The MCP-Ambari-API server provides a powerful natural language interface to automate Apache Ambari operations for comprehensive Hadoop cluster management via AI/LLM tools.
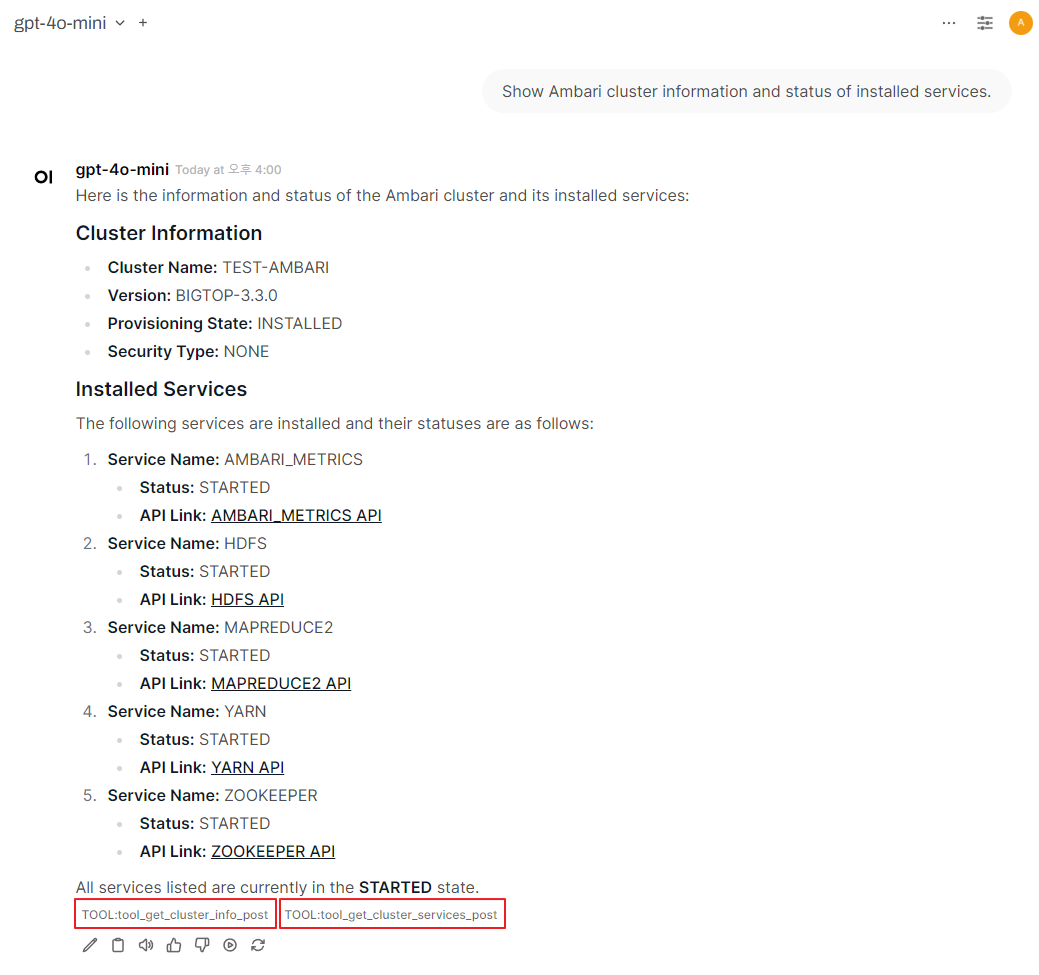
Cluster Management: Retrieve cluster information, status, and track active operations and request progress
Service Operations: Start, stop, and restart individual Hadoop services (HDFS, YARN, Spark, HBase, etc.) or all services simultaneously, with real-time status monitoring
Configuration Management: Unified configuration introspection, filtering, and bulk operations across all service types
Host Management: List hosts and retrieve detailed information including hardware metrics, component states, and service assignments
User Management: List users and retrieve detailed profiles, permissions, and authentication information
Alert Management: Retrieve current and historical alerts with advanced filtering by state, service, host, time range, and maintenance status
AI/LLM Integration: Natural language interface designed for seamless integration with modern AI workflows
Flexible Deployment: Supports both local (
stdio) and remote (streamable-http) connection modes
Provides comprehensive management of Apache Hadoop clusters through Ambari API, enabling service control (start/stop/restart HDFS, YARN, Spark, etc.), configuration management, real-time monitoring, alert management, host administration, and user management via natural language commands.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@MCP-Ambari-APIshow me the status of all HDFS services"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
MCP Ambari API - Apache Hadoop Cluster Management Automation
🚀 Automate Apache Ambari operations with AI/LLM: Conversational control for Hadoop cluster management, service monitoring, configuration inspection, and precise Ambari Metrics queries via Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools.
Architecture & Internal (DeepWiki)
Related MCP server: CloudWatch Logs MCP Server
📋 Overview
MCP Ambari API is a powerful Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that enables seamless Apache Ambari cluster management through natural language commands. Built for DevOps engineers, data engineers, and system administrators who work with Hadoop ecosystems.
