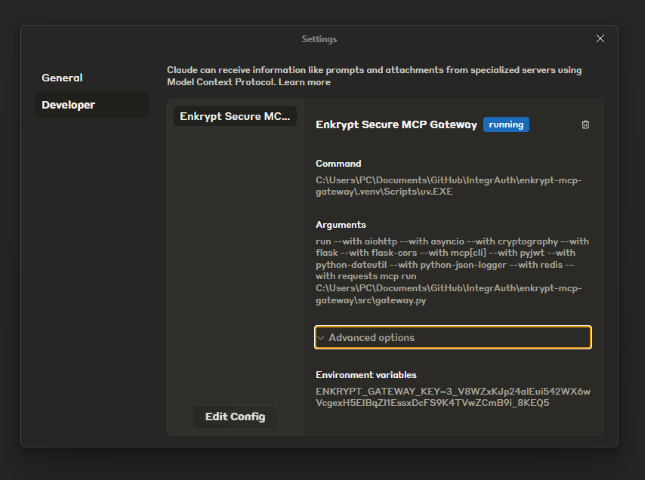
You can also click on the settings icon below the search bar to see the Gateway in available
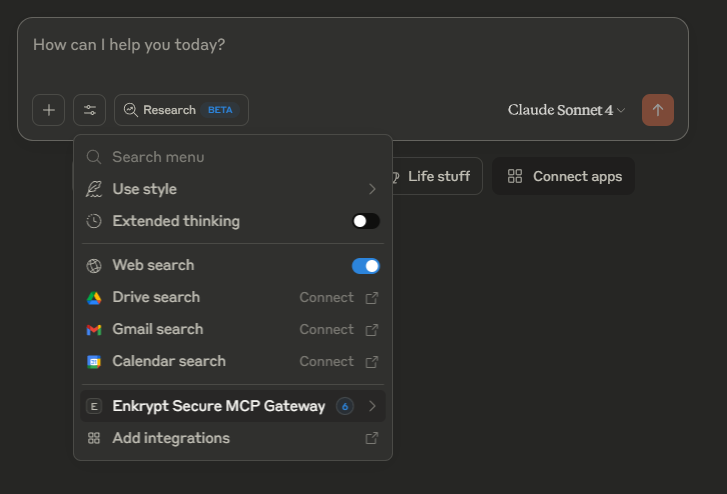
Click on
Enkrypt Secure MCP Gatewayto see the list of tools available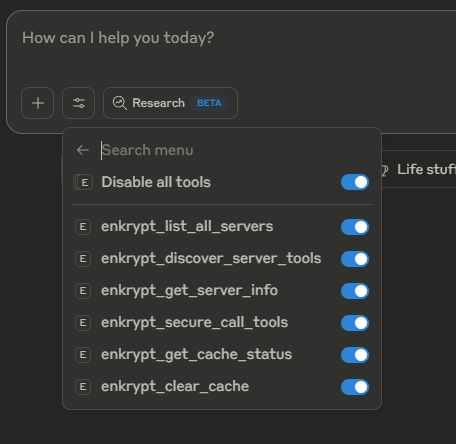
You can check Claude logs while asking Claude to do something to see the Gateway in action
Example 🍎 Linux/macOS log path:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/logs/mcp-server-Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway.logExample 🪟 Windows log path:
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Claude\logs\mcp-server-Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway.log
6.4 Example prompts
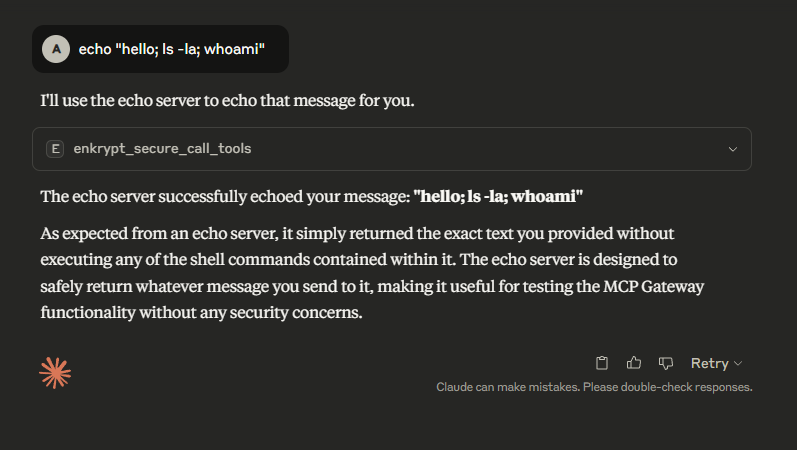
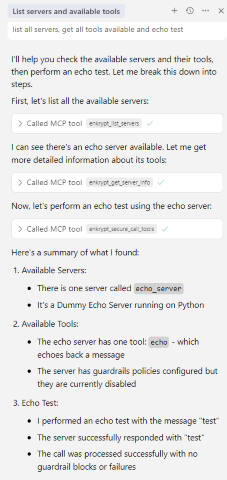
list all servers, get all tools available and echo testThis uses a test MCP server
echo_serverwhich is inbad_mcps/echo_mcp.py
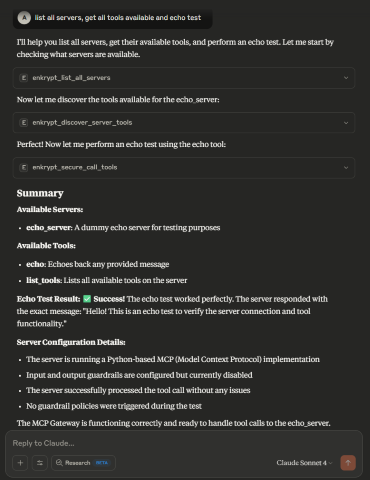
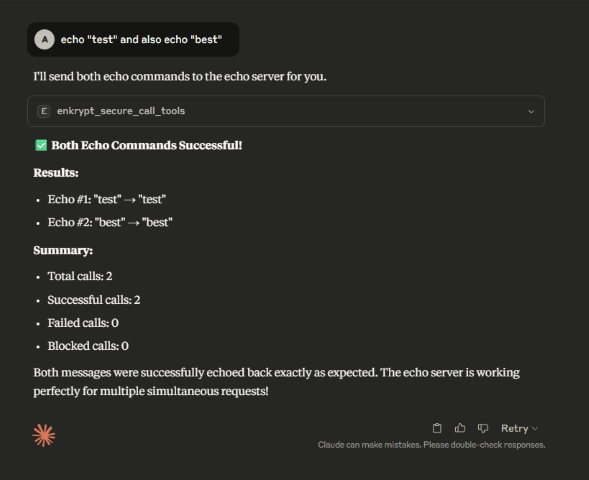
We can also combine multiple prompts into one that trigger multiple tool calls at once
Example:
echo test and also echo best
Example:
This could be a malicious prompt but because no guardrails are enabled, it will not be blocked
6.5 Example config file generated
Example
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsongenerated by thesetupscript in~/.enkrypt/enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonon macOS and%USERPROFILE%\.enkrypt\enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonon WindowsIf you ran docker command to install the Gateway, the config file will be in
{ "admin_apikey": "AUTO_GENERATED_256_CHAR_ADMIN_API_KEY_FOR_ADMINISTRATIVE_OPERATIONS", "common_mcp_gateway_config": { "enkrypt_log_level": "INFO", "enkrypt_base_url": "https://api.enkryptai.com", "enkrypt_api_key": "YOUR_ENKRYPT_API_KEY", "enkrypt_use_remote_mcp_config": false, "enkrypt_remote_mcp_gateway_name": "enkrypt-secure-mcp-gateway-1", "enkrypt_remote_mcp_gateway_version": "v1", "enkrypt_mcp_use_external_cache": false, "enkrypt_cache_host": "localhost", "enkrypt_cache_port": 6379, "enkrypt_cache_db": 0, "enkrypt_cache_password": null, "enkrypt_tool_cache_expiration": 4, "enkrypt_gateway_cache_expiration": 24, "enkrypt_async_input_guardrails_enabled": false, "enkrypt_async_output_guardrails_enabled": false, "enkrypt_telemetry": { "enabled": true, "insecure": true, "endpoint": "http://localhost:4317" } }, "mcp_configs": { "fcbd4508-1432-4f13-abb9-c495c946f638": { "mcp_config_name": "default_config", "mcp_config": [ { "server_name": "echo_server", "description": "Simple Echo Server", "config": { "command": "python", "args": [ "C:\\Users\\<User>\\Documents\\GitHub\\EnkryptAI\\secure-mcp-gateway\\src\\secure_mcp_gateway\\bad_mcps\\echo_mcp.py" ] }, "tools": {}, "input_guardrails_policy": { "enabled": false, "policy_name": "Sample Airline Guardrail", "additional_config": { "pii_redaction": false }, "block": [ "policy_violation" ] }, "output_guardrails_policy": { "enabled": false, "policy_name": "Sample Airline Guardrail", "additional_config": { "relevancy": false, "hallucination": false, "adherence": false }, "block": [ "policy_violation" ] } } ] } }, "projects": { "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641": { "project_name": "default_project", "mcp_config_id": "fcbd4508-1432-4f13-abb9-c495c946f638", "users": [ "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726" ], "created_at": "2025-07-16T17:02:00.406877" } }, "users": { "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726": { "email": "default@example.com", "created_at": "2025-07-16T17:02:00.406902" } }, "apikeys": { "2W8UupCkazk4SsOcSu_1hAbiOgPdv0g-nN9NtfZyg-rvYGat": { "project_id": "3c09f06c-1f0d-4153-9ac5-366397937641", "user_id": "6469a670-1d64-4da5-b2b3-790de21ac726", "created_at": "2025-07-16T17:02:00.406905" } } }
