PolicyGuard is an MCP server that provides security governance for AI agents through policy-based access control, incident tracking, and compliance monitoring.
Core Capabilities:
Policy Enforcement: Create and manage security policies with pattern matching (e.g.,
delete_*,*_production) to control agent actions. Policies support conditions (tool patterns, trust levels) and actions (allow, deny, require_approval)Action Validation: Validate agent actions before execution using multi-layered evaluation of suspension status, denied/allowed lists, and policy rules via the
validate_actiontoolAgent Management: Register agents with configurable trust levels (low, medium, high, admin), tool permissions, and metadata
Audit Logging: Query comprehensive audit logs of all validations filtered by agent, action type, status, and time range (1h to 30d) with unique action IDs for correlation
Incident Management: Report and track security incidents (policy violations, suspicious activity, unauthorized access, data exfiltration) with severity levels (low, medium, high, critical), evidence collection, and auto-suspension for critical events
Compliance Monitoring: Generate compliance reports with security health metrics, active incidents, policy summaries, violations, and recommendations
Pattern-Based Security: Use wildcard patterns for flexible policy application to tool names
Human Approval Workflows: Require manual review for high-risk actions
Kubernetes Integration: Deploy via Helm chart and integrate with kagent for Kubernetes-native AI agent management
Multi-Protocol Support: Run in HTTP mode or via MCP protocol for integration with various AI platforms
Includes a Helm chart for Kubernetes-native deployment, enabling declarative management of the PolicyGuard service and its security policies.
Provides security and governance for AI agents within Kubernetes environments, supporting declarative agent management through kagent integration and custom resource definitions (CRDs).
Supports integration with Ollama as a local LLM provider for running AI agents governed by PolicyGuard security rules.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@PolicyGuardCheck if agent-alpha is authorized to execute 'delete_records' on production"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
PolicyGuard
Security & Governance MCP Server for AI Agents
PolicyGuard is an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server that provides policy-based access control, incident tracking, and compliance monitoring for AI agents.
Built for MCP_HACK//26 hackathon - "MCP & AI Agents Starter Track" and "Secure & Govern MCP" categories.
Note: This project demonstrates working integration with kagent (AI agent platform) and can be extended with kgateway (API gateway) for additional network-level security.
Table of Contents
Overview
As AI agents become more autonomous, organizations need controls to govern their behavior. PolicyGuard is my first MCP server project - built to explore how security and governance can be implemented at the MCP layer.