Features
✅ Interactive Ambari Operations Hub – Provides an MCP-based foundation for querying and managing services through natural language instead of console or UI interfaces.
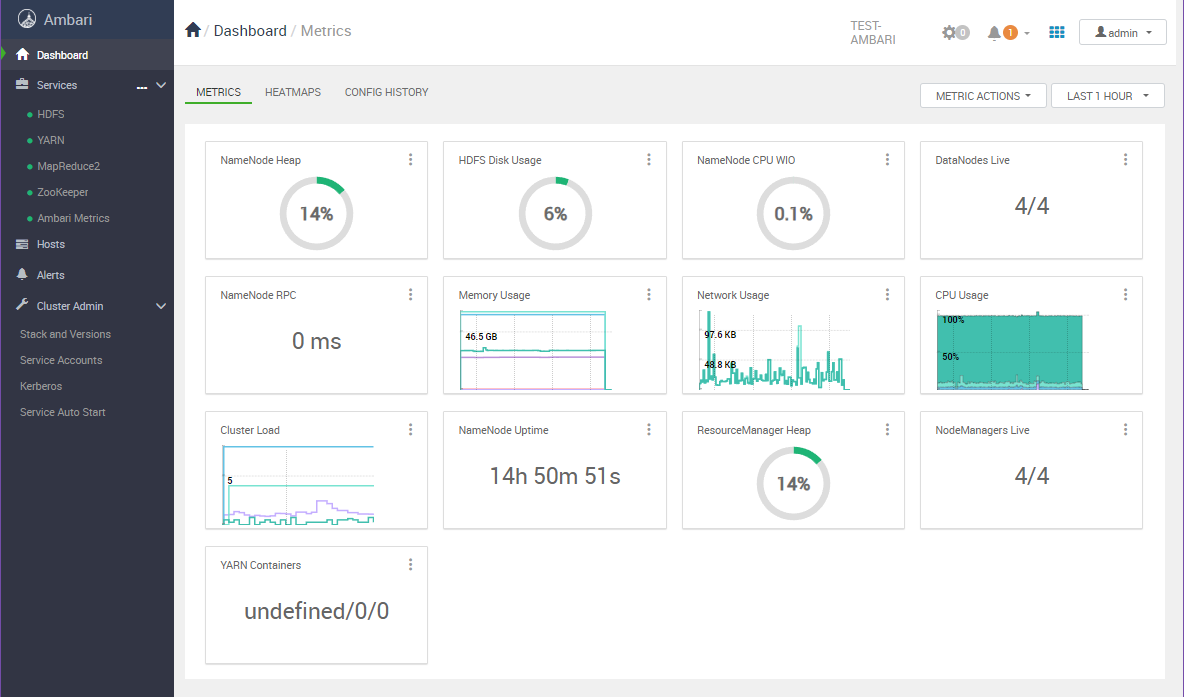
✅ Real-time Cluster Visibility – Comprehensive view of key metrics including service status, host details, alert history, and ongoing requests in a single interface.
✅ Metrics Intelligence Pipeline – Dynamically discovers and filters AMS appIds and metric names, connecting directly to time-series analysis workflows.
✅ Automated Operations Workflow – Consolidates repetitive start/stop operations, configuration checks, user queries, and request tracking into consistent scenarios.
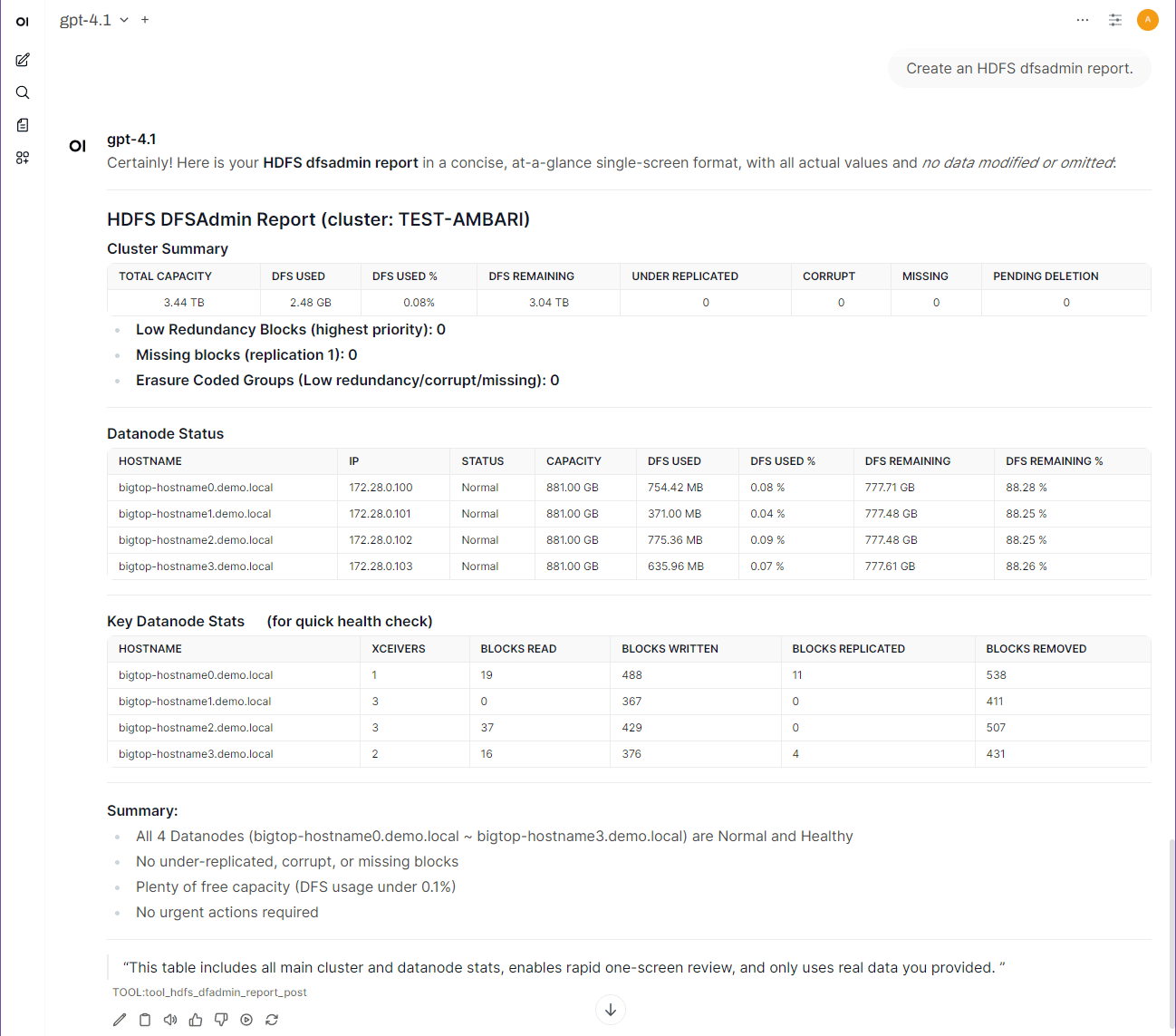
✅ Built-in Operational Reports – Instantly delivers dfsadmin-style HDFS reports, service summaries, and capacity metrics through LLM or CLI interfaces.
✅ Safety Guards and Guardrails – Requires user confirmation before large-scale operations and provides clear guidance for risky commands through prompt templates.
✅ LLM Integration Optimization – Includes natural language examples, parameter mapping, and usage guides to ensure stable AI agent operations.
✅ Flexible Deployment Models – Supports stdio/streamable-http transport, Docker Compose, and token authentication for deployment across development and production environments.