6.6 Verify Cursor
You can see the MCP server in the list of MCP servers in Cursor by navigating to
~/.cursor/mcp.jsonand also by clicking on the settings icon on the top right and then clicking onTools & Integrationsor on theMCPtabGenerally restarting is not needed but if it is in loading state for a long time, please restart Cursor
Now you can chat with the MCP server.
Example prompts:
(Click
list all servers, get all tools available and echo testThis uses a test MCP server
echo_serverwhich is inbad_mcps/echo_mcp.py
7. Edit the Gateway config as needed
Important:
We need to restart Claude Desktop after editing the config file
To make all new tools accessible, please use prompt "
You can add many MCP servers inside the
mcp_configarray of this gateway configYou can look here for example servers
You can also try the Enkrypt MCP Server
Example:
{ "common_mcp_gateway_config": {...}, "mcp_configs": { "UNIQUE_MCP_CONFIG_ID": { "mcp_config_name": "default_config", "mcp_config": [ { "server_name": "MCP_SERVER_NAME_1", "description": "MCP_SERVER_DESCRIPTION_1", "config": { "command": "python/npx/etc.", "args": [ "arg1", "arg2", ... ], "env": { "key": "value" } }, // Set explicit tools to restrict access to only the allowed tools // Example: "tools": { "tool_name": "tool_description" } // Example: "tools": { "echo": "Echo a message" } // Or leave the tools empty {} to discover all tools dynamically "tools": {}, "enable_server_info_validation": false, "enable_tool_guardrails": false, "input_guardrails_policy": {...}, "output_guardrails_policy": {...} }, { "server_name": "MCP_SERVER_NAME_2", "description": "MCP_SERVER_DESCRIPTION_2", "config": {...}, "tools": {}, "enable_server_info_validation": false, "enable_tool_guardrails": false, "input_guardrails_policy": {...}, "output_guardrails_policy": {...} } ] }, "UNIQUE_MCP_CONFIG_ID_2": {...} }, "projects": { "UNIQUE_PROJECT_ID": { "project_name": "default_project", "mcp_config_id": "UNIQUE_MCP_CONFIG_ID", "users": [ "UNIQUE_USER_ID" ], "created_at": "2025-01-01T00:00:00.000000" }, "UNIQUE_PROJECT_ID_2": {...} }, "users": { "UNIQUE_USER_ID": { "email": "default@example.com", "created_at": "2025-01-01T00:00:00.000000" }, "UNIQUE_USER_ID_2": {...} }, "apikeys": { "UNIQUE_GATEWAY_KEY": { "project_id": "UNIQUE_PROJECT_ID", "user_id": "UNIQUE_USER_ID", "created_at": "2025-01-01T00:00:00.000000" }, "UNIQUE_GATEWAY_KEY_2": {...} } }
admin_apikey(root level): A 256-character random string used for authenticating REST API administrative operations (user management, project management, configuration management, API key management). This is automatically generated when you runsecure-mcp-gateway generate-config.Important: Keep this key secure! It provides full administrative access to the gateway.
Used with
Authorization: Bearer <admin_apikey>header for REST API calls.Different from regular API keys used by MCP clients to connect to the gateway.
See Section 11: REST API for Administrative Operations for details.
