Enables running the MCP server in a container with configurable environment variables, simplifying deployment and dependency management across different environments.
Supports configuration through environment variables stored in .env files for local development, allowing customization of connection parameters and API credentials.
Enables interaction with Kestra workflows through GitHub Copilot's Agent mode in VS Code, allowing users to query and manage Kestra resources via natural language.
Integrates with Google Gemini AI models to provide code generation capabilities, with configurable model selection for agent and codegen functions.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Kestra Python MCP Servershow me the latest workflow executions"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Kestra Python MCP Server
You can run the MCP Server in a Docker container. This is useful if you want to avoid managing Python environments or dependencies on your local machine.
Using Kestra AI Agent
See kestra_mcp_docker.
Minimal configuration for OSS users
Paste the following configuration into your MCP settings (e.g., Cursor, Claude, or VS Code):
Minimal configuration for EE users
Detailed Configuration using Docker
Notes:
Replace
<your_kestra_api_token>,<your_google_api_key>, and<your_helicone_api_key>with your actual credentials.For OSS installations, you can use
KESTRA_USERNAMEandKESTRA_PASSWORDinstead ofKESTRA_API_TOKEN.To disable Enterprise Edition tools in OSS, set
KESTRA_MCP_DISABLED_TOOLS=ee.The
host.docker.internalhostname allows the Docker container to access services running on your host machine (such as the Kestra API server on port 8080). This works on macOS and Windows. On Linux, you may need to use the host network mode or set up a custom bridge.The
-eflags pass environment variables from your MCP configuration into the Docker container.
Available Tools
🔄 backfill
⚙️ ee (Enterprise Edition tools)
▶️ execution
📁 files
🔀 flow
🗝️ kv
🌐 namespace
🔁 replay
♻️ restart
⏸️ resume
Note: The ee tool group contains Enterprise Edition specific functionality and is only available in EE/Cloud editions. For OSS users, you can disable EE tools by adding KESTRA_MCP_DISABLED_TOOLS=ee to your .env file.
Optionally, you can include KESTRA_MCP_DISABLED_TOOLS in your .env file listing the tools that you prefer to disable. For example, if you want to disable Namespace Files tools, add this to your .env file:
To disable multiple tools, separate them with comma:
Logging Configuration
By default, the MCP server only logs ERROR level messages to minimize noise. You can control the logging level using the KESTRA_MCP_LOG_LEVEL environment variable:
When using Docker, add the environment variable to your MCP configuration:
Local development
To run the MCP Server for Kestra locally (e.g. if you want to extend it with new tools), make sure to create a virtual environment first:
Create an .env file in the root directory of the project similar to the .env_example file. For OSS installations, you can use basic authentication with KESTRA_USERNAME and KESTRA_PASSWORD. For EE/Cloud installations, use KESTRA_API_TOKEN. To disable Enterprise Edition tools in OSS, add KESTRA_MCP_DISABLED_TOOLS=ee to your .env file.
Then, follow the instructions below explaining how to test your local server in Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code or Claude Desktop.
Usage in Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code or Claude Desktop
To use the Python MCP Server with Claude or modern IDEs, first check what is the path to uv on your machine:
Copy the path returned by which uv and paste it into the command section.
Then, replace the --directory by the path where you cloned the Kestra MCP Server repository. For example:
You can paste that in the Cursor MCP settings or Claud Developer settings.
VS Code setup
In your VS Code project directory, add a folder .vscode and within that folder, create a file called mcp.json. Paste your MCP configuration into that file (note that in VS Code, the key is servers instead of mcpServers):
A small Start button should show up, click on it to start the server.