✅ Performance-Oriented Caching Architecture – Built-in AMS metadata cache and request logging ensure fast responses even in large-scale clusters.
✅ Scalable Code Architecture – Asynchronous HTTP, structured logging, and modularized tool layers enable easy addition of new features.
✅ Production-Validated – Based on tools validated in test Ambari clusters, ready for immediate use in production environments.
✅ Diversified Deployment Channels – Available through PyPI packages, Docker images, and other preferred deployment methods.
Docuement for Airflow REST-API
Topics
apache-ambari hadoop-cluster mcp-server cluster-automation devops-tools big-data infrastructure-management ai-automation llm-tools python-mcp
Example Queries - Cluster Info/Status
Go to More Example Queries
🚀 QuickStart Guide /w Docker
Note: The following instructions assume you are using the
streamable-httpmode for MCP Server.
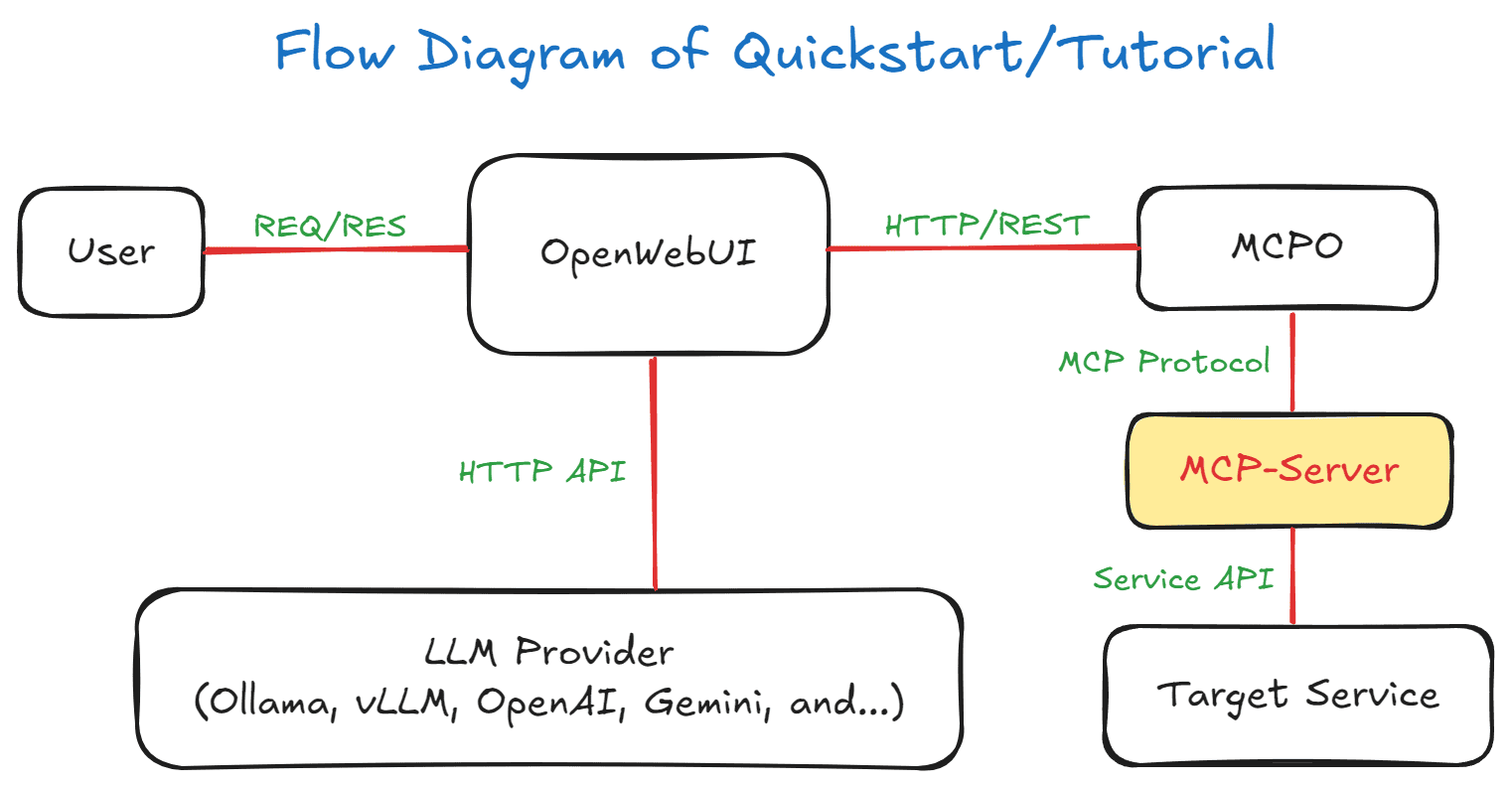
Flow Diagram of Quickstart/Tutorial
1. Prepare Ambari Cluster (Test Target)
To set up a Ambari Demo cluster, follow the guide at: Install Ambari 3.0 with Docker
2. Run Docker-Compose
Start the MCP-Server, MCPO(MCP-Proxy for OpenAPI), and OpenWebUI.
Ensure Docker and Docker Compose are installed on your system.
Clone this repository and navigate to its root directory.
Set up environment configuration:
# Copy environment template and configure your settings cp .env.example .env # Edit .env with your Ambari cluster informationConfigure your Ambari connection in
# Ambari cluster connection AMBARI_HOST=host.docker.internal AMBARI_PORT=7070 AMBARI_USER=admin AMBARI_PASS=admin AMBARI_CLUSTER_NAME=TEST-AMBARI # Ambari Metrics (AMS) collector AMBARI_METRICS_HOST=host.docker.internal AMBARI_METRICS_PORT=16188 AMBARI_METRICS_PROTOCOL=http AMBARI_METRICS_TIMEOUT=15 # (Optional) Enable authentication for streamable-http mode # Recommended for production environments REMOTE_AUTH_ENABLE=false REMOTE_SECRET_KEY=your-secure-secret-key-hereRun:
docker-compose up -d
OpenWebUI will be available at:
http://localhost:${DOCKER_EXTERNAL_PORT_OPENWEBUI}(default: 3001)The MCPO-Proxy will be accessible at:
http://localhost:${DOCKER_EXTERNAL_PORT_MCPO_PROXY}(default: 8001)The MCPO API Docs:
http://localhost:${DOCKER_EXTERNAL_PORT_MCPO_PROXY}/mcp-ambari-api/docs
3. Registering the Tool in OpenWebUI
📌 Note: Web-UI configuration instructions are based on OpenWebUI v0.6.22. Menu locations and settings may differ in newer versions.
logging in to OpenWebUI with an admin account
go to "Settings" → "Tools" from the top menu.
Enter the
mcp-ambari-apiTool address (e.g.,http://localhost:8000/mcp-ambari-api) to connect MCP Tools with your Ambari cluster.