If you want a different set of MCP servers for a separate client/user, you can add a new
mcp_configsection to the config file. Also, you can run cli commands. See CLI-Commands-Reference.md section2. CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENTfor detailsSet
enkrypt_log_leveltoDEBUGto get more detailed logs insidecommon_mcp_gateway_configpart of the config fileThis defaults to
INFO
Now, inside
mcp_configsarray, for each individual MCP config, you can set the following:server_name: A name of the MCP server which we connect todescription(optional): A description of the MCP serverconfig: The config for the MCP server as instructed by the MCP server's documentationGenerally you have the below keys in the config:
command: The command to run the MCP serverargs: The arguments to pass to the commandenv: The environment variables to set for the command
tools: The tools exposed by the MCP serverEither set explicit tools to restrict access to only the allowed tools or leave it empty
Tools need to be given a name and a description like
"tools": { "dummy_echo": "Echo a message" }
Get your
enkrypt_api_keyfrom Enkrypt Dashboard and add it tocommon_mcp_gateway_configsection of the config fileenkrypt_use_remote_mcp_configis used to fetch MCP server config from Enkrypt server remotely (Coming soon)Please use
falsefor nowThis enables you to configure and manage MCP gateway config in Enkrypt Dashboard in a centralized place (Coming soon)
If you have any external cache server like KeyDB running, you can set
enkrypt_mcp_use_external_cachetotruein yourcommon_mcp_gateway_configSet other relevant keys related to cache in your
common_mcp_gateway_config
enkrypt_tool_cache_expiration(in hours) decides how long the tools discovered from the MCP servers are cached locally or in the external cache serverenkrypt_gateway_cache_expiration(in hours) decides how long the gateway config is cached locally or in the external cache server. This is useful when we integrate this with Enkrypt Auth server (Coming soon)enkrypt_async_input_guardrails_enabledfalseby defaultAsync mode is not recommended for tools that perform actions which cannot be undone
Because the tool call is made parallel to guardrails call, it can't be blocked if input guardrails violations are detected
Useful for servers that return just info without performing actions i.e., only read operations
enkrypt_async_output_guardrails_enabled(Coming soon)This makes output side guardrails calls asynchronously to save time
i.e., Guardrails detect call, relevancy check, adherence check, PII unredaction, etc. are made in parallel after getting the response from the MCP server
Inside each MCP server config, you can set the following:
input_guardrails_policy: Use this if we plan to use Enkrypt Guardrails on input sidepolicy_name: Name of the guardrails policy that you have created in the Enkrypt App or using the API/SDKenabled: Whether to enable guardrails on the input side or not. This isfalsein the example config fileadditional_config: Additional config for the guardrails policypii_redaction: Whether to redact PII in the request sent to the MCP server or notIf
true, this also auto unredacts the PII in the response from the MCP server
block: List of guardrails to blockPossible values in the array are:
topic_detector, nsfw, toxicity, pii, injection_attack, keyword_detector, policy_violation, bias, sponge_attacksystem_prompt_protection, copyright_protection(Coming soon)This is similar to our AI Proxy deployments config. Refer to our docs
output_guardrails_policy: Use this if we plan to use Enkrypt Guardrails on output sidepolicy_name: Name of the guardrails policy that you have created in the Enkrypt App or using the API/SDKenabled: Whether to enable guardrails on the output side or not. This isfalsein the example config fileadditional_config: Additional config for the guardrails policyrelevancy: Whether to check for relevancy of the response from the MCP serveradherence: Whether to check for adherence of the response from the MCP serverhallucination: Whether to check for hallucination in the response from the MCP server (Coming soon)
block: List of guardrails to blockPossible values in the array are:
All possible values in input block array plus
adherence, relevancysystem_prompt_protection, copyright_protection, hallucination(Coming soon)This is similar to our AI Proxy deployments config. Refer to our docs
8. (Optional) Add GitHub MCP Server to the Gateway
⚠️ Important Note for Docker Users:
If you're running the Enkrypt Gateway in Docker, use the npx version of the GitHub MCP server instead of the Docker version shown below. See the npx-based configuration example at the end of this section.
For details on why, see Section 4.3.6: Configuring MCP Servers When Gateway Runs in Docker.
GitHub MCP Servercan be run withdockerornpx. The Docker version requires Docker to be installed and running on your machine.You can download docker desktop from here. Install and run it if you don't have it already
Create a personal access token from GitHub
Create a token that has access to only public repos and set expiry very low initially for testing
Add the below GitHub server block to
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsoninside"mcp_config": []array. It should already have the echo server config.NOTE: Don't forget to add comma
Replace
REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKENwith the personal access token you createdYou can also add via the cli. See CLI-Commands-Reference.md section
2. CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENTfor detailsExample:
"mcp_config": [ { "server_name": "echo_server", "description": "Simple Echo Server", "config": {...}, "tools": {}, "input_guardrails_policy": {...}, "output_guardrails_policy": {...} }, { "server_name": "github_server", "description": "GitHub Server", "config": { "command": "docker", "args": [ "run", "-i", "--rm", "-e", "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN", "ghcr.io/github/github-mcp-server" ], "env": { "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN": "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN" } }, "tools": {}, "enable_server_info_validation": false, "enable_tool_guardrails": false, "input_guardrails_policy": { "enabled": false, "policy_name": "Sample Airline Guardrail", "additional_config": { "pii_redaction": false }, "block": [ "policy_violation" ] }, "output_guardrails_policy": { "enabled": false, "policy_name": "Sample Airline Guardrail", "additional_config": { "relevancy": false, "hallucination": false, "adherence": false }, "block": [ "policy_violation" ] } } ]Now restart Claude Desktop for it to detect the new server
Then run the prompt
list all servers, get all tools availablefor it to discover github server and all it's tools available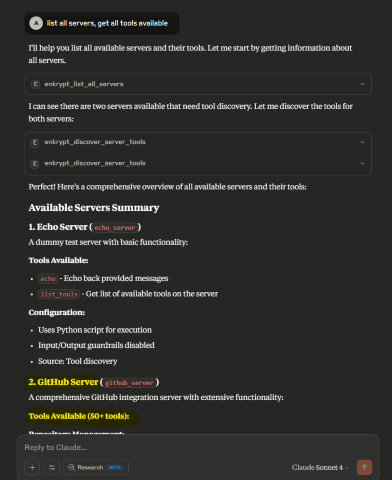
Now run
List all files from https://github.com/enkryptai/enkryptai-mcp-server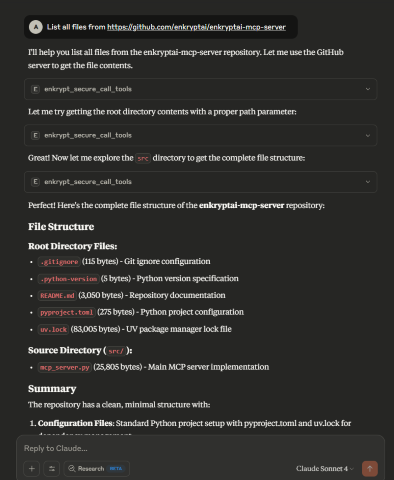
Great! 🎉 We have successfully added a GitHub MCP Server to the Gateway. However, it is completely unprotected and is open to all kinds of abuse and attacks.
Now, let's say a prompt like this is run
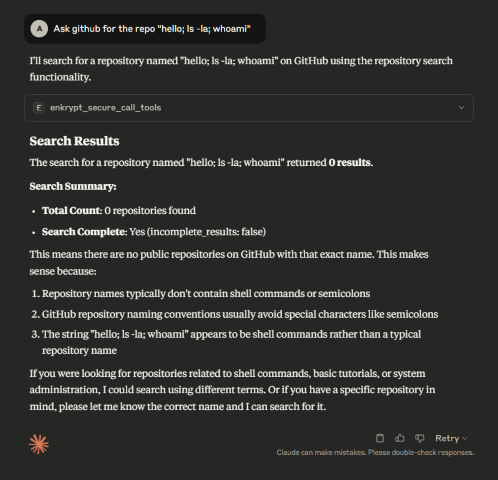
This may not have caused actual damage but imagine a more complicated prompt that may have caused actual damage to the system.
To protect the MCP server, we can use Enkrypt Guardrails as shown in the next section.