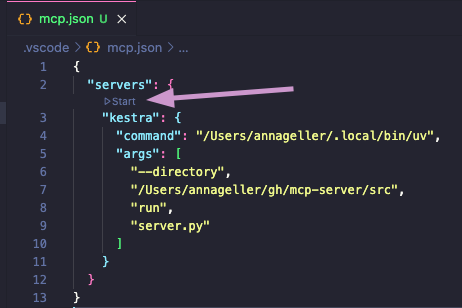
If you now navigate to the GitHub Copilot tab and switch to the Agent mode, you will be able to directly interact with the Kestra MCP Server tools. For example, try typing the prompt: "List all flows in the tutorial namespace".
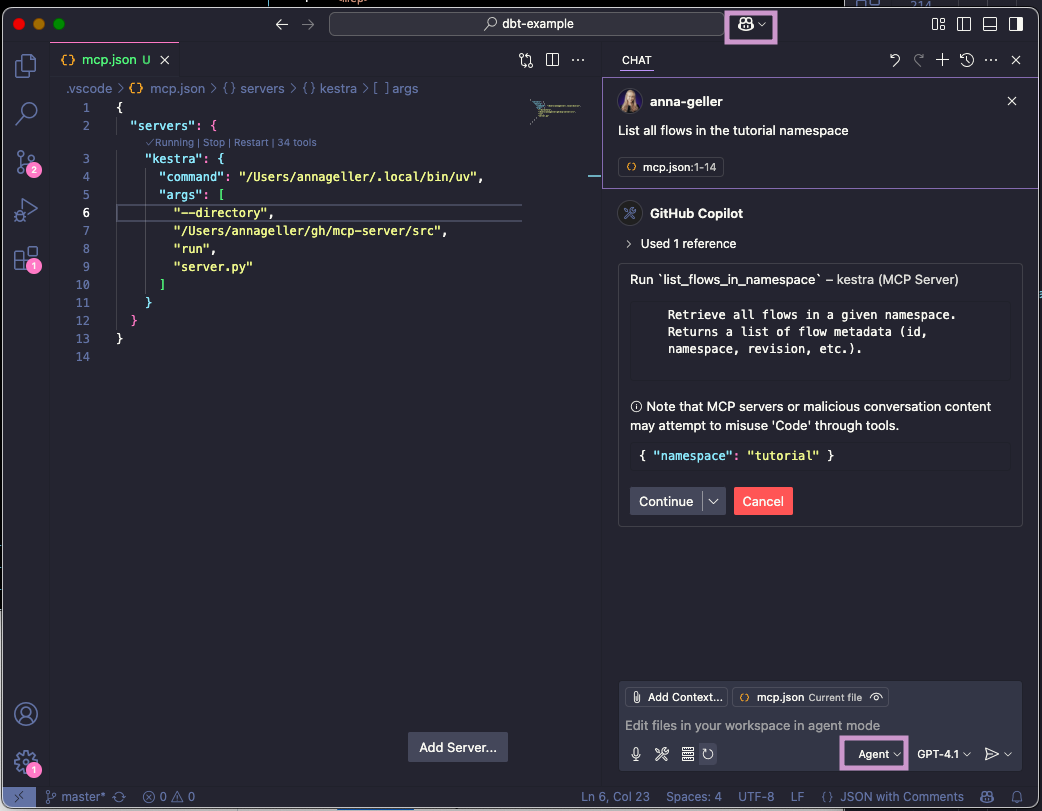
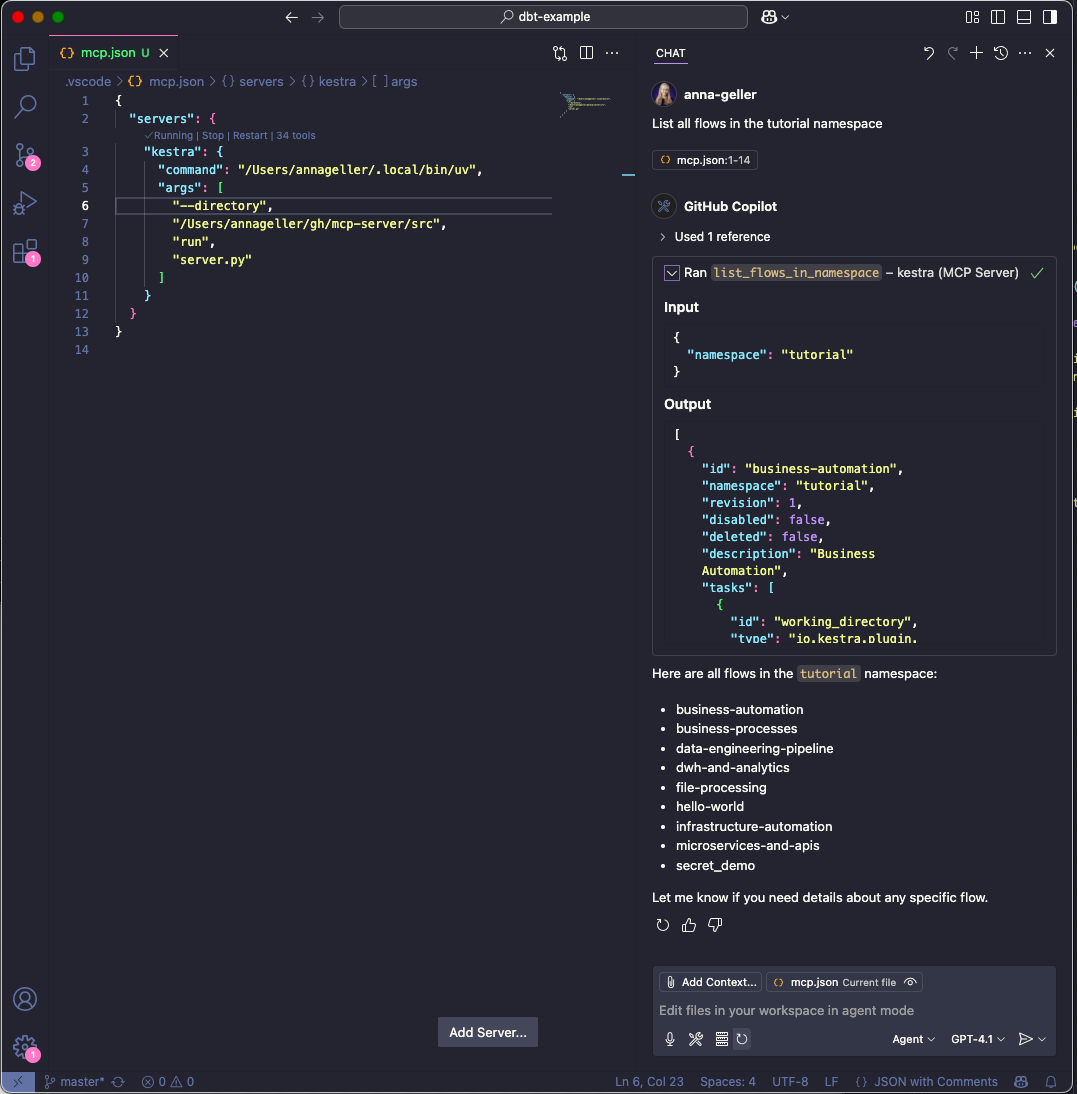
If you click on continue, you will see the result of the command in the output window.
FAQ
Question: Do I have to manually start the server as an always-on process?
No, you don't have to run the server manually, as when using the stdio transport, the AI IDEs/chat-interfaces (Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code or Claude Desktop) launch the MCP server as a subprocess. This subprocess communicates with AI IDEs via JSON-RPC messages over standard input and output streams. The server receives messages through stdin and sends responses through stdout.
Question: Do I have to manually activate the virtual environment for the MCP Server?
No, because we use uv. Unlike traditional Python package managers, where virtual environment activation modifies shell variables like PATH, uv directly uses the Python interpreter and packages from the .venv directory without requiring environment variables to be set first. Just make sure you have created a uv virtual environment with uv venv and installed the required packages with uv pip install as described in the previous section.