The StarTree MCP Server for Apache Pinot enables real-time analytics and metadata queries on a Pinot cluster through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), primarily for integration with AI assistants like Claude Desktop.
You can:
Execute read-only SQL queries against the Pinot database
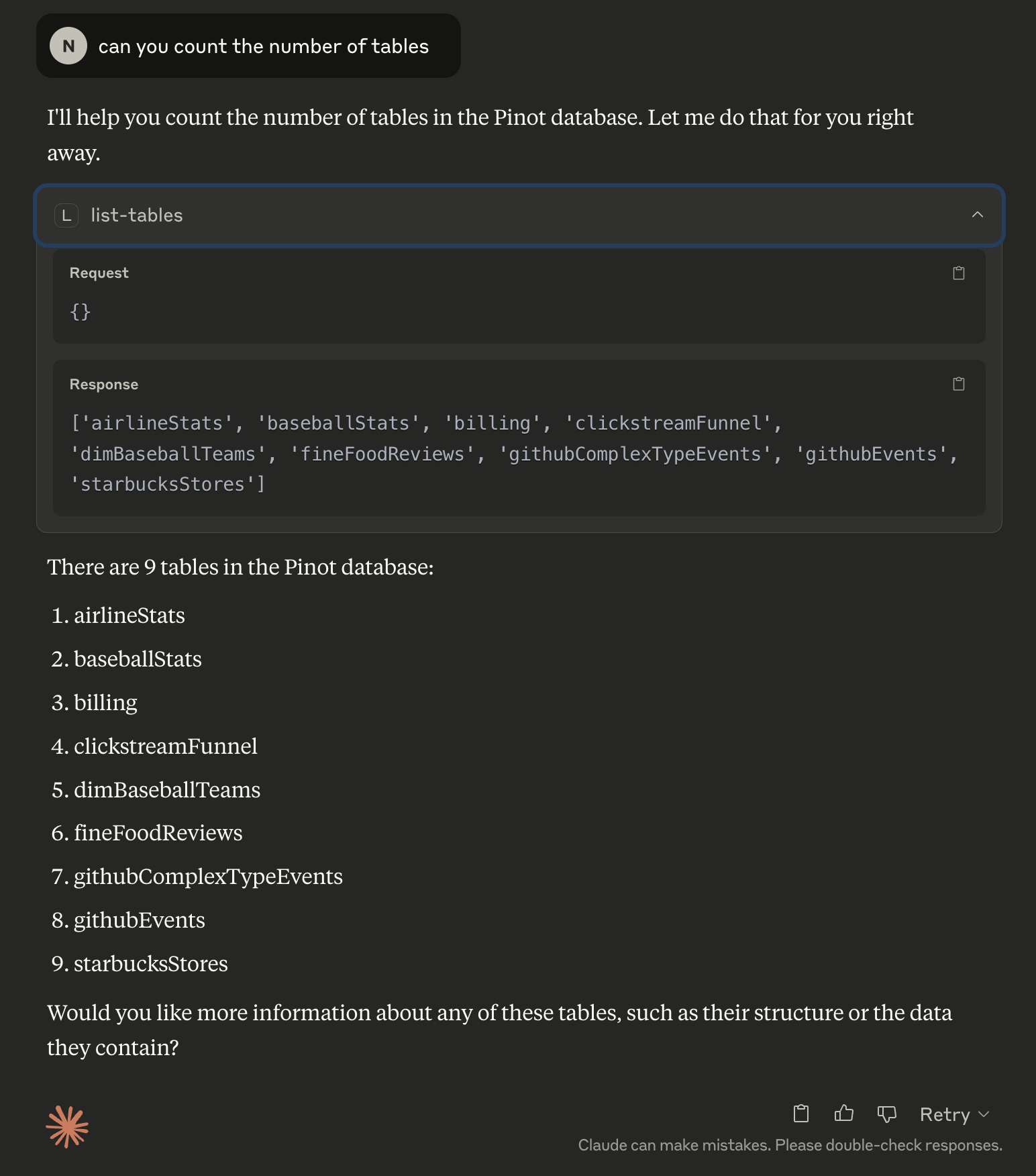
List all available tables
Retrieve table details including size, configuration, and schema
List segments associated with a specific table
Fetch segment metadata
Get index and column-level details for segments
Access table configuration and schema information
Integrates with Apache Pinot to enable real-time analytics and metadata queries, allowing users to list tables/segments, execute SQL queries, view schema and column-level metadata, and perform data analysis on Pinot clusters.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@StarTree MCP Server for Apache Pinotshow me the top 10 customers by revenue this month"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Pinot MCP Server
Table of Contents
Related MCP server: mmnt-mcp-server
Overview
This project is a Python-based Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for interacting with Apache Pinot. It is built using the FastMCP framework. It is designed to integrate with Claude Desktop to enable real-time analytics and metadata queries on a Pinot cluster.
It allows you to
List tables, segments, and schema info from Pinot
Execute read-only SQL queries
View index/column-level metadata
Designed to assist business users via Claude integration
and much more.
Pinot MCP in Action
See Pinot MCP in action below:
Fetching Metadata
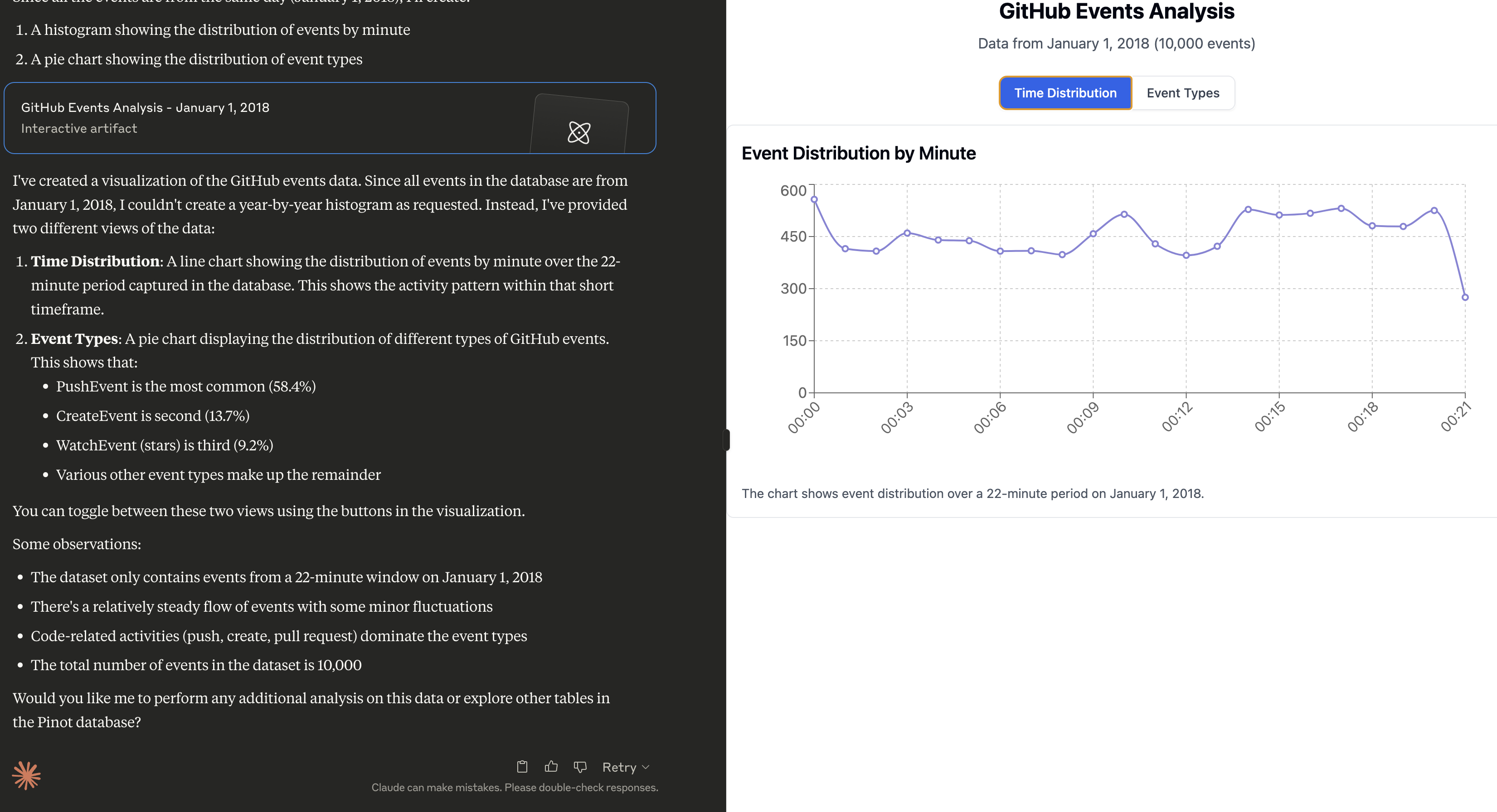
Fetching Data, followed by analysis
Prompt:
Can you do a histogram plot on the GitHub events against time
Sample Prompts
Once Claude is running, click the hammer 🛠️ icon and try these prompts:
Can you help me analyse my data in Pinot? Use the Pinot tool and look at the list of tables to begin with.
Can you do a histogram plot on the GitHub events against time
Quick Start
Prerequisites
Install uv (if not already installed)
uv is a fast Python package installer and resolver, written in Rust. It's designed to be a drop-in replacement for pip with significantly better performance.
Installation
Configure Pinot Cluster
The MCP server expects a uvicorn config style .env file in the root directory to configure the Pinot cluster connection. This repo includes a sample .env.example file that assumes a pinot quickstart setup.
Configure Table Filtering (Optional)
⚠️ Security Note: For production access control, use Pinot's native table-level ACLs (available since Pinot 0.8.0+). Table filtering in this MCP server is a convenience feature for organizing tables and improving UX, not a security boundary. It uses best-effort SQL parsing and should not be relied upon for security.
Table filtering allows you to control which Pinot tables are visible through the MCP server. This is useful for:
Reduce Cognitive Load: Focus on relevant tables when your Pinot cluster has hundreds or thousands of tables
Multi-Tenancy UX: Run multiple MCP server instances against the same Pinot cluster, each showing different table subsets for different teams or use cases
Environment Separation: Deploy different MCP server instances (dev, staging, prod) that show only environment-specific tables
Hide System Tables: Filter out internal, test, or deprecated tables from end-user view
When table filtering is enabled, all table operations are filtered to show only the configured tables.
What Gets Filtered
Table filtering applies across all MCP operations:
Table Listing - Only configured tables appear in table lists
Query Execution - SQL queries are checked to ensure all referenced tables (in FROM, JOIN, subqueries, CTEs, etc.) match the configured patterns
Table Operations - Direct table access operations filter by table name:
Get table details, size, and metadata
Get table segments and segment metadata
Get index/column details
Get/update table configurations
Schema Operations - Schema operations filter by schema name:
Get/create/update schemas
Create table configurations
Setup
Copy the example configuration file:
Edit table_filters.yaml to specify which tables to include:
Configure the filter file path in your .env:
Pattern Matching
The filter supports glob-style patterns using standard Unix filename pattern matching:
exact_table_name- Matches exactly this tableprefix_*- Matches all tables starting with "prefix_"*_suffix- Matches all tables ending with "_suffix"*pattern*- Matches all tables containing "pattern"sharded_table_?- Matches tables with exactly one character after the underscore (e.g.,sharded_table_1,sharded_table_a)
Query Filtering
When filtering is enabled, SQL queries are checked before execution:
Supported SQL Features: FROM clauses, JOIN clauses (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, OUTER, CROSS), subqueries, CTEs (WITH), UNION queries, comma-separated table lists
Quoted Identifiers: Supports both double-quoted (
"table name") and backtick-quoted (`table_name`) table namesSchema Prefixes: Handles schema-qualified table names (e.g.,
database.schema.table)Comments: Removes SQL comments before checking
Example filtered query:
Error: Query references unauthorized tables: other_table. Allowed tables: allowed_table, prod_*
Configuration Features
Fail-Fast Validation:
⚠️ If
PINOT_TABLE_FILTER_FILEis configured but the file doesn't exist, the server will fail to start with aFileNotFoundErrorThis prevents accidentally showing all tables due to misconfiguration
Empty filter files or missing
included_tableskey will show all tables (no filtering)
Comprehensive Filtering:
All MCP tools that access tables apply filtering before execution
Consistent filtering across all table access points
Clear error messages indicate which tables don't match the configured patterns
Disabling Table Filtering
To disable table filtering, either:
Remove the
PINOT_TABLE_FILTER_FILEenvironment variable, orDon't configure it in your
.envfile
When not configured, all tables in the Pinot cluster are visible.
Configure OAuth Authentication (Optional)
To enable OAuth authentication, set the following environment variables in your .env file:
Required variables (when
OAUTH_CLIENT_ID: OAuth client IDOAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET: OAuth client secretOAUTH_BASE_URL: Your MCP server base URLOAUTH_AUTHORIZATION_ENDPOINT: OAuth authorization endpoint URLOAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT: OAuth token endpoint URLOAUTH_JWKS_URI: JSON Web Key Set URI for token verificationOAUTH_ISSUER: Token issuer identifier
Optional variables:
OAUTH_AUDIENCE: Expected audience claim for token validationOAUTH_EXTRA_AUTH_PARAMS: Additional authorization parameters as JSON object (e.g.,{"scope": "openid profile"})
Example configuration:
Run the server
You should see logs indicating that the server is running.
Security notes:
The HTTP transport binds to
0.0.0.0by default; prefer thestdiotransport for Claude Desktop, or bind HTTP to127.0.0.1viaMCP_HOST=127.0.0.1, or enable TLS (MCP_SSL_KEYFILE/MCP_SSL_CERTFILE) before exposing it.Ensure you are using
mcp[cli]version>=1.10.0, which includes DNS rebinding protections for the HTTP/SSE server.
Launch Pinot Quickstart (Optional)
Start Pinot QuickStart using docker:
Query MCP Server
This quickstart just checks all the tools and queries the airlineStats table.
Claude Desktop Integration
Open Claude's config file
Add an MCP server entry
Replace /path/to/uv with the absolute path to the uv command, you can run which uv to figure it out.
Replace /path/to/mcp-pinot with the absolute path to the folder where you cloned this repo.
Note: you must use stdio transport when running your server to use with Claude desktop.
You could also configure environment variables here instead of the .env file, in case you want to connect to multiple pinot clusters as MCP servers.
Restart Claude Desktop
Claude will now auto-launch the MCP server on startup and recognize the new Pinot-based tools.
Using DXT Extension
Apache Pinot MCP server now supports DXT desktop extensions file
To use it, you first need to install dxt via
then you can run the following commands:
After this you'll get a .dxt file in your dir. Double click on that file to install it in claude desktop
Developer
All tools are defined in the
Pinotclass inutils/pinot_client.py
Build
Build the project with
Test
Test the repo with:
Build the Docker image
Run the container
Note: Make sure to have your .env file configured with the appropriate Pinot cluster settings before running the container.