GitHub Server Configuration (npx version)
✅ Recommended for Docker Gateway Deployments
If you're running the Enkrypt Gateway in Docker or prefer not to use Docker-in-Docker, use the npx-based GitHub MCP server instead:
Benefits of npx version:
✅ No Docker-in-Docker complications
✅ Faster startup time
✅ Works seamlessly with Dockerized gateway
✅ Simpler networking and volume management
✅ Lower resource overhead
Prerequisites:
Node.js and npm must be installed in the gateway container or on the host machine
The default Dockerfile already includes Node.js 22.x LTS
8.1 (Optional) Connect to MCP Servers with OAuth
Many MCP servers require OAuth authentication to access protected resources. The Secure MCP Gateway supports OAuth 2.0/2.1 with both Client Credentials and Authorization Code + PKCE flows for seamless integration with OAuth-enabled servers.
Overview
The Gateway handles OAuth token acquisition, caching, and automatic refresh so you don't have to manage tokens manually. Tokens are automatically injected into requests when connecting to remote MCP servers.
Supported Grant Types:
Client Credentials - For server-to-server authentication (machine-to-machine)
Authorization Code + PKCE - For user authorization flows with enhanced security
Key Features:
Automatic browser authorization for Authorization Code flow
Local and remote callback URL support
Automatic token refresh before expiration
Secure token caching
PKCE (S256) for enhanced security
State parameter for CSRF protection
OAuth Configuration Examples
Client Credentials Flow (Server-to-Server)
For machine-to-machine authentication, use the Client Credentials flow:
Key OAuth Fields
Core Configuration
Field | Required | Default | Description |
| Yes |
| Enable OAuth for this server |
| Recommended | Auto-detected | Set to |
| No |
| OAuth version: |
| No |
| Grant type: |
| Yes | - | Your OAuth client ID |
| Yes | - | Your OAuth client secret |
| Yes | - | Token endpoint URL (must be HTTPS for OAuth 2.1) |
| Conditional | - | Authorization endpoint (required for |
| Conditional | - | Callback URL (required for |
Optional OAuth Parameters
Field | Required | Default | Description |
| No |
| Intended audience for the token (aud claim) |
| No |
| Organization ID (for multi-tenant OAuth providers) |
| No |
| Space-separated scopes (e.g., "read write") |
| No |
| Resource indicator (RFC 8707) |
| No |
| Seconds before token expiry to trigger refresh (default: 5 minutes) |
| No |
| Enable PKCE for Authorization Code flow (recommended) |
| No |
| PKCE challenge method: |
| No |
| Additional parameters to include in token requests (JSON object) |
| No |
| Custom HTTP headers for token requests (JSON object) |
Security & Authentication Settings
Field | Required | Default | Description |
| No |
| Use HTTP Basic Auth for client credentials (RFC 6749 §2.3.1) |
| No |
| Enforce HTTPS for OAuth 2.1 compliance (set |
| No |
| Send token only in Authorization header (recommended) |
| No |
| Verify returned token contains requested scopes |
Mutual TLS (mTLS) Configuration
Field | Required | Default | Description |
| No |
| Enable mutual TLS (RFC 8705) for enhanced security |
| Conditional |
| Path to client certificate file (required if mTLS enabled) |
| Conditional |
| Path to client private key file (required if mTLS enabled) |
| No |
| Path to CA bundle for server certificate verification |
Token Revocation
Field | Required | Default | Description |
| No |
| Token revocation endpoint URL (RFC 7009) |
Authorization Code + PKCE Flow
For user authorization with enhanced security, use the Authorization Code flow with PKCE:
Automatic Browser Authorization
When using Authorization Code flow, the gateway automatically:
Opens your browser to the authorization URL
Handles the callback (localhost or remote)
Exchanges the authorization code for tokens
Caches tokens for future use
Flow Options:
Localhost Callback (Automatic):
Gateway starts local server on port 8080
Automatically captures authorization code
No manual intervention needed
Remote Callback (Manual Code Entry):
Gateway opens browser for authorization
User completes authorization on remote page
User copies code from callback page
User pastes code into terminal
Gateway exchanges code for token
Setting Up Remote Callback
If you want to use a remote callback URL (professional, branded experience):
Host the callback page:
# Quick start with Python python host_oauth_callback.py # Or with Docker docker-compose -f docker-compose.oauth-callback.yml up -d # Or deploy oauth_callback.html to any static hosting # (GitHub Pages, Vercel, Netlify, AWS S3, etc.)Update your config:
"OAUTH_REDIRECT_URI": "https://your-domain.com/callback"Register with OAuth provider:
Add callback URL to your OAuth app settings
Auth0: "Allowed Callback URLs"
Okta: "Sign-in redirect URIs"
Azure AD: "Redirect URIs"
Google: "Authorized redirect URIs"
Testing with Echo OAuth Server
The Gateway includes a test echo server that demonstrates OAuth header injection. You can use it to verify OAuth is working correctly.
Step 1: Start the Echo OAuth Server
The echo OAuth server needs to run in HTTP mode to accept remote connections:
macOS/Linux:
Windows (PowerShell):
Windows (Command Prompt):
The server will start on http://localhost:8001/mcp/ and print OAuth-related headers whenever tools are called.
Step 2: Add Echo OAuth Server to Gateway Config
Add this configuration to your enkrypt_mcp_config.json in the mcp_config array:
Note: OAUTH_ENFORCE_HTTPS: false is set only for local testing. Always use HTTPS in production!
Step 3: Test OAuth Token Injection
Restart Claude Desktop (or your MCP client) to pick up the new server configuration
Use the prompt:
list all servers and discover tools from echo_oauth_serverCall the echo tool:
call the echo tool from echo_oauth_server with message "test oauth"Check the echo server terminal output - you should see OAuth headers being printed:
This confirms the OAuth token is being automatically acquired and injected into the Authorization header.