4. More Examples: Using MCP Tools to Query Ambari Cluster
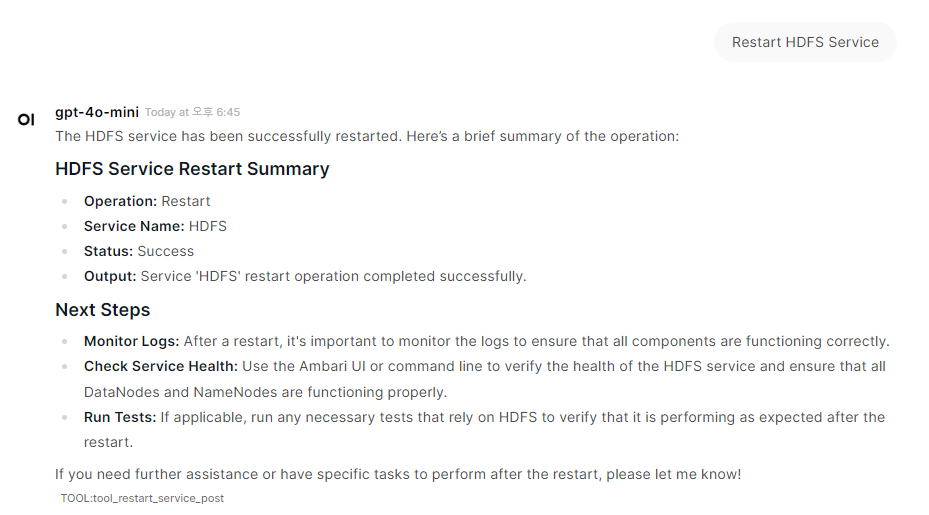
Below is an example screenshot showing how to query the Ambari cluster using MCP Tools in OpenWebUI:
Example Query - Cluster Configuration Review & Recommendations

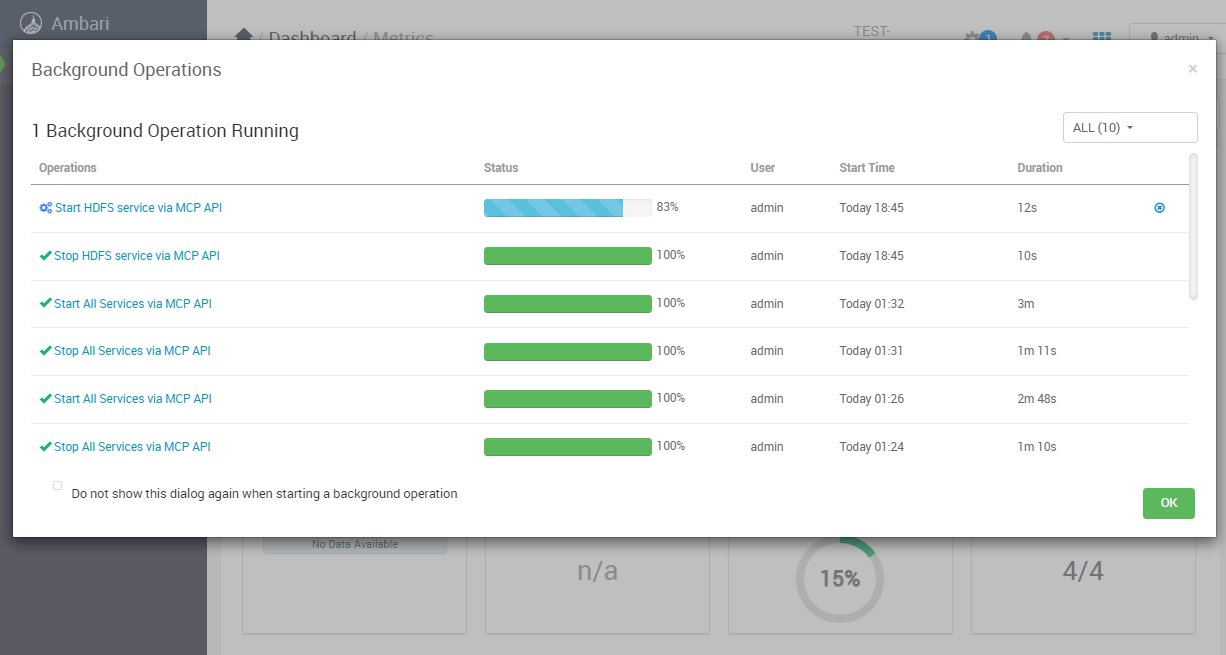
Example Query - Restart HDFS Service
📈 Metrics & Trends
Terminology quick reference
appId: Ambari Metrics Service groups every metric under an application identifier (e.g.,
namenode,datanode,ambari_server,HOST). Think of it as the component or service emitting that timeseries.metric name: The fully qualified string Ambari uses for each timeseries (e.g.,
jvm.JvmMetrics.MemHeapUsedM,dfs.datanode.BytesWritten). Exact names are required when querying AMS.
list_common_metrics_catalog: keyword search against the live metadata-backed metric catalog (cached locally). Usesearch="heap"or similar to narrow suggestions before running a time-series query.
Example: “Show the heap-related metrics available for the NameNode appId.”list_ambari_metric_apps: list discovered AMSappIdvalues, optionally including metric counts; passrefresh=trueorlimitto control output.
Example: “List every appId currently exposed by AMS.”The natural-language query “AMS에서 사용 가능한 appId 목록만 보여줘” maps to
list_ambari_metric_appsand returns the exact identifiers you can copy into other tools.list_ambari_metrics_metadata: raw AMS metadata explorer (supportsapp_id,metric_name_filter,host_filter,search, adjustablelimit, default 50).
Example: “Give me CPU-related metric metadata under HOST.”query_ambari_metrics: fetch time-series data; the tool auto-selects curated metric names, falls back to metadata search when needed, and honors Ambari's default precision unless you explicitly supplyprecision="SECONDS", etc.