The Problem
AI agents can call any tool they have access to. Without governance:
Agents might perform destructive operations
No audit trail of agent actions
No way to enforce security policies
No visibility into compliance
The Solution
PolicyGuard adds a security layer that agents call before taking action:
Features
Feature | Description |
Policy Enforcement | Validate actions against security rules |
Trust Levels | low, medium, high, admin hierarchy |
Pattern Matching | Wildcard patterns like |
Auto-Registration | Unknown agents get minimal trust |
Incident Tracking | Automatic violation logging |
Audit Trail | Complete action history |
Compliance Dashboard | Security metrics at a glance |
Architecture
MCP Tools
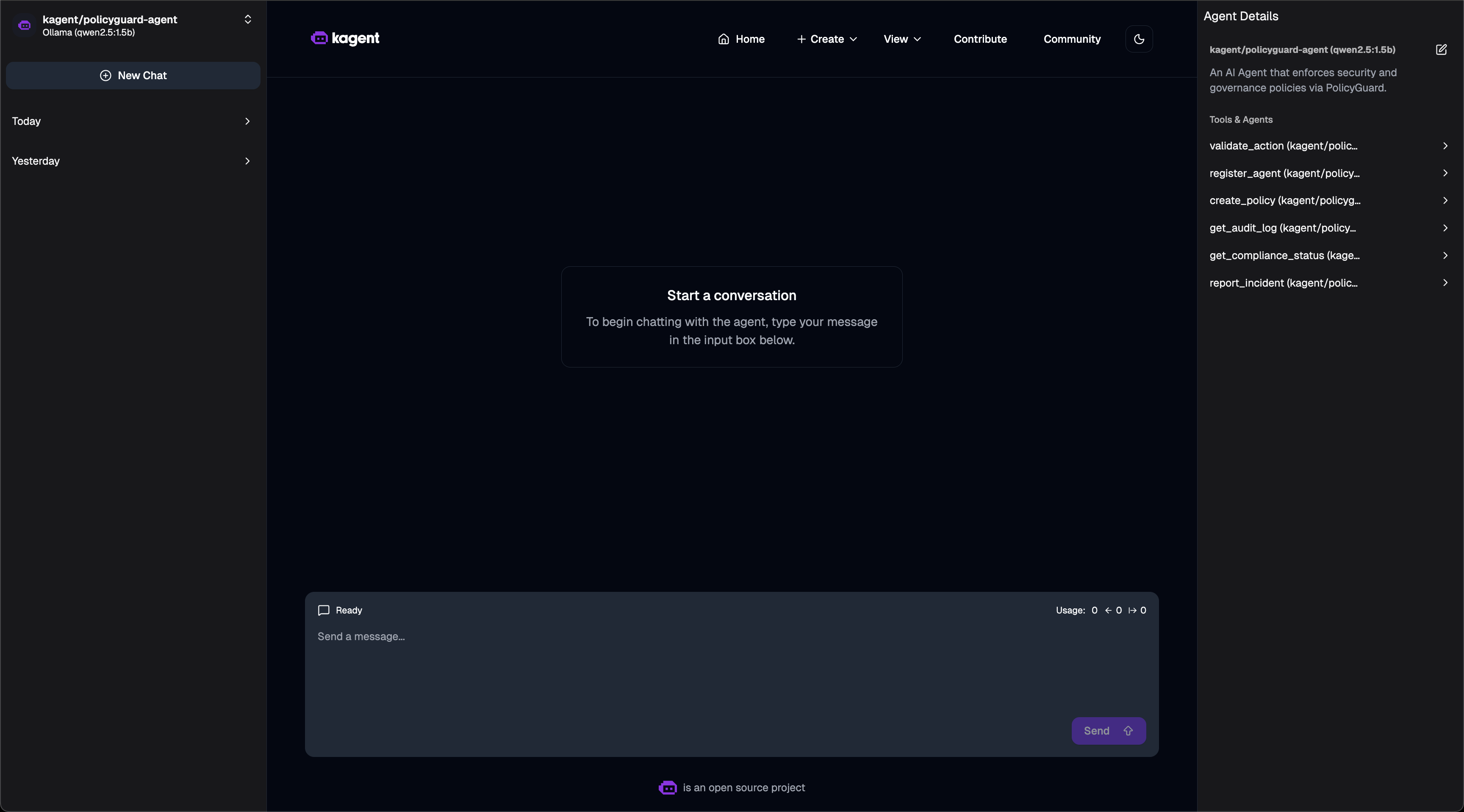
PolicyGuard exposes 6 tools via MCP:
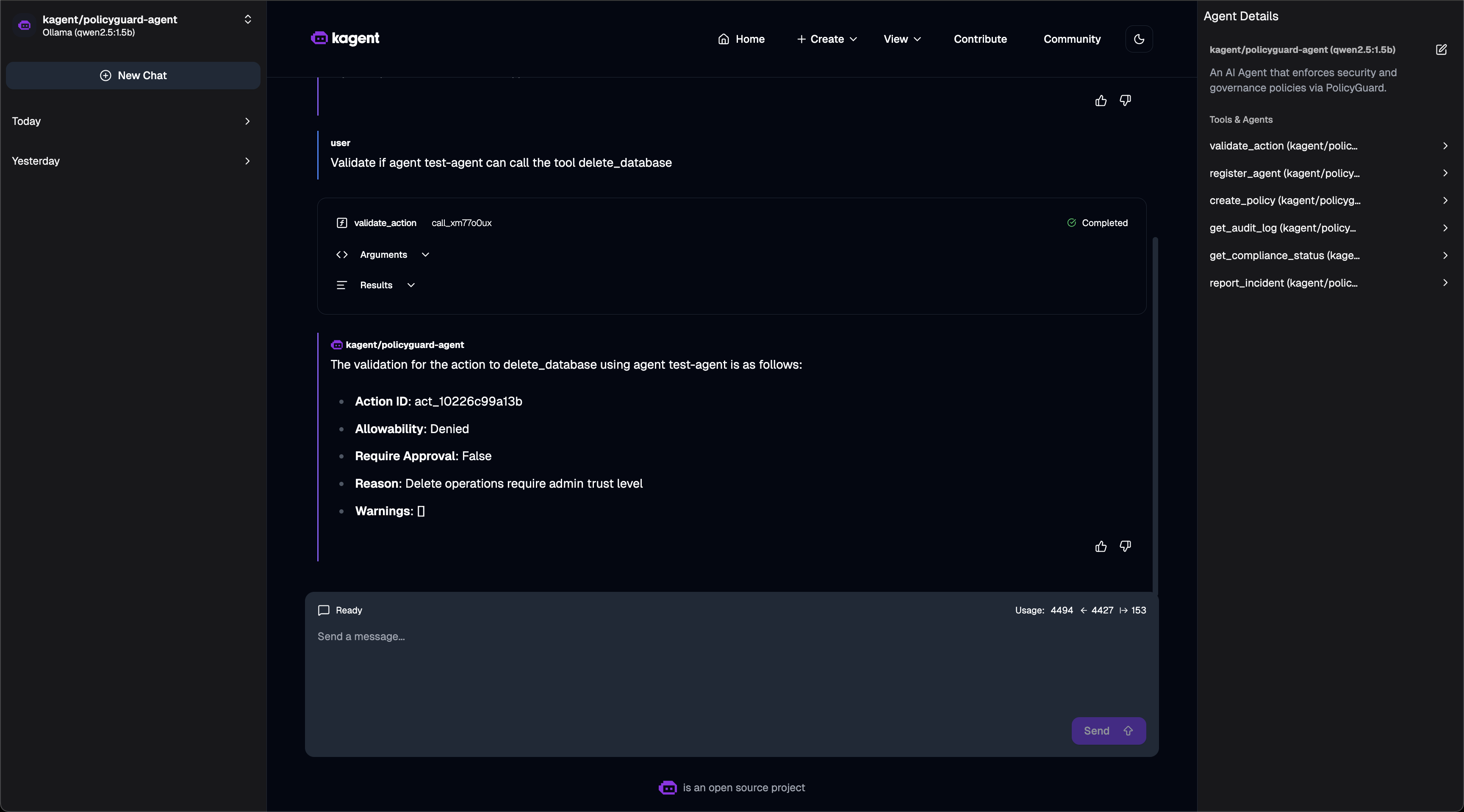
1. validate_action ⭐ Primary Tool
Check if an action is allowed before executing it.
Response:
2. register_agent
Register an agent with a trust level.
3. create_policy
Create security rules.
4. get_audit_log
Query action history.
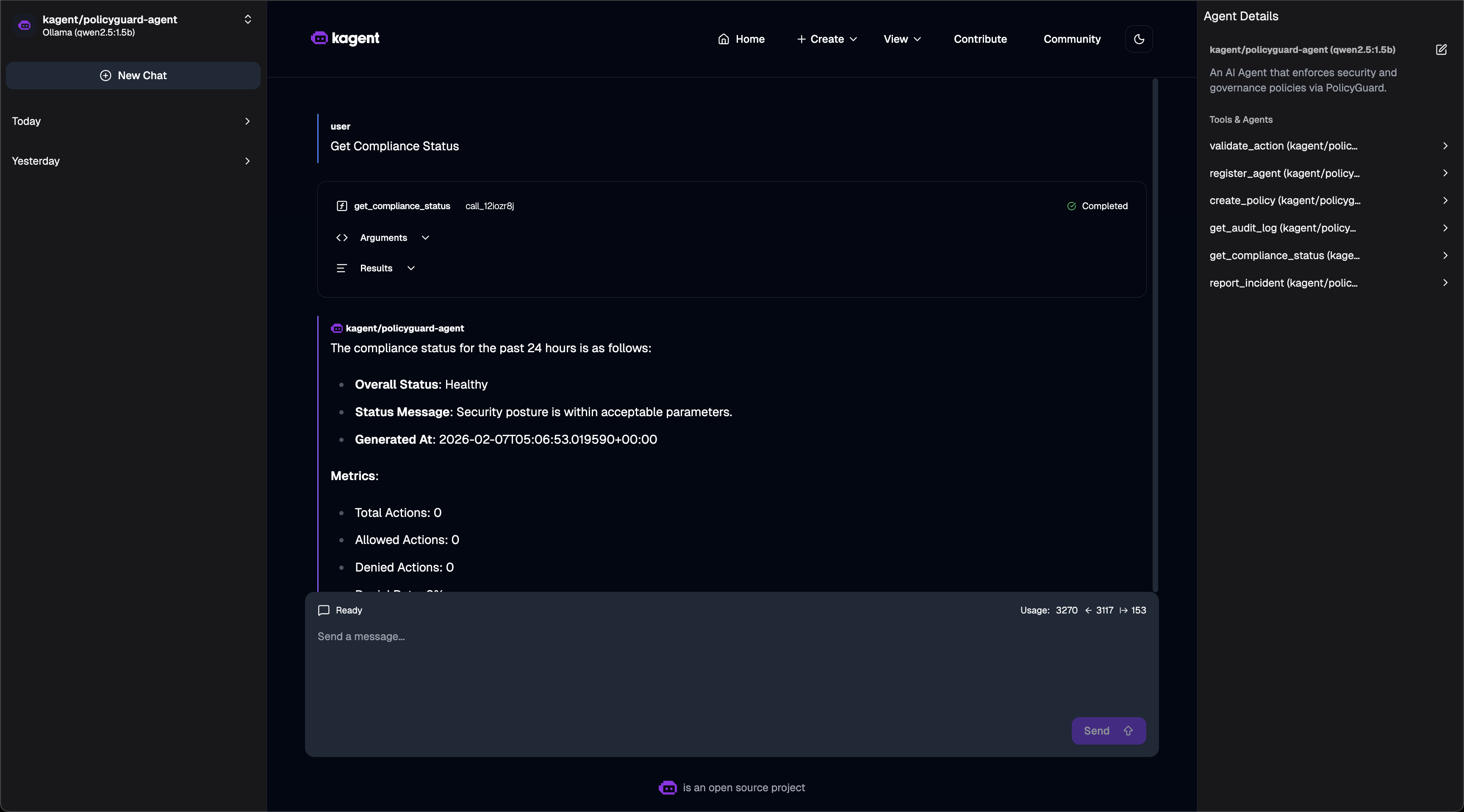
5. get_compliance_status
Get security dashboard metrics.
6. report_incident
Manually report security incidents.
Quick Start
Prerequisites
Python 3.10+
pip
Local Installation
Test the Tools
HTTP Mode
Kubernetes Deployment
PolicyGuard includes a Helm chart for Kubernetes deployment.
Using Kind
Port Forward
Testing
