Provides a containerized deployment option for the MCP server, with Oracle Client libraries pre-installed for connecting to Oracle databases
Enables GitHub Copilot in VSCode Insiders to access Oracle database schema information and execute database operations through the MCP protocol
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Oracle MCP Servershow me the schema for the CUSTOMERS table"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
MCP Server - Oracle DB Context
A powerful Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides contextual database schema information for large Oracle databases, enabling AI assistants to understand and work with databases containing thousands of tables.
Table of Contents
Related MCP server: OracleDB MCP Server
Overview
The MCP Oracle DB Context server solves a critical challenge when working with very large Oracle databases: how to provide AI models with accurate, relevant database schema information without overwhelming them with tens of thousands of tables and relationships.
By intelligently caching and serving database schema information, this server allows AI assistants to:
Look up specific table schemas on demand
Search for tables that match specific patterns
Understand table relationships and foreign keys
Get database vendor information
Features
Smart Schema Caching: Builds and maintains a local cache of your database schema to minimize database queries
Targeted Schema Lookup: Retrieve schema for specific tables without loading the entire database structure
Table Search: Find tables by name pattern matching
Relationship Mapping: Understand foreign key relationships between tables
Oracle Database Support: Built specifically for Oracle databases
MCP Integration: Works seamlessly with GitHub Copilot in VSCode, Claude, ChatGPT, and other AI assistants that support MCP
Usage
Integration with GitHub Copilot in VSCode Insiders
To use this MCP server with GitHub Copilot in VSCode Insiders, follow these steps:
Install VSCode Insiders
Download and install the latest version of VSCode Insiders
Install GitHub Copilot Extension
Open VSCode Insiders
Go to the Extensions marketplace
Search for and install "GitHub Copilot"
Configure MCP Server
Recommended:
Alternative: Using UV
Enable Agent Mode
Open Copilot chat in VSCode Insiders
Click on "Copilot Edits"
Choose "Agent mode"
Click the refresh button in the chat input to load the available tools
After completing these steps, you'll have access to all database context tools through GitHub Copilot's chat interface.
Option 1: Using Docker (Recommended)
In VSCode Insiders, go to your user or workspace settings.json file and add the following:
When using Docker (recommended approach):
All dependencies are included in the container
Set
THICK_MODE=1in the environment variables to enable thick mode if neededIf you use
THICK_MODE, you can optionally set the path where Oracle Client libraries are installed withORACLE_CLIENT_LIB_DIRif it differs from the default location.
Option 2: Using UV (Local Installation)
This option requires installing and setting up the project locally:
Prerequisites
Python 3.12 or higher
Oracle database access
Oracle instant client (required for the
oracledbPython package)
Install UV
# Install uv using curl (macOS/Linux) curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh # Or using PowerShell (Windows) irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iexMake sure to restart your terminal after installing uv.
Project Setup
# Clone repository git clone https://github.com/yourusername/oracle-mcp-server.git cd oracle-mcp-server # Create and activate virtual environment uv venv # Activate (On Unix/macOS) source .venv/bin/activate # Activate (On Windows) .venv\Scripts\activate # Install dependencies uv pip install -e .Configure VSCode Settings
"mcp": { "inputs": [ { "id": "db-password", "type": "promptString", "description": "Oracle DB Password", "password": true, } ], "servers": { "oracle": { "command": "/path/to/your/.local/bin/uv", "args": [ "--directory", "/path/to/your/oracle-mcp-server", "run", "main.py" ], "env": { "ORACLE_CONNECTION_STRING":"<db-username>/${input:db-password}@<host>:1521/<service-name>", "TARGET_SCHEMA":"", "CACHE_DIR":".cache", "THICK_MODE":"", // Optional: set to "1" to enable thick mode "ORACLE_CLIENT_LIB_DIR":"" // Optional: in case you use thick mode and if you want to set a non-default directory for client libraries } } } }
Replace the paths with your actual uv binary path and oracle-mcp-server directory path
For both options:
Replace the
ORACLE_CONNECTION_STRINGwith your actual database connection stringThe
TARGET_SCHEMAis optional, it will default to the user's schemaThe
CACHE_DIRis optional, defaulting to.cachewithin the MCP server root folder
Option 3:Useing Cherry Studio
run by stdio
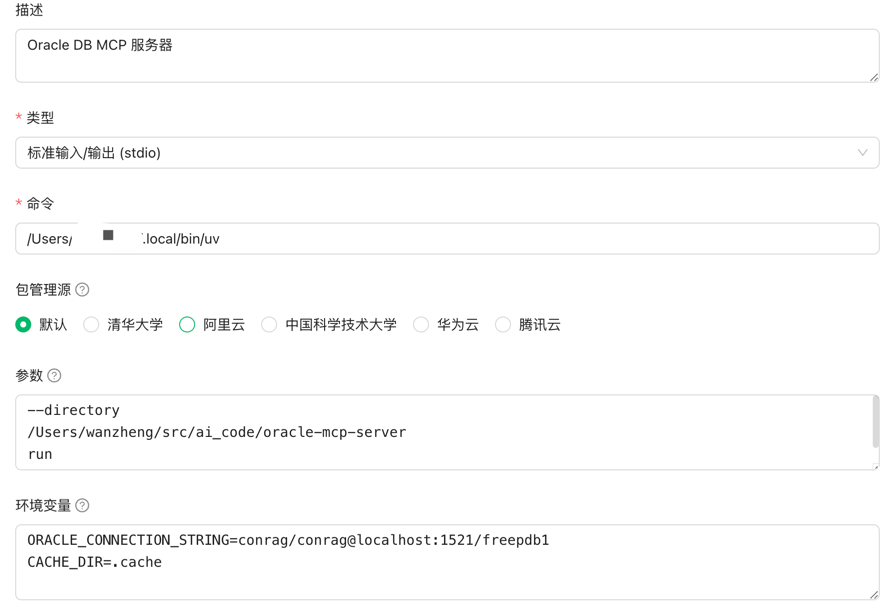
run by sse