Examples: “Plot the last 30 minutes ofjvm.JvmMetrics.MemHeapUsedMfor the NameNode.” / “Comparejvm.JvmMetrics.MemHeapUsedMfor DataNode hostsbigtop-hostname0.demo.localandbigtop-hostname1.demo.localover the past 30 minutes.”hdfs_dfadmin_report: produce a DFSAdmin-style capacity/DataNode summary (mirrorshdfs dfsadmin -report).
Live Metric Catalog (via AMS metadata)
Metric names are discovered on demand from
/ws/v1/timeline/metrics/metadataand cached for quick reuse.Use
list_common_metrics_catalogor theambari-metrics://catalog/allresource (append?refresh=trueto bypass the cache) to inspect the latestappId → metricmapping. Queryambari-metrics://catalog/appsto list appIds orambari-metrics://catalog/<appId>for a single app.Typical appIds include
ambari_server,namenode,datanode,nodemanager,resourcemanager, andHOST, but the list adapts to whatever the Ambari Metrics service advertises in your cluster.
🔍 Ambari Metrics Query Requirements (Exact-Match Workflow)
Recent updates removed natural-language metric guessing in favor of deterministic, catalog-driven lookups. Keep the following rules in mind when you (or an LLM agent) call query_ambari_metrics:
Always pass an explicit If it is missing or unsupported, the tool returns a list of valid appIds and aborts so you can choose one manually.
Specify exact metric names. Use
list_common_metrics_catalog(app_id="<target>", search="keyword"),list_ambari_metric_apps(to discover appIds), or theambari-metrics://catalog/<appId>resource to browse the live per-app metric set and copy the identifier (e.g.,jvm.JvmMetrics.MemHeapUsedM).Host-scope behavior: When
hostnamesis omitted the API returns cluster-wide aggregates. Provide one or more hosts (comma-separated) to focus on specific nodes.No fuzzy matches. The server now calls Ambari exactly as requested. If the metric is wrong or empty, Ambari will simply return no datapoints—double-check the identifier via
/ws/v1/timeline/metrics/metadata.
Example invocation:
For multi-metric lookups, pass a comma-separated list of exact names. Responses document any auto-applied host filters so you can copy/paste them into subsequent requests.
🐛 Usage & Configuration
This MCP server supports two connection modes: stdio (traditional) and streamable-http (Docker-based). You can configure the transport mode using CLI arguments or environment variables.
Configuration Priority: CLI arguments > Environment variables > Default values
CLI Arguments
--type(-t): Transport type (stdioorstreamable-http) - Default:stdio--host: Host address for HTTP transport - Default:127.0.0.1--port(-p): Port number for HTTP transport - Default:8000--auth-enable: Enable Bearer token authentication for streamable-http mode - Default:false--secret-key: Secret key for Bearer token authentication (required when auth enabled)
Environment Variables
Variable | Description | Default | Project Default |
| Python module search path for MCP server imports | - |
|
| Server logging verbosity (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR) |
|
|
| MCP transport protocol (stdio for CLI, streamable-http for web) |
|
|
| HTTP server bind address (0.0.0.0 for all interfaces) |
|
|
| HTTP server port for MCP communication |
|
|
| Enable Bearer token authentication for streamable-http mode Default: false (if undefined, empty, or null) |
|
|
| Secret key for Bearer token authentication Required when REMOTE_AUTH_ENABLE=true | - |
|
| Ambari server hostname or IP address |
|
|
| Ambari server port number |
|
|
| Username for Ambari server authentication |
|
|
| Password for Ambari server authentication |
|
|
| Name of the target Ambari cluster |
|
|
| Host port mapping for Open WebUI container |
|
|
| Host port mapping for MCP server container |
|
|
| Host port mapping for MCPO proxy container |
|
|
Note: AMBARI_CLUSTER_NAME serves as the default target cluster for operations when no specific cluster is specified. All environment variables can be configured via the .env file.
Transport Selection Logic:
Configuration Priority: CLI arguments > Environment variables > Default values
Transport Selection Logic:
CLI Priority:
--type streamable-http --host 0.0.0.0 --port 18001Environment Priority:
FASTMCP_TYPE=streamable-http FASTMCP_HOST=0.0.0.0 FASTMCP_PORT=18001Legacy Support:
FASTMCP_PORT=18001(automatically enables streamable-http mode)Default:
stdiomode when no configuration is provided
Environment Setup
🔐 Security & Authentication
Bearer Token Authentication
For streamable-http mode, this MCP server supports Bearer token authentication to secure remote access. This is especially important when running the server in production environments.
Configuration
Enable Authentication:
Or via CLI:
Security Levels
stdio mode (Default): Local-only access, no authentication needed
streamable-http + REMOTE_AUTH_ENABLE=false/undefined: Remote access without authentication ⚠️ NOT RECOMMENDED for production
streamable-http + REMOTE_AUTH_ENABLE=true: Remote access with Bearer token authentication ✅ RECOMMENDED for production
🔒 Default Policy:
REMOTE_AUTH_ENABLEdefaults tofalseif undefined, empty, or null. This ensures the server starts even without explicit authentication configuration.