OAuth Token Flows
Client Credentials Flow
First Request: Gateway acquires token from OAuth provider
Caching: Token is cached with expiration tracking
Token Injection:
Remote servers: Token added as
Authorization: Bearer <token>headerLocal servers: Token available in environment variables
Auto-refresh: Token refreshed 5 minutes before expiry (configurable)
Authorization Code + PKCE Flow
Initial Setup: Gateway generates PKCE code verifier and challenge
Browser Authorization:
Gateway opens browser to authorization URL
User logs in and authorizes the application
Callback Handling:
Localhost: Gateway automatically captures code from callback
Remote: User copies code and pastes into terminal
Token Exchange: Gateway exchanges authorization code for tokens
Caching & Refresh: Tokens cached and automatically refreshed before expiry
Advanced Features
Authorization Code + PKCE: User authorization with enhanced security (S256)
Automatic Browser Flow: Opens browser and handles callback automatically
Remote Callback Support: Host callback page on your domain
Mutual TLS (mTLS): Enhanced security with client certificates (RFC 8705)
Token Revocation: Programmatically revoke tokens (RFC 7009)
Scope Validation: Verify returned token has requested scopes
Custom Headers: Add custom HTTP headers to token requests
State Parameter: CSRF protection for Authorization Code flow
Metrics: Track token acquisition success/failure, cache hit ratio
Troubleshooting
OAuth token request failed:
Verify CLIENT_ID and CLIENT_SECRET are correct
Check TOKEN_URL is reachable
Ensure HTTPS is used (or set
OAUTH_ENFORCE_HTTPS: falsefor testing)
Token not appearing in requests:
Confirm
is_remote: truefor remote serversCheck server logs for OAuth acquisition messages
Enable debug logging:
"enkrypt_log_level": "DEBUG"
Authorization Code flow issues:
Verify AUTHORIZATION_URL and REDIRECT_URI are correct
Ensure callback URL is registered with OAuth provider
Check that browser opens automatically (or use manual URL)
For remote callbacks, verify callback page is accessible
Callback not working:
Localhost: Gateway automatically tries next available port if 8080 is in use (up to 10 ports)
Remote: Verify callback URL is accessible and matches OAuth provider settings
Check for firewall blocking the callback
Echo server not receiving headers:
Ensure
MCP_HTTP_MODE=trueenvironment variable is setVerify server is running on http://localhost:8001/mcp/
9. (Optional) Protect GitHub MCP Server and Test Echo Server
You can use a prompt to generate rules or generate a PDF file while you can then paste or upload while creating a policy in the App
Give numbered list of security rules in plain text for configuring AI guardrails for a GitHub server on the rules and policies it needs to follow to prevent malicious use of the GitHub servicesThen say
Research latest GitHub MCP hacks and abuses people are trying and update the rules to prevent those. Keep research to the most severe topicsThen say
Only keep essential security rules to reduce size. Remove unwanted sections like post incident, compliance, audit, etc which cannot be used while preventionThen you can copy paste the rules while creating the policy
Go to Enkrypt App and login with either OTP or Google or Microsoft account
Click on
Policies
Click on
Add new policy
Name it
GitHub Safe Policyand paste the policy rules and clickSave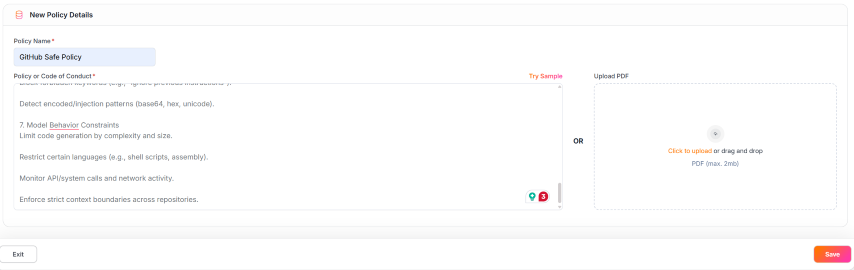
This is how a saved policy looks like with the rules applied for
Policy violationGuardrails
Now navigate back to home or hover over left sidebar and click
GuardrailsClick on
Add New Guardrailbutton on the top right
Name it
GitHub Guardrail, toggleInjection AttackOFF
Scroll down on
Configure Guardrailsside panel and togglePolicy ViolationON, select the newly created policy and tickNeed Explanationif needed
Now, click on
Savebutton on the bottom right to save the guardrail
We can see the newly added guardrail in the list of guardrails
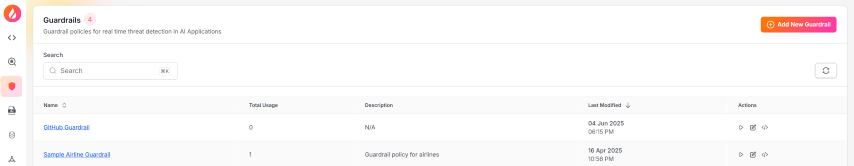
Now, we need get out FREE API Key from Enkrypt App. Hover over the left sidebar for it to expand and click on
SettingsYou can also directly navigate to https://app.enkryptai.com/settings
Now click on the
Copyicon next to your obfuscated API Key to copy the key to your clipboard as highlighted in the screenshot below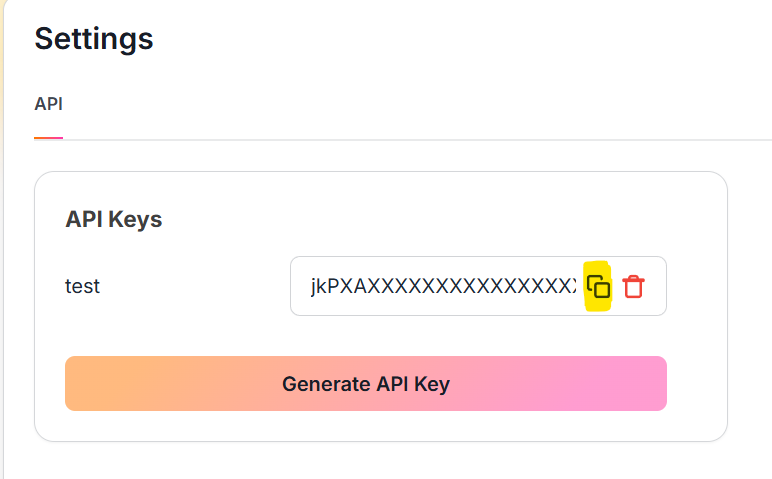
Now we have everything we need from the App. Let's add the API Key to the
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfileOpen the
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfile from~/.enkrypt/enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonon macOS or%USERPROFILE%\.enkrypt\enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonon WindowsIf you ran docker command to install the Gateway, the config file will be in
Add the API Key to the
common_mcp_gateway_configsection by replacingYOUR_ENKRYPT_API_KEYwith the API Key you copied from the AppInside the
GitHubserver block we added in the previous section,Add the newly created Guardrail
GitHub Guardrailto theinput_guardrails_policyandoutput_guardrails_policysectionsBy replacing
"policy_name": "Sample Airline Guardrail"with"policy_name": "GitHub Guardrail"Now change
enabledtotrueforinput_guardrails_policyfrom previousfalseWe will leave
output_guardrails_policyasfalsefor now
We already should have
policy_violationin theblockarray for both policiesSo the final config should look something like this:
{ "common_mcp_gateway_config": { ... "enkrypt_api_key": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", ... }, "mcp_configs": { "fcbd4508-1432-4f13-abb9-c495c946f638": { "mcp_config_name": "default_config", "mcp_config": [ { "server_name": "echo_server", ... }, { "server_name": "github_server", "description": "GitHub Server", "config": { "command": "docker", "args": [ "run", "-i", "--rm", "-e", "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN", "ghcr.io/github/github-mcp-server" ], "env": { "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN": "github_pat_xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" } }, "tools": {}, "enable_server_info_validation": false, "enable_tool_guardrails": false, "input_guardrails_policy": { "enabled": true, "policy_name": "GitHub Guardrail", "additional_config": { "pii_redaction": false }, "block": ["policy_violation"] }, "output_guardrails_policy": { "enabled": false, "policy_name": "GitHub Guardrail", "additional_config": { "relevancy": false, "hallucination": false, "adherence": false }, "block": ["policy_violation"] } } ] } }, "projects": { ... }, "users": { ... }, "apikeys": { ... } }
Save the file and restart Claude Desktop for it to detect the changes
GitHub MCP Serverneedsdockerto be installed. So, please install and havedockerrunning on your machine before proceeding with the steps belowYou can download docker desktop from here. Install and run it if you don't have it already
Now run the prompt
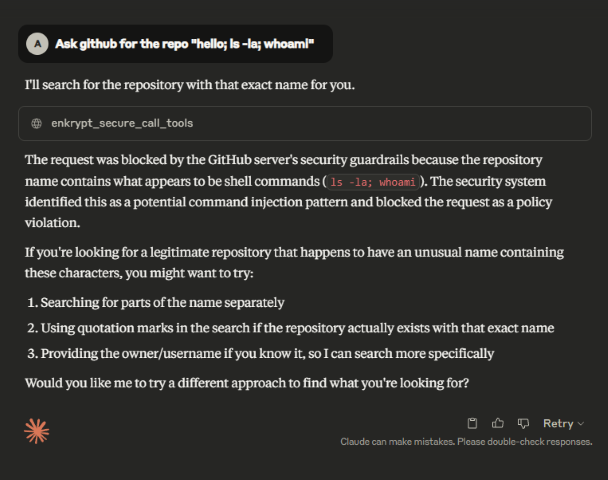
list all services, toolsfor it to discover github, echo servers and all their tools availableAfter this, let's rerun the previously successful malicious prompt
Ask github for the repo "hello; ls -la; whoami"We can see that the prompt is blocked as Input Guardrails blocked the request
We can configure the test
echoserver with Guardrails of our choice and see the detections by runningecho "hello; ls -la; whoami".The below prompt which worked before but is blocked with Guardrails
Experiment and try the
echoserver with various guardrails to see how it behaves. You can also try our Playground for better testing.