Unit Tests
Test Results
E2E Test Output
kagent Integration
PolicyGuard integrates with kagent for Kubernetes-native AI agent management.
Screenshots
Agent List - PolicyGuard agent registered and ready:
Agent Tools - 6 PolicyGuard MCP tools available:
Compliance Dashboard - Asking for compliance status:
Policy Validation - Action denied based on policy:
Quick Setup
Verified Working
Access kagent UI
Security Model
Trust Levels
Level | Score | Use Case |
| 1 | Unknown agents, read-only |
| 2 | Verified agents |
| 3 | Trusted agents |
| 4 | Full access |
Policy Rules
Evaluation Order
Agent suspended? → DENY
Tool in denied list? → DENY
Tool not in allowed list? → DENY
Policy match? → Apply rule
Default → ALLOW
Project Structure
Technologies Used
FastMCP - Python MCP server SDK
Pydantic - Data validation
Helm - Kubernetes packaging
pytest - Testing
Future Improvements
Database backend (PostgreSQL)
Web dashboard UI
Prometheus metrics
RBAC integration
Policy versioning
License
MIT License
Hackathon
MCP_HACK//26 - "MCP & AI Agents Starter Track"
This is my first MCP server project! I built PolicyGuard to learn:
How MCP servers work
How to expose tools to AI agents
How to deploy MCP servers on Kubernetes
How security/governance can be implemented at the MCP layer
What I Built
✅ 6 MCP tools for security governance
✅ Policy engine with pattern matching
✅ Trust level system
✅ Audit logging and incident tracking
✅ Helm chart for Kubernetes
✅ 16 unit tests
✅ kagent integration examples