Client Configuration
When authentication is enabled, MCP clients must include the Bearer token in the Authorization header:
Security Best Practices
Always enable authentication when using streamable-http mode in production
Use strong, randomly generated secret keys (32+ characters recommended)
Use HTTPS when possible (configure reverse proxy with SSL/TLS)
Restrict network access using firewalls or network policies
Rotate secret keys regularly for enhanced security
Monitor access logs for unauthorized access attempts
Error Handling
When authentication fails, the server returns:
401 Unauthorized for missing or invalid tokens
Detailed error messages in JSON format for debugging
Method 1: Local MCP (transport="stdio")
Method 2: Remote MCP (transport="streamable-http")
On MCP-Client Host:
With Bearer Token Authentication (Recommended for production):
Example usage: Claude-Desktop
claude_desktop_config.json
(Option) Configure Multiple Ambari Cluster
Remote Access with Authentication (Claude Desktop):
🎯 Core Features & Capabilities
Service Operations
Hadoop Service Management: Start, stop, restart HDFS, YARN, Spark, HBase, and more
Bulk Operations: Control all cluster services simultaneously
Status Monitoring: Real-time service health and performance tracking
Configuration Management
Unified Config Tool: Single interface for all configuration types (yarn-site, hdfs-site, etc.)
Bulk Configuration: Export and manage multiple configurations with filtering
Configuration Validation: Syntax checking and validation before applying changes
Monitoring & Alerting
Real-time Alerts: Current and historical cluster alerts with filtering
Request Tracking: Monitor long-running operations with detailed progress
Host Monitoring: Hardware metrics, component states, and resource utilization
Administration
User Management: Check cluster user administration
Host Management: Node registration, component assignments, and health monitoring
Available MCP Tools
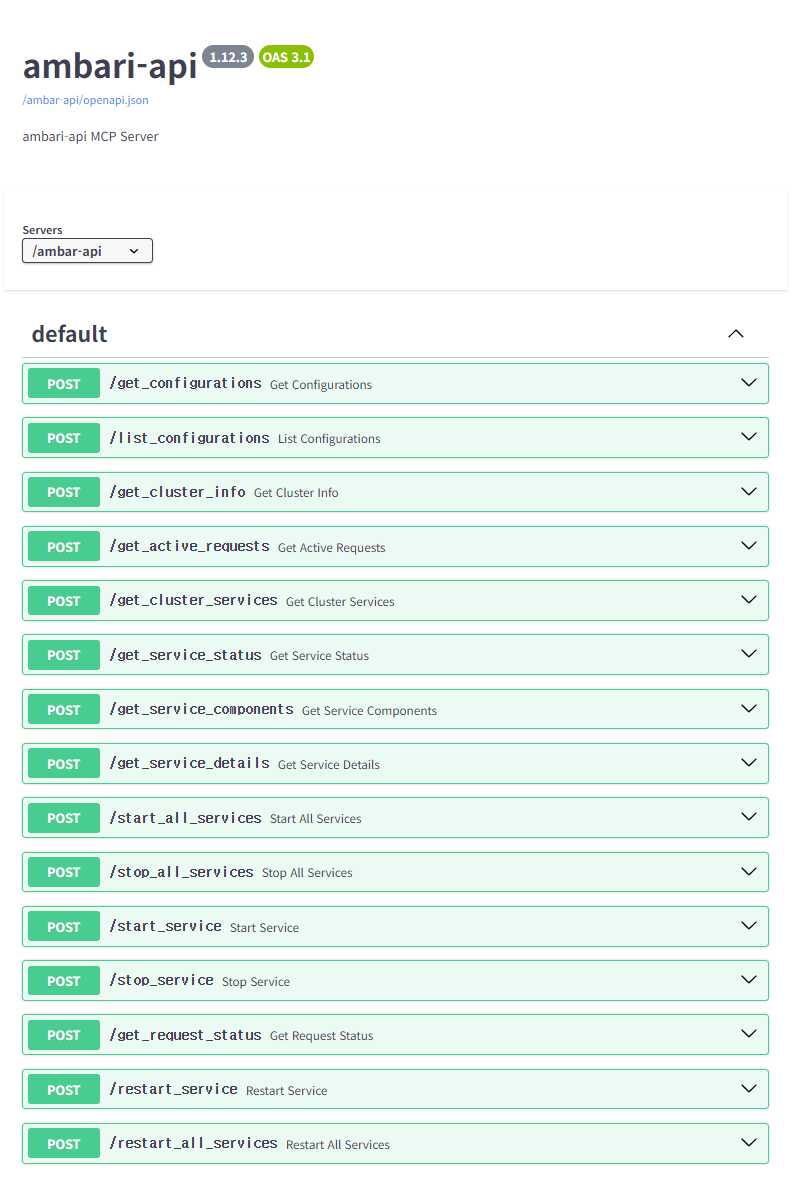
This MCP server provides the following tools for Ambari cluster management:
Cluster Management
get_cluster_info- Retrieve basic cluster information and statusget_active_requests- List currently active/running operationsget_request_status- Check status and progress of specific requests
Service Management
get_cluster_services- List all services with their statusget_service_status- Get detailed status of a specific serviceget_service_components- List components and host assignments for a serviceget_service_details- Get comprehensive service informationstart_service- Start a specific servicestop_service- Stop a specific servicerestart_service- Restart a specific servicestart_all_services- Start all services in the clusterstop_all_services- Stop all services in the clusterrestart_all_services- Restart all services in the cluster
Configuration Tools
dump_configurations- Unified configuration tool (replacesget_configurations,list_configurations, and the former internaldump_all_configurations). Supports:Single type:
dump_configurations(config_type="yarn-site")Bulk summary:
dump_configurations(summarize=True)Filter by substring (type or key):
dump_configurations(filter="memory")Service filter (narrow types by substring):
dump_configurations(service_filter="yarn", summarize=True)Keys only (no values):
dump_configurations(include_values=False)Limit number of types:
dump_configurations(limit=10, summarize=True)
Breaking Change:
get_configurationsandlist_configurationswere removed in favor of this single, more capable tool.