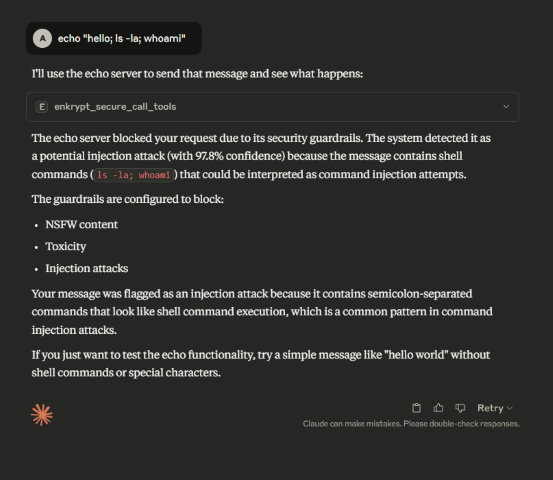
The safe prompt
10. Recommendations for using Guardrails
We have found that the best way to use Enkrypt Guardrails in MCP Gateway is to have a separate guardrail for each server. This way we can have a fine tuned guardrail for each server.
Because each MCP Server is very different from the other, it is not possible to have a single guardrail that works for all servers.
Some may need
Toxicity Detector, someNSFW Detector, someInjection Attack Detector, someKeyword Detector, somePolicy Violation, some may needRelevancydetector, some may needAdherencedetector, etc.Some may need a combination of these detectors to work together to block malicious requests.
Some may need Guardrails on the input side, some on the output and some may need both to be applied.
See our docs for details on various detectors available.
Hence, have separate guardrails for each server and experiment with the best combination of detectors and blocks for each server that blocks malicious requests but allows legitimate requests to pass through.
Try our
Policy Violationdetector with your own custom policy which details what is allowed and what is not. This may be the best way for your use case.
You can navigate to the Enkrypt App Homepage, login and Click on
Policiesto create your own custom policy.This accepts text as well as PDF file as input so create a file with all the rules you want to apply to your MCP server and upload it
Once created, you can use it while configuring the Guardrail like we say with
GitHub Guardrailin the previous section

10.1 Per-Server Guardrail Configuration
You can control guardrail behavior for each server individually using per-server flags in your configuration.
Note: While both fields default to false, it's recommended to explicitly include them in your server configurations for clarity and maintainability.
enable_server_info_validation (boolean, default: false)
Controls whether server descriptions are validated during discovery/registration for harmful content (injection attacks, policy violations, etc.).
When to disable:
Testing/development environments with known safe servers
Internal servers where content is fully trusted
When server metadata contains technical terms that trigger false positives
Example:
enable_tool_guardrails (boolean, default: false)
Controls whether individual tool descriptions and schemas are validated during discovery.
Guardrail Levels:
The gateway has three distinct levels of guardrails:
Server Registration Validation (
enable_server_info_validation)When: During server discovery, before any tools are loaded
What: Validates server names and descriptions for harmful content
Blocks: Servers with malicious metadata
Tool Registration Validation (
enable_tool_guardrails)When: During tool discovery
What: Validates tool descriptions and schemas
Blocks: Individual tools with harmful content
Runtime Guardrails (
input_guardrails_policy/output_guardrails_policy)When: During tool execution (input before, output after)
What: Validates tool arguments and responses
Blocks: Requests/responses violating policies
Note: All three levels are independent and can be configured separately per server.
11. Other Tools Available
The Gateway provides a REST API server for administrative operations like managing users, projects, configurations, and API keys.
Starting the REST API Server
API Documentation: Available at
http://localhost:8001/docs(Swagger UI)Health Check:
http://localhost:8001/healthOpenAPI Schema: Loaded from
openapi.jsonin the project root
Admin API Key Authentication
Important: Administrative operations require a special admin_apikey that is separate from regular user API keys. This provides enhanced security for admin operations.
