The Notion MCP Server provides an interface to interact with Notion's API via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It allows AI clients to:
Manage Users: Retrieve user information, list all users, and get bot user details
Query Databases: Query, filter, create, update, and retrieve database content
Search Content: Search for pages or databases by title
Manage Blocks: Retrieve, append, update, or delete blocks in Notion
Manage Pages: Retrieve, create, or update pages and their properties
Handle Comments: Retrieve or create comments on pages or blocks
Allows interaction with the Notion API, enabling capabilities to search content, add comments, create pages, and retrieve page content. The integration connects to a Notion workspace through an integration token with configurable permissions.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Notion MCP Serversearch for my meeting notes from last week"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Notion MCP Server
We’ve introduced Notion MCP, a remote MCP server with the following improvements:
Easy installation via standard OAuth. No need to fiddle with JSON or API tokens anymore.
Powerful tools tailored to AI agents, including editing pages in Markdown. These tools are designed with optimized token consumption in mind.
Learn more and get started at Notion MCP documentation.
We are prioritizing, and only providing active support for, Notion MCP (remote). As a result:
We may sunset this local MCP server repository in the future.
Issues and pull requests here are not actively monitored.
Please do not file issues relating to the remote MCP here; instead, contact Notion support.
This project implements an MCP server for the Notion API.
⚠️ Version 2.0.0 breaking changes
Version 2.0.0 migrates to the Notion API 2025-09-03 which introduces data sources as the primary abstraction for databases.
What changed
Removed tools (3):
post-database-query- replaced byquery-data-sourceupdate-a-database- replaced byupdate-a-data-sourcecreate-a-database- replaced bycreate-a-data-source
New tools (7):
query-data-source- Query a data source (database) with filters and sortsretrieve-a-data-source- Get metadata and schema for a data sourceupdate-a-data-source- Update data source propertiescreate-a-data-source- Create a new data sourcelist-data-source-templates- List available templates in a data sourcemove-page- Move a page to a different parent locationretrieve-a-database- Get database metadata including its data source IDs
Parameter changes:
All database operations now use
data_source_idinstead ofdatabase_idSearch filter values changed from
["page", "database"]to["page", "data_source"]Page creation now supports both
page_idanddatabase_idparents (for data sources)
Do I need to migrate?
No code changes required. MCP tools are discovered automatically when the server starts. When you upgrade to v2.0.0, AI clients will automatically see the new tool names and parameters. The old database tools are no longer available.
If you have hardcoded tool names or prompts that reference the old database tools, update them to use the new data source tools:
Old Tool (v1.x) | New Tool (v2.0) | Parameter Change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No change (uses |
Note:
retrieve-a-databaseis still available and returns database metadata including the list of data source IDs. Useretrieve-a-data-sourceto get the schema and properties of a specific data source.
Total tools now: 22 (was 19 in v1.x)
Installation
1. Setting up integration in Notion
Go to https://www.notion.so/profile/integrations and create a new internal integration or select an existing one.