Host Management
list_hosts- List all hosts in the clusterget_host_details- Get detailed information for specific or all hosts (includes component states, hardware metrics, and service assignments)
User Management
list_users- List all users in the Ambari system with their usernames and API linksget_user- Get detailed information about a specific user including:Basic profile (ID, username, display name, user type)
Status information (admin privileges, active status, login failures)
Authentication details (LDAP user status, authentication sources)
Group memberships, privileges, and widget layouts
Alert Management
get_alerts_history- Unified alert tool for both current and historical alerts:Current mode (
mode="current"): Retrieve current/active alerts with real-time statusCurrent alert states across cluster, services, or hosts
Maintenance mode filtering (ON/OFF)
Summary formats: basic summary and grouped by definition
Detailed alert information including timestamps and descriptions
History mode (
mode="history"): Retrieve historical alert events from the clusterScope filtering: cluster-wide, service-specific, or host-specific alerts
Time range filtering: from/to timestamp support
Pagination support for large datasets
Common features (both modes):
State filtering: CRITICAL, WARNING, OK, UNKNOWN alerts
Definition filtering: filter by specific alert definition names
Multiple output formats: detailed, summary, compact
Unified API for consistent alert querying experience
🤝 Contributing & Support
How to Contribute
🐛 Report Bugs: GitHub Issues
💡 Request Features: Feature Requests
🔧 Submit PRs: Contributing Guidelines
📖 Improve Docs: Help make documentation better
Technologies Used
Language: Python 3.12
Framework: Model Context Protocol (MCP)
API: Apache Ambari REST API
Transport: stdio (local) and streamable-http (remote)
Deployment: Docker, Docker Compose, PyPI
Dev Env.
WSL2(networkingMode = bridged) + Docker-Desktop
.wslconfig: tested withnetworkingMode = bridged
Python 3.12 venv
### Option-1: with uv uv venv --python 3.12 --seed ### Option-2: with pip python3.12 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate pip install -U pip
🛠️ Adding Custom Tools
After you've thoroughly explored the existing functionality, you might want to add your own custom tools for specific monitoring or management needs. This MCP server is designed for easy extensibility.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Add Helper Functions (Optional)
Add reusable data functions to src/mcp_ambari_api/functions.py:
2. Create Your MCP Tool
Add your tool function to src/mcp_ambari_api/mcp_main.py:
3. Update Imports
Add your helper function to the imports section in src/mcp_ambari_api/mcp_main.py:
4. Update Prompt Template (Recommended)
Add your tool description to src/mcp_ambari_api/prompt_template.md for better AI recognition:
5. Test Your Tool
Important Notes
Always use for proper registration and logging
Follow the existing error handling patterns - return English error messages starting with "Error:"
Use for all Ambari API calls to ensure consistent authentication and error handling
Validate all input parameters before using them in API calls
Test thoroughly with both valid and invalid inputs
Example Use Cases
Custom service health checks beyond standard Ambari monitoring
Specialized configuration validation for your organization's standards
Custom alert aggregation and reporting formats
Integration with external monitoring systems via Ambari data
Automated compliance checking for cluster configurations
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What Ambari versions are supported?
A: Ambari 2.7+ is recommended. Earlier versions may work but are not officially tested.
Q: Can I use this with cloud-managed Hadoop clusters?
A: Yes, as long as Ambari API endpoints are accessible, it works with on-premise, cloud, and hybrid deployments.
Q: How do I troubleshoot connection issues?
A: Check your AMBARI_HOST, AMBARI_PORT, and network connectivity. Enable debug logging with MCP_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG.
Q: How does this compare to Ambari Web UI?
A: This provides programmatic access via AI/LLM commands, perfect for automation, scripting, and integration with modern DevOps workflows.
Contributing
🤝 Got ideas? Found bugs? Want to add cool features?
We're always excited to welcome new contributors! Whether you're fixing a typo, adding a new monitoring tool, or improving documentation - every contribution makes this project better.
Ways to contribute:
🐛 Report issues or bugs
💡 Suggest new Ambari monitoring features
📝 Improve documentation
🚀 Submit pull requests
⭐ Star the repo if you find it useful!
Pro tip: The codebase is designed to be super friendly for adding new tools. Check out the existing @mcp.tool() functions in mcp_main.py and follow the Adding Custom Tools guide above.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.