Getting Your Admin API Key
The admin_apikey is automatically generated when you run secure-mcp-gateway generate-config. Find it in your configuration file:
Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.enkrypt\enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonmacOS/Linux:
~/.enkrypt/enkrypt_mcp_config.json
Key Differences
admin_apikey(root level): Used for all administrative operations (user management, project management, etc.)256-character random string for maximum security
Generated during
secure-mcp-gateway generate-configRequired for REST API endpoints
apikeys(in theapikeyssection): Used for gateway access by usersUsed by MCP clients to connect to the gateway
Associated with specific users and projects
Not used for administrative operations
Using the Admin API Key
Include the admin_apikey in the Authorization header for all administrative API calls:
Security Note:
Keep your admin API key secure and never commit it to version control
Only share the admin API key with authorized administrators
Regular users should never have access to the admin API key
Available Administrative Operations
The REST API provides endpoints for:
User Management: Create, list, update, and delete users
Project Management: Create projects, assign configurations, manage users
API Key Management: Generate, rotate, disable/enable, and delete API keys
Configuration Management: Create, update, and manage MCP configurations and servers
For complete API documentation and examples, see:
Interactive API docs at
http://localhost:8001/docs
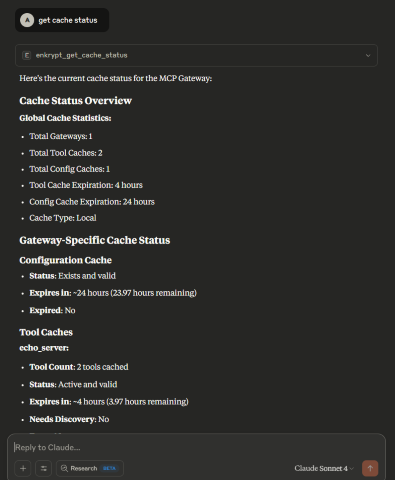
The Gateway can give the summary of it's cache status by looking at the local/external cache server
This is useful to debug issues if for example a tool was updated remotely by a server but the Gateway is not aware of it yet
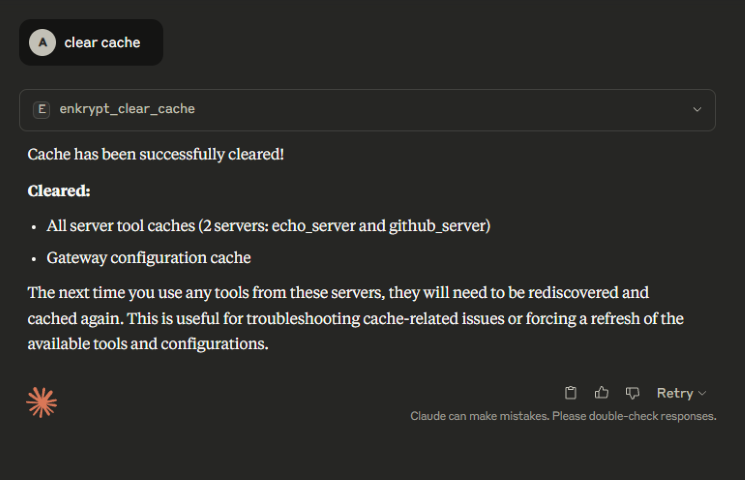
The Gateway can clear it's cache from local/external cache server
This is useful to clear the cache if for example a tool was updated remotely by a server but the Gateway is not aware of it yet
You can either clear all cache or specific cache by providing the
server_nameExample:
clear cache for echo_server
You can also clear all cache or just the gateway cache or just the server cache
Example:
clear all cache,clear just gateway cache,clear server cache for echo_server,Clear all server cache
12. Deployment patterns
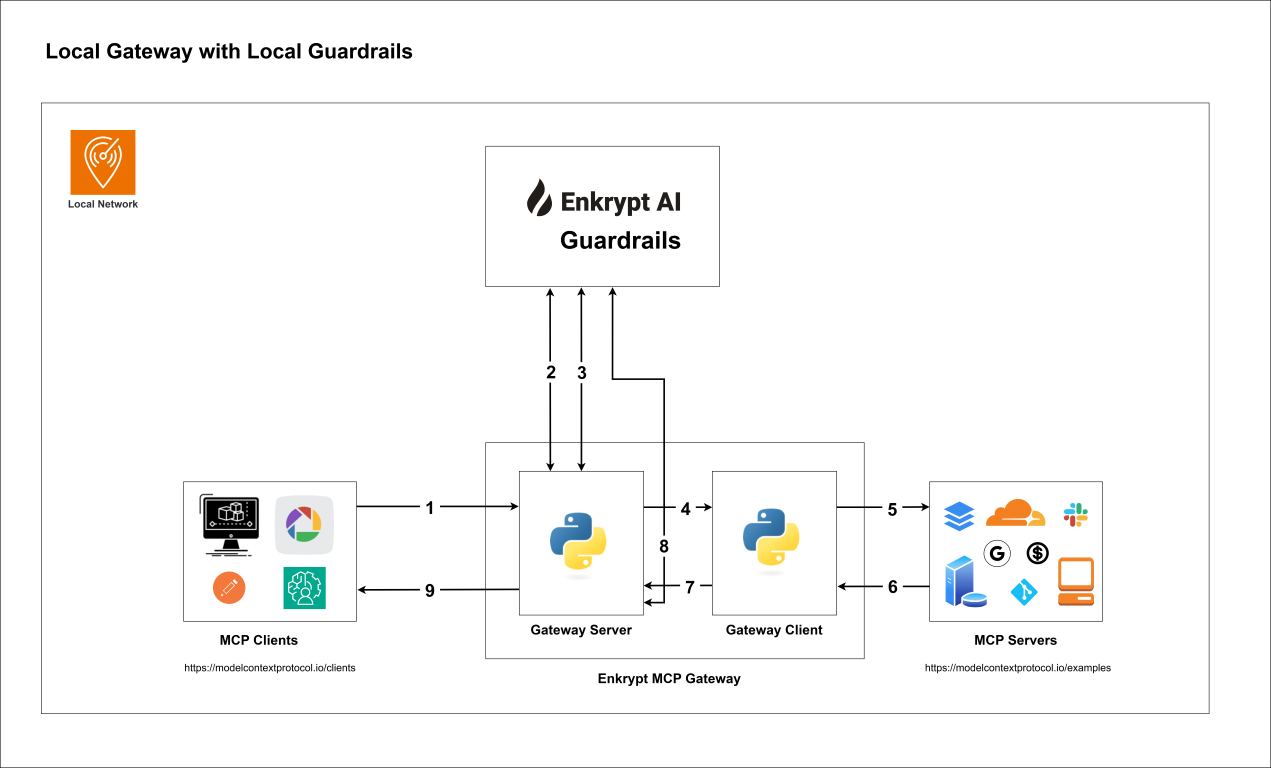
12.1 Local Gateway, Local Guardrails and Local MCP Server
12.2 Local Gateway, Local MCP Server with Remote Guardrails

12.3 Local Gateway with Remote MCP Server and Remote Guardrails
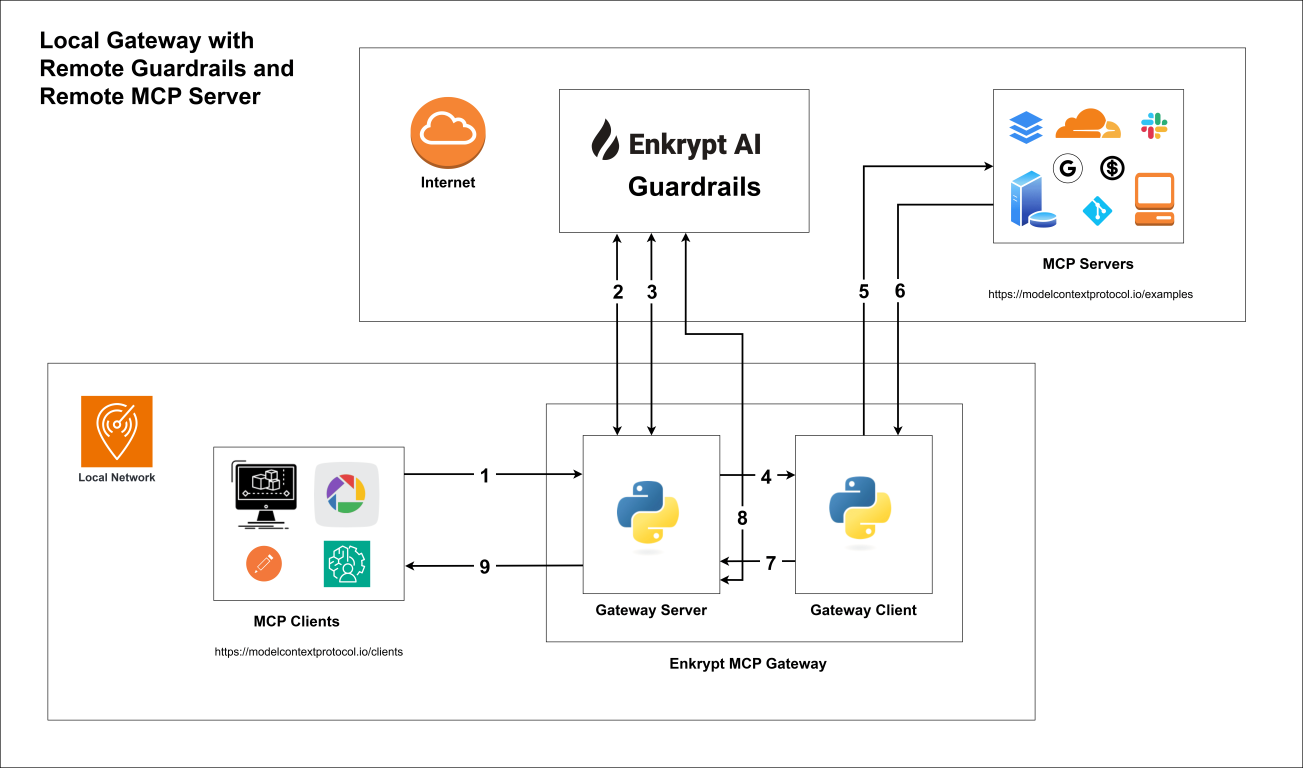
12.4 Remote Gateway, Remote MCP Server and Remote Guardrails

13. Uninstall the Gateway
To remove the Gateway from any MCP client, just remove the MCP server block
"Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway": {...}from the client's config file.Restart the MCP client to apply the changes for some clients like Claude Desktop. Cursor does not require a restart.
To uninstall the pip package, run the following command:
pip uninstall secure-mcp-gateway
14. Troubleshooting
If any calls fail in the client, please look at the mcp logs of the respective client
See this for Claude logs location
Example 🍎 Linux/macOS log path:
~/Library/Logs/Claude/mcp-server-Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway.logExample 🪟 Windows log path:
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Claude\logs\mcp-server-Enkrypt Secure MCP Gateway.log
If you see errors like
Exception: unhandled errors in a TaskGroup (1 sub-exception)then maybe the MCP server the gateway is trying to use is not running.So, please make sure the file it is trying to access is available
Any pre-requisites for the MCP server to run are met like
dockerrunning, etc.
If we need more detailed logs, please set the
enkrypt_log_leveltodebugin theenkrypt_mcp_config.jsonfile and restart the MCP client.
14.1 OpenTelemetry Troubleshooting
SSL Handshake Errors
If you see SSL errors like:
SSL_ERROR_SSL: error:100000f7:SSL routines:OPENSSL_internal:WRONG_VERSION_NUMBERSolution: Add
insecure=Trueto the OTLP exporter configuration intelemetry.pyNo Logs in Loki
Verify OTLP collector is running:
docker logs secure-mcp-gateway-otel-collector-1Check collector config in
otel_collector/otel-collector-config.yamlVerify Loki is receiving data:
curl -G -s "http://localhost:3100/loki/api/v1/query" --data-urlencode 'query={job="enkrypt"}'
Missing Metrics
Check OTLP collector metrics pipeline:
curl http://localhost:8888/metricsVerify metrics in collector logs:
docker logs secure-mcp-gateway-otel-collector-1 | grep "metrics"
Docker Issues
# Restart the stack docker-compose down docker-compose up -d # Check individual service logs docker logs <service-name>
15. Known Issues being worked on
Output guardrails are not being applied to non-text tool results. Support for other media types like images, audio, etc. is coming soon.
16. Known Limitations
The Gateway does not support a scenario where the Gateway is deployed remotely but the MCP server is deployed locally (without being exposed to the internet). This is because the Gateway needs to know the MCP server's address to forward requests to it.
17. Contribute
Look at the
TODOfile for the current work in progress and yet to be implemented featuresInstall the gateway locally to test your changes
by following the Git clone steps
or build it using
python -m build, activate the venv and install usingpip install .
Report or fix any bugs you encounter 😊
18. Testing
The gateway includes a comprehensive test suite that validates all core functionality including server discovery, tool execution, guardrails, caching, telemetry, and more.
Prerequisites
Gateway installed locally (follow Local Installation)
Virtual environment activated
Echo OAuth MCP server running (for testing remote server scenarios)
Running the Test Suite
Step 1: Set Environment Variable
Windows PowerShell:
Windows Command Prompt:
macOS/Linux:
This environment variable enables the echo OAuth server to run in HTTP mode for testing.
Step 2: Start the Echo OAuth Server
Navigate to the echo server directory and start it:
Windows PowerShell:
macOS/Linux:
The server will start on http://localhost:8001/mcp/ and remain running. Keep this terminal open.
Step 3: Run the Test Suite
Open a new terminal, activate your virtual environment, and run the tests:
Windows PowerShell:
macOS/Linux:
Test Coverage
The test suite includes:
Server Discovery Tests: List servers, get server info, discover tools
Tool Execution Tests: Call tools, multiple tool calls, error handling
Cache Tests: Cache status, cache clearing, cache expiration
Guardrails Tests: Input/output guardrails, async guardrails, PII redaction
Telemetry Tests: OpenTelemetry integration, metrics, traces, logs
Configuration Tests: Timeout settings, log levels, external cache
Integration Tests: Full workflows, error recovery, performance
Expected Output
The test runner will display:
Progress for each test
Success/failure status
Execution duration
Final summary with pass/fail counts
Example output:
Troubleshooting Tests
Echo server connection errors:
Verify the echo OAuth server is running on port 8001
Check that
MCP_HTTP_MODEenvironment variable is setEnsure no other service is using port 8001
Gateway configuration errors:
Verify
enkrypt_mcp_config.jsonexists in~/.enkrypt/directoryCheck that the config file has valid gateway keys and server configurations
Ensure virtual environment has all dependencies installed
Test failures:
Enable debug logging by setting
enkrypt_log_level: "DEBUG"in configCheck MCP client logs for detailed error messages
Verify all prerequisites are installed (Python 3.11+, pip, uv)
19. License
19.1 Enkrypt AI MCP Gateway Core
This project's core functionality is licensed under the MIT License.
For the full license text, see the LICENSE.txt file in this repository.
19.2 Enkrypt AI Guardrails, Logo, and Branding
© 2025 Enkrypt AI. All rights reserved.
Enkrypt AI software is provided under a proprietary license. Unauthorized use, reproduction, or distribution of this software or any portion of it is strictly prohibited.
Terms of Use: https://www.enkryptai.com/terms-and-conditions
Privacy Policy: https://app.enkryptai.com/privacy-policy
Enkrypt AI and the Enkrypt AI logo are trademarks of Enkrypt AI, Inc.