This mcp-confluent server enables AI assistants to interact with Confluent Cloud REST APIs through natural language commands, providing comprehensive management capabilities for:
Kafka: List, create, and delete topics; produce and consume messages; alter topic configurations
Flink SQL: Create, read, list, and delete SQL statements and view their results
Schema Registry: Search, list, and manage schemas
Connectors: List, create, retrieve, and delete Kafka connectors
Tags: Create tag definitions, assign tags to topics, list topics by tags, and manage tag associations
Cluster & Environment: List clusters and environments, retrieve environment details
These capabilities allow for complete management of Confluent Cloud resources through conversational AI interactions.
Allows configuration of Confluent Cloud credentials and endpoints through environment variables, supporting secure authentication with various Confluent services.
Enables AI assistants to interact with Confluent Cloud REST APIs, providing tools for managing Kafka topics, connectors, and Flink SQL statements through natural language interactions.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@mcp-confluentlist all Kafka topics in my production cluster"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
mcp-confluent
An MCP server implementation that enables AI assistants to interact with Confluent Cloud REST APIs. This server allows AI tools like Claude Desktop and Goose CLI to manage Kafka topics, connectors, and Flink SQL statements through natural language interactions.
Demo
Goose CLI
Claude Desktop
Related MCP server: MCP Server
Table of Contents
User Guide
Getting Started
Create a Copy the example
.envfile structure (shown below) into a new file named.envin the root of your project.Populate the Fill in the necessary values for your Confluent Cloud environment. See the Configuration section for details on each variable.
Install Node.js (if not already installed)
We recommend using NVM (Node Version Manager) to manage Node.js versions
Install and use Node.js:
nvm install 22 nvm use 22
Configuration
Create a .env file in the root directory of your project with the following configuration:
Prerequisites & Setup for Tableflow Commands
In order to leverage Tableflow commands to interact with your data ecosystem and successfully execute these Tableflow commands and manage resources (e.g., interacting with data storage like AWS S3 and metadata catalogs like AWS Glue), certain IAM (Identity and Access Management) permissions and configurations are essential.
It is crucial to set up the necessary roles and policies in your cloud environment (e.g., AWS) and link them correctly within Confluent Cloud. This ensures your Flink SQL cluster, which powers Tableflow, has the required authorization to perform operations on your behalf.
Please refer to the following Confluent Cloud documentation for detailed instructions on setting up these permissions and integrating with custom storage and Glue:
Confluent Cloud Tableflow Quick Start with Custom Storage & Glue: https://docs.confluent.io/cloud/current/topics/tableflow/get-started/quick-start-custom-storage-glue.html
Ensuring these prerequisites are met will prevent authorization errors when the mcp-server attempts to provision or manage Tableflow-enabled tables.
Authentication for HTTP/SSE Transports
When using HTTP or SSE transports, the MCP server requires API key authentication to prevent unauthorized access and protect against DNS rebinding attacks. This is enabled by default.
Generating an API Key
Generate a secure API key using the built-in utility:
This will output a 64-character key generated using secure cryptography:
Configuring Authentication
Add the generated key to your .env file:
Making Authenticated Requests
Include the API key in the cflt-mcp-api-Key header for all HTTP/SSE requests:
DNS Rebinding Protection
The server includes additional protections against DNS rebinding attacks:
Host Header Validation: Only requests with allowed Host headers are accepted
Configure allowed hosts if needed:
Additional security to prevent internet exposure of MCP server
Localhost Binding: Server binds to
127.0.0.1by default (not0.0.0.0)
Disabling Authentication (Development Only)
For local development, you can disable authentication:
Warning: Never disable authentication in production or when the server is network-accessible.
Environment Variables Reference
Variable | Description | Default Value | Required |
HTTP_HOST | Host to bind for HTTP transport. Defaults to localhost only for security. | "127.0.0.1" | Yes |
HTTP_MCP_ENDPOINT_PATH | HTTP endpoint path for MCP transport (e.g., '/mcp') (string) | "/mcp" | Yes |
HTTP_PORT | Port to use for HTTP transport (number (min: 0)) | 8080 | Yes |
LOG_LEVEL | Log level for application logging (trace, debug, info, warn, error, fatal) | "info" | Yes |
MCP_API_KEY | API key for HTTP/SSE authentication. Generate using | No* | |
MCP_AUTH_DISABLED | Disable authentication for HTTP/SSE transports. WARNING: Only use in development environments. | false | No |
MCP_ALLOWED_HOSTS | Comma-separated list of allowed Host header values for DNS rebinding protection. | "localhost,127.0.0.1" | No |
SSE_MCP_ENDPOINT_PATH | SSE endpoint path for establishing SSE connections (e.g., '/sse', '/events') (string) | "/sse" | Yes |
SSE_MCP_MESSAGE_ENDPOINT_PATH | SSE message endpoint path for receiving messages (e.g., '/messages', '/events/messages') (string) | "/messages" | Yes |
BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS | List of Kafka broker addresses in the format host1:port1,host2:port2 used to establish initial connection to the Kafka cluster (string) | No | |
CONFLUENT_CLOUD_API_KEY | Master API key for Confluent Cloud platform administration, enabling management of resources across your organization (string (min: 1)) | No | |
CONFLUENT_CLOUD_API_SECRET | Master API secret paired with CONFLUENT_CLOUD_API_KEY for comprehensive Confluent Cloud platform administration (string (min: 1)) | No | |
CONFLUENT_CLOUD_REST_ENDPOINT | Base URL for Confluent Cloud's REST API services (default) | No | |
FLINK_API_KEY | Authentication key for accessing Confluent Cloud's Flink services, including compute pools and SQL statement management (string (min: 1)) | No | |
FLINK_API_SECRET | Secret token paired with FLINK_API_KEY for authenticated access to Confluent Cloud's Flink services (string (min: 1)) | No | |
FLINK_COMPUTE_POOL_ID | Unique identifier for the Flink compute pool, must start with 'lfcp-' prefix (string) | No | |
FLINK_DATABASE_NAME | Name of the associated Kafka cluster used as a database reference in Flink SQL operations (string (min: 1)) | No | |
FLINK_ENV_ID | Unique identifier for the Flink environment, must start with 'env-' prefix (string) | No | |
FLINK_ENV_NAME | Human-readable name for the Flink environment used for identification and display purposes (string (min: 1)) | No | |
FLINK_ORG_ID | Organization identifier within Confluent Cloud for Flink resource management (string (min: 1)) | No | |
FLINK_REST_ENDPOINT | Base URL for Confluent Cloud's Flink REST API endpoints used for SQL statement and compute pool management (string) | No | |
KAFKA_API_KEY | Authentication credential (username) required to establish secure connection with the Kafka cluster (string (min: 1)) | No | |
KAFKA_API_SECRET | Authentication credential (password) paired with KAFKA_API_KEY for secure Kafka cluster access (string (min: 1)) | No | |
KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID | Unique identifier for the Kafka cluster within Confluent Cloud ecosystem (string (min: 1)) | No | |
KAFKA_ENV_ID | Environment identifier for Kafka cluster, must start with 'env-' prefix (string) | No | |
KAFKA_REST_ENDPOINT | REST API endpoint for Kafka cluster management and administration (string) | No | |
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_API_KEY | Authentication key for accessing Schema Registry services to manage and validate data schemas (string (min: 1)) | No | |
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_API_SECRET | Authentication secret paired with SCHEMA_REGISTRY_API_KEY for secure Schema Registry access (string (min: 1)) | No | |
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_ENDPOINT | URL endpoint for accessing Schema Registry services to manage data schemas (string) | No | |
TABLEFLOW_API_KEY | Authentication key for accessing Confluent Cloud's Tableflow services (string (min: 1)) | No | |
TABLEFLOW_API_SECRET | Authentication secret paired with TABLEFLOW_API_KEY for secure Tableflow access (string (min: 1)) | No |
Usage
This MCP server is designed to be used with various MCP clients, such as Claude Desktop or Goose CLI/Desktop. The specific configuration and interaction will depend on the client you are using. However, the general steps are:
Start the Server: You can run the MCP server in one of two ways:
From source: Follow the instructions in the Developer Guide to build and run the server from source. This typically involves:
Installing dependencies (
npm install)Building the project (
npm run buildornpm run dev)
With npx: You can start the server directly using npx (no build required):
npx -y @confluentinc/mcp-confluent -e /path/to/confluent-mcp-server/.env
Configure your MCP Client: Each client will have its own way of specifying the MCP server's address and any required credentials. You'll need to configure your client (e.g., Claude, Goose) to connect to the address where this server is running (likely
localhostwith a specific port). The port the server runs on may be configured by an environment variable.Start the MCP Client: Once your client is configured to connect to the MCP server, you can start your mcp client and on startup - it will stand up an instance of this MCP server locally. This instance will be responsible for managing data schemas and interacting with Confluent Cloud on your behalf.
Interact with Confluent through the Client: Once the client is connected, you can use the client's interface to interact with Confluent Cloud resources. The client will send requests to this MCP server, which will then interact with Confluent Cloud on your behalf.
Configuring Claude Desktop
See here for more details about installing Claude Desktop and MCP servers.
To configure Claude Desktop to use this MCP server:
Open Claude Desktop Configuration
On Mac:
~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.jsonOn Windows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
Edit Configuration File
Open the config file in your preferred text editor
Add or modify the configuration using one of the following methods:
{ "mcpServers": { "confluent": { "command": "node", "args": [ "/path/to/confluent-mcp-server/dist/index.js", "--env-file", "/path/to/confluent-mcp-server/.env" ] } } }{ "mcpServers": { "confluent": { "command": "npx", "args": [ "-y" "@confluentinc/mcp-confluent", "-e", "/path/to/confluent-mcp-server/.env" ] } } }Replace
/path/to/confluent-mcp-server/with the actual path where you've installed this MCP server.Restart Claude Desktop
Close and reopen Claude Desktop for the changes to take effect
The MCP server will automatically start when Claude Desktop launches
Now Claude Desktop will be configured to use your local MCP server for Confluent interactions.
Configuring Goose CLI
See here for detailed instructions on how to install the Goose CLI.
Once installed, follow these steps:
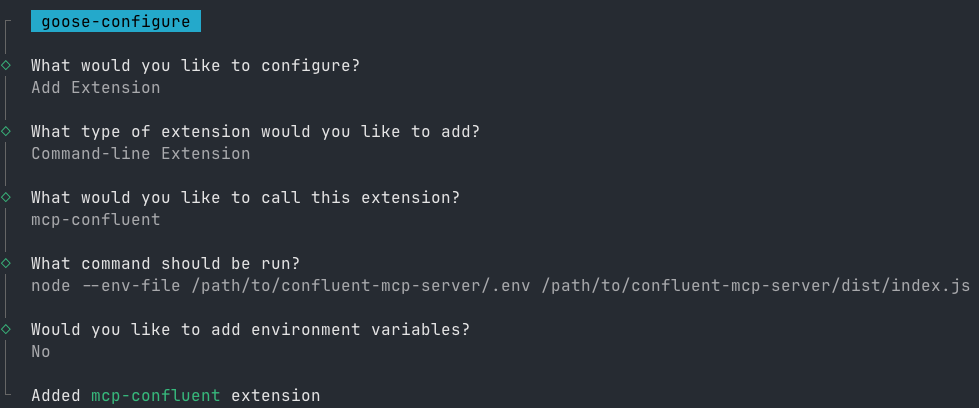
Run the Configuration Command:
goose configureFollow the Interactive Prompts:
Select
Add extensionChoose
Command-line ExtensionEnter
mcp-confluentas the extension nameChoose one of the following configuration methods:
node /path/to/confluent-mcp-server/dist/index.js --env-file /path/to/confluent-mcp-server/.envnpx -y @confluentinc/mcp-confluent -e /path/to/confluent-mcp-server/.env
Replace /path/to/confluent-mcp-server/ with the actual path where you've installed this MCP server.
Configuring Gemini CLI
For detailed information about Gemini CLI extensions and MCP servers, please refer to the official documentation:
Here's how to get mcp-confluent running with Gemini CLI:
Install Gemini CLI: If you haven't already, install the Gemini CLI. You can find installation instructions on the official GitHub repository.
Install the
gemini extensions install https://github.com/confluentinc/mcp-confluent # Navigate to the root directory of this project (where `gemini-extension.json` is located) and run: # gemini extensions install .This command registers the
mcp-confluentserver with Gemini CLI and creates a dedicated directory for it under~/.gemini/extensions/mcp-confluent.Provide Environment Variables: The extension requires your Confluent Cloud credentials and configuration to be available in a
.envfile.First, ensure you have a correctly populated
.envfile in the root of this project. For instructions, see the Configuration section.Next, copy your
.envfile into the extension's directory so Gemini CLI can access it (the Gemini extension expects the.envfile at${extensionPath}${pathSeparator}.env; see the variables documentation for details):
cp .env ~/.gemini/extensions/mcp-confluent/.envVerify and Use: You can now start using the Confluent tools via Gemini CLI. To verify that the tools are available, you can list them:
gemini -l # or `gemini extensions list`And here's an example of invoking a tool:
gemini .... 🟢 mcp-confluent (from mcp-confluent) - Ready (24 tools) .... Using: 1 MCP server (ctrl+t to toggle) ╭───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮ │ > list topics │ ╰───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯ ╭────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮ │ ✓ list-topics (mcp-confluent MCP Server) {} │ │ │ │ Kafka topics: │ │ products_summarized,products,topic_8,products_summarized_with_embeddings,elastic_minimized,user_message_related_products,user_message_embeddin │ │ gs,dlq-lcc-d3738o,user_message,elastic │ ╰────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯ ✦ Okay, I see the following topics: products_summarized, products, topic_8, products_summarized_with_embeddings, elastic_minimized, user_message_related_products, user_message_embeddings, dlq-lcc-d3738o, user_message, and elastic.
mcp-confluent CLI Usage
The MCP server provides a flexible command line interface (CLI) for advanced configuration and control. The CLI allows you to specify environment files, transports, and fine-tune which tools are enabled or blocked.
Basic Usage
You can view all CLI options and help with:
Example: Deploy using all transports
Example: Allow Only Specific Tools
Example: Block Certain Tools
Example: Use Tool Lists from Files
Example: List All Available Tools
Tip: The allow-list is applied before the block-list. If neither is provided, all tools are enabled by default.
Developer Guide
Project Structure
Building and Running
Install Dependencies:
npm installDevelopment Mode (watch for changes):
npm run devThis command compiles the TypeScript code to JavaScript and automatically rebuilds when changes are detected in the
src/directory.Production Build (one-time compilation):
npm run buildStart the Server:
npm run start
Docker
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following installed on your system:
Docker Desktop (or Docker Engine and Docker Compose): https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop
Environment Variables
The MCP server requires several environment variables to connect to Confluent Cloud and other relevant services. These should be provided in the .env file in the root directory of this project. Or you can add them directly in the docker-compose.yml
Building and Running with Docker
Here's how to build your Docker image and run it in different modes.
Navigate to your project directory. Open your terminal or command prompt and change to the directory containing the
Dockerfile.cd /path/to/repo/mcp-confluentBuild the Docker image.
This command creates the
mcp-serverimage based on theDockerfilein the current directory.docker build -t mcp-server .Run the container
--rm: Automatically removes the container when it exits. This helps keep your system clean.-i: Keeps STDIN open (runs the server using stdio transport by default).-d: Runs the container in detached mode (in the background).-p 3000:3000: Maps port 3000 on your host machine to port 3000 inside the container. Adjust this if your app listens on a different port.
docker run --rm -i -d -p 3000:3000 mcp-server(Optional)
-tTransport Mode to enable http transport
docker run --rm -d -p 3000:3000 mcp-server -t http
Building and Running with Docker Compose
Navigate to the project root: Open your terminal or command prompt and change to the directory containing Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml.
cd /path/to/repo/mcp-confluentBuild and run the service: Docker Compose will build the Docker image (if not already built) and start the mcp-server service.
docker compose up --buildThe --build flag ensures that Docker Compose rebuilds the image before starting the container. You can omit this flag on subsequent runs if you haven't changed the Dockerfile or source code.
The server will be accessible on http://localhost:3000 (or the port specified in HTTP_PORT in your .env file).
Stopping the Server To stop the running MCP server and remove the containers, press Ctrl+C in the terminal where docker compose up is running.
Alternatively, in a new terminal from the project root, you can run:
docker compose downThis command stops and removes the containers, networks, and volumes created by docker compose up.
Testing
MCP Inspector
For testing MCP servers, you can use MCP Inspector which is an interactive developer tool for testing and debugging MCP servers.
Adding a New Tool
Add a new enum to the enum class
ToolName.Add your new tool to the handlers map in the
ToolFactoryclass.Create a new file, exporting the class that extends
BaseToolHandler.Implement the
handlemethod of the base class.Implement the
getToolConfigmethod of the base class.
Once satisfied, add it to the set of
enabledToolsinindex.ts.
Generating Types
Contributing
Bug reports and feedback is appreciated in the form of Github Issues. For guidelines on contributing please see CONTRIBUTING.md