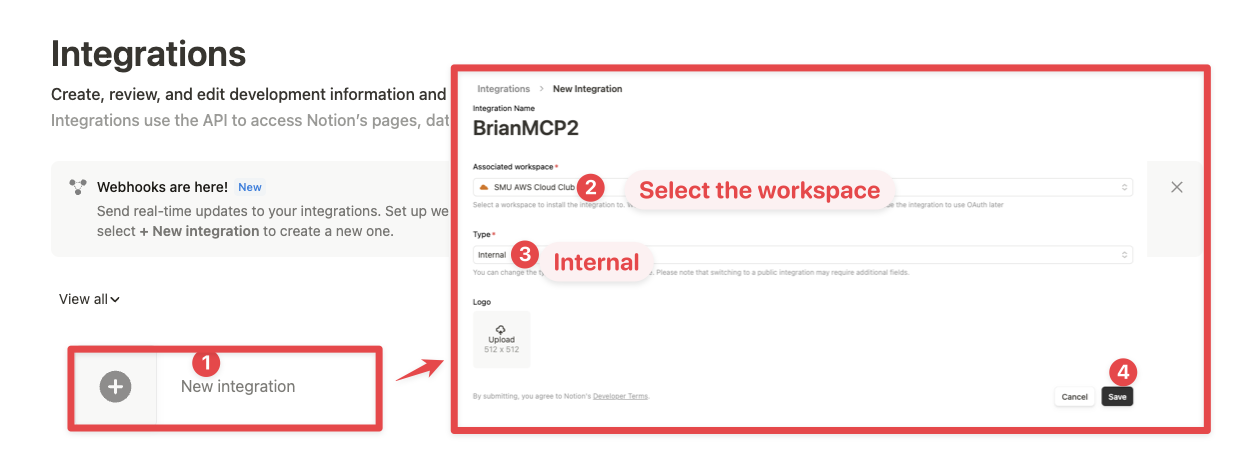
While we limit the scope of Notion API's exposed (for example, you will not be able to delete databases via MCP), there is a non-zero risk to workspace data by exposing it to LLMs. Security-conscious users may want to further configure the Integration's Capabilities.
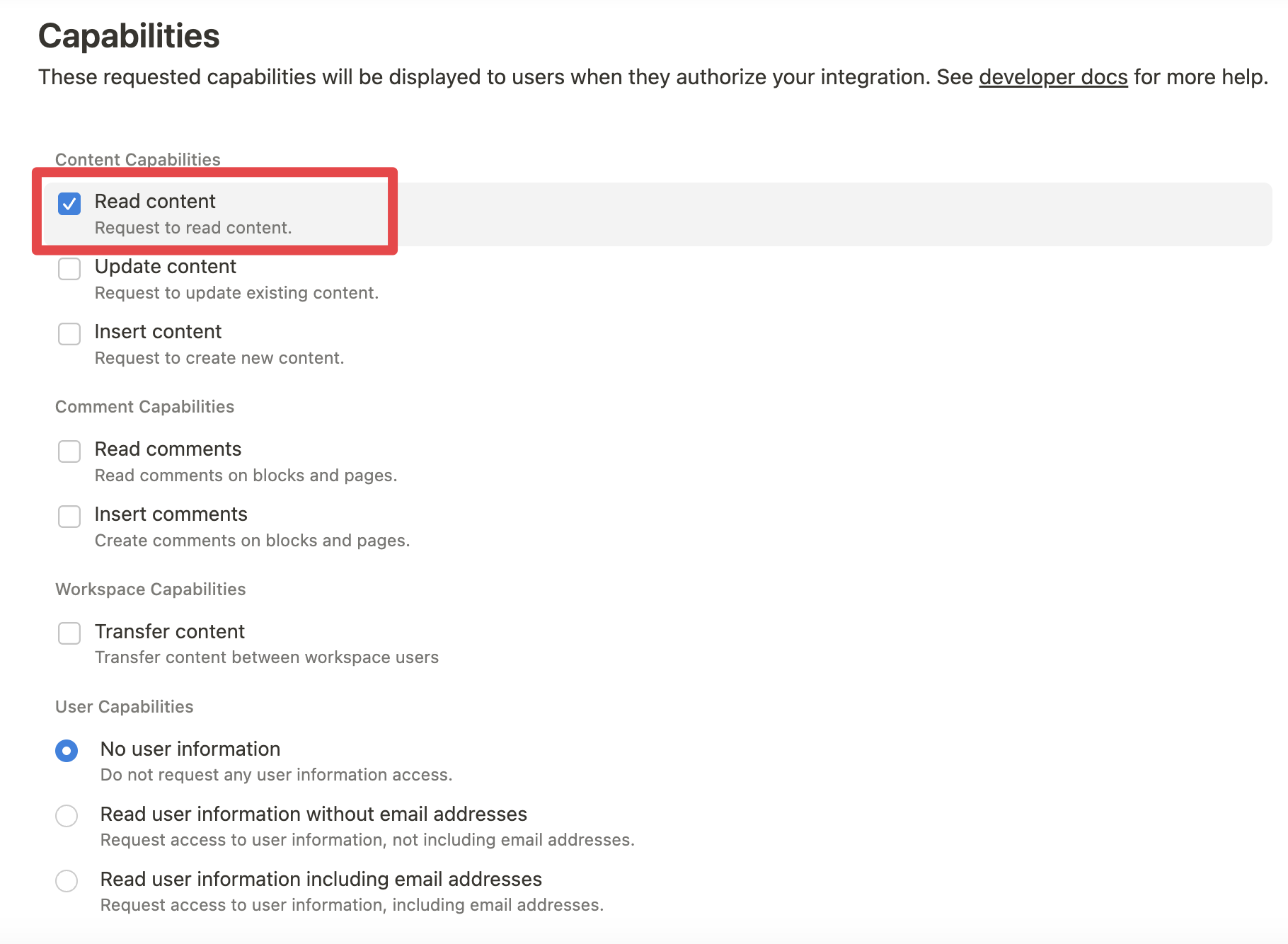
For example, you can create a read-only integration token by giving only "Read content" access from the "Configuration" tab:
2. Connecting content to integration
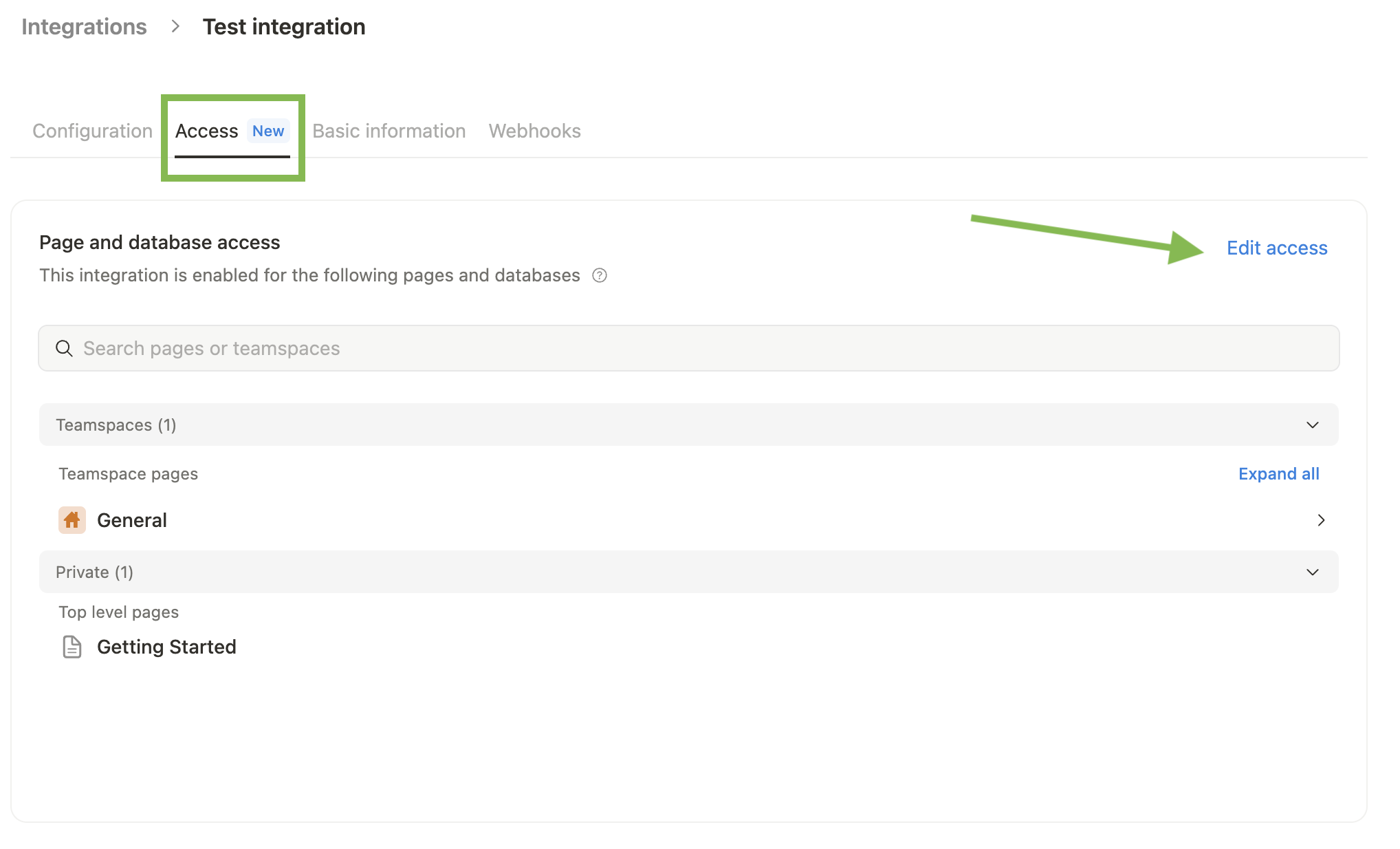
Ensure relevant pages and databases are connected to your integration.
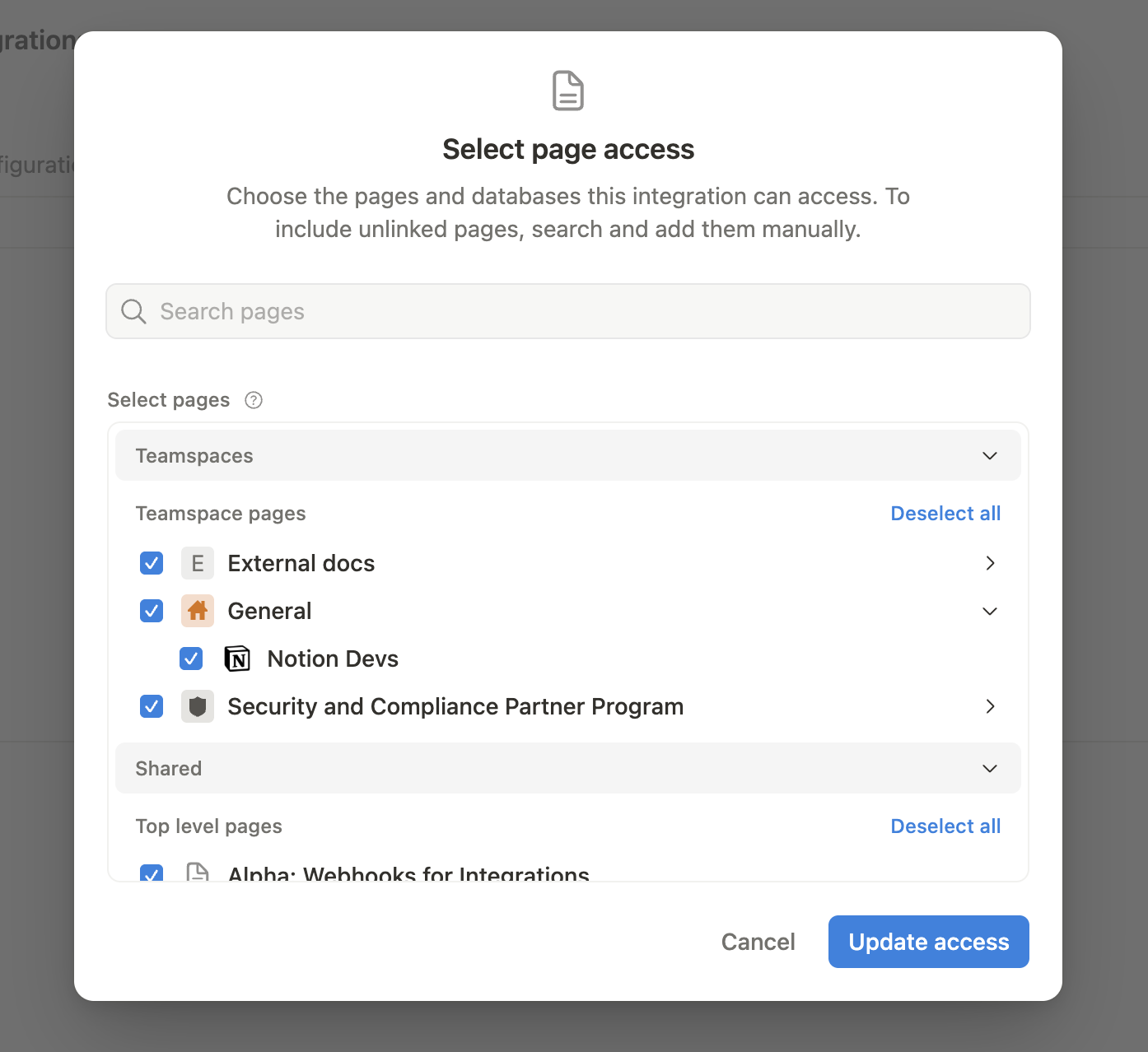
To do this, visit the Access tab in your internal integration settings. Edit access and select the pages you'd like to use.
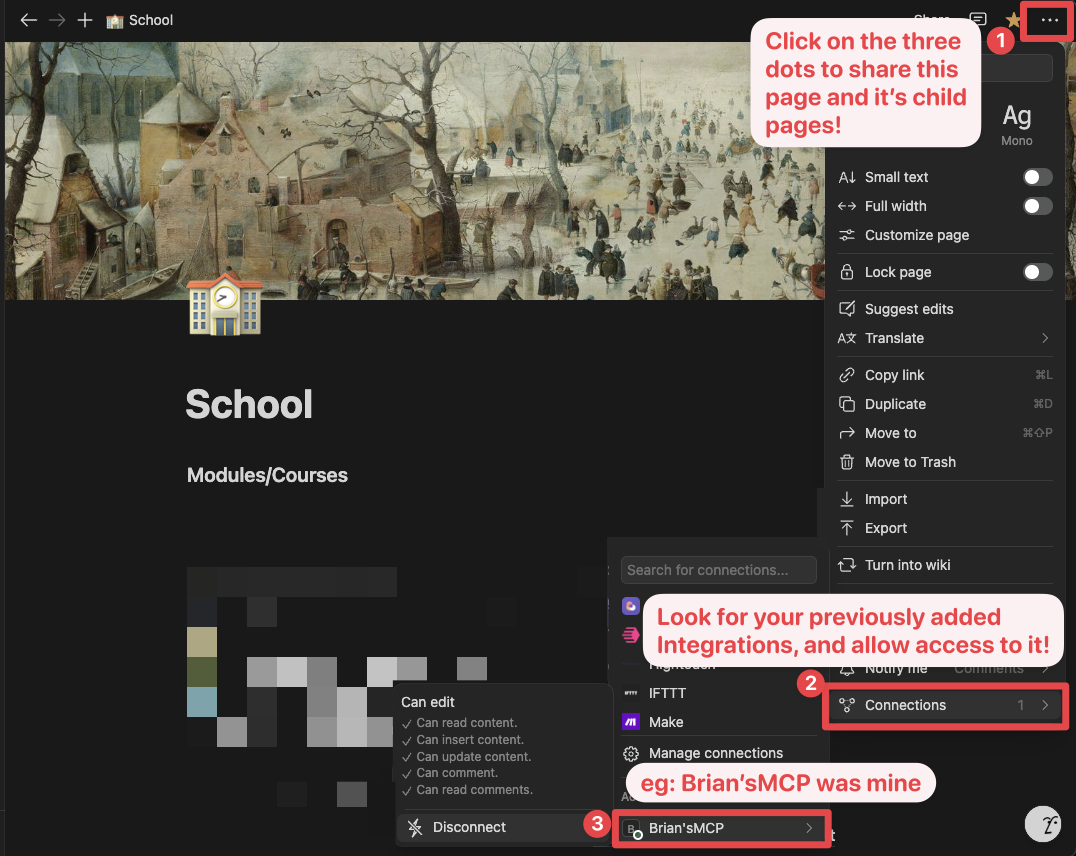
Alternatively, you can grant page access individually. You'll need to visit the target page, and click on the 3 dots, and select "Connect to integration".
3. Adding MCP config to your client
Using npm
Cursor & Claude
Add the following to your .cursor/mcp.json or claude_desktop_config.json (MacOS: ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json)
Option 1: Using NOTION_TOKEN (recommended)
Option 2: Using OPENAPI_MCP_HEADERS (for advanced use cases)
Zed
Add the following to your settings.json
GitHub Copilot CLI
Use the Copilot CLI to interactively add the MCP server:
Alternatively, create or edit the configuration file ~/.copilot/mcp-config.json and add:
For more information, see the Copilot CLI documentation.
Using Docker
There are two options for running the MCP server with Docker:
Option 1: Using the official Docker Hub image
Add the following to your .cursor/mcp.json or claude_desktop_config.json
Using NOTION_TOKEN (recommended):
Using OPENAPI_MCP_HEADERS (for advanced use cases):
This approach:
Uses the official Docker Hub image
Properly handles JSON escaping via environment variables
Provides a more reliable configuration method
Option 2: Building the Docker image locally
You can also build and run the Docker image locally. First, build the Docker image:
Then, add the following to your .cursor/mcp.json or claude_desktop_config.json
Using NOTION_TOKEN (recommended):
Using OPENAPI_MCP_HEADERS (for advanced use cases):
Don't forget to replace ntn_**** with your integration secret. Find it from your integration configuration tab:
Transport options
The Notion MCP Server supports two transport modes:
STDIO transport (default)
The default transport mode uses standard input/output for communication. This is the standard MCP transport used by most clients like Claude Desktop.
Streamable HTTP transport
For web-based applications or clients that prefer HTTP communication, you can use the Streamable HTTP transport:
When using Streamable HTTP transport, the server will be available at http://0.0.0.0:<port>/mcp.
Authentication
The Streamable HTTP transport requires bearer token authentication for security. You have three options:
Option 1: Auto-generated token (recommended for development)
The server will generate a secure random token and display it in the console:
Option 2: Custom token via command line (recommended for production)
Option 3: Custom token via environment variable (recommended for production)
The command line argument --auth-token takes precedence over the AUTH_TOKEN environment variable if both are provided.
Making HTTP requests
All requests to the Streamable HTTP transport must include the bearer token in the Authorization header:
Note: Make sure to set either the NOTION_TOKEN environment variable (recommended) or the OPENAPI_MCP_HEADERS environment variable with your Notion integration token when using either transport mode.
Examples
Using the following instruction
AI will correctly plan two API calls, v1/search and v1/comments, to achieve the task
Similarly, the following instruction will result in a new page named "Notion MCP" added to parent page "Development"
You may also reference content ID directly
Development
Build & test
Execute
Testing changes locally in Cursor:
Run
npm linkcommand from repository root to create a machine-global symlink to thenotion-mcp-serverpackage.Merge the configuration snippet below into Cursor's
mcp.json(or other MCP client you want to test with).(Cleanup) run
npm unlinkfrom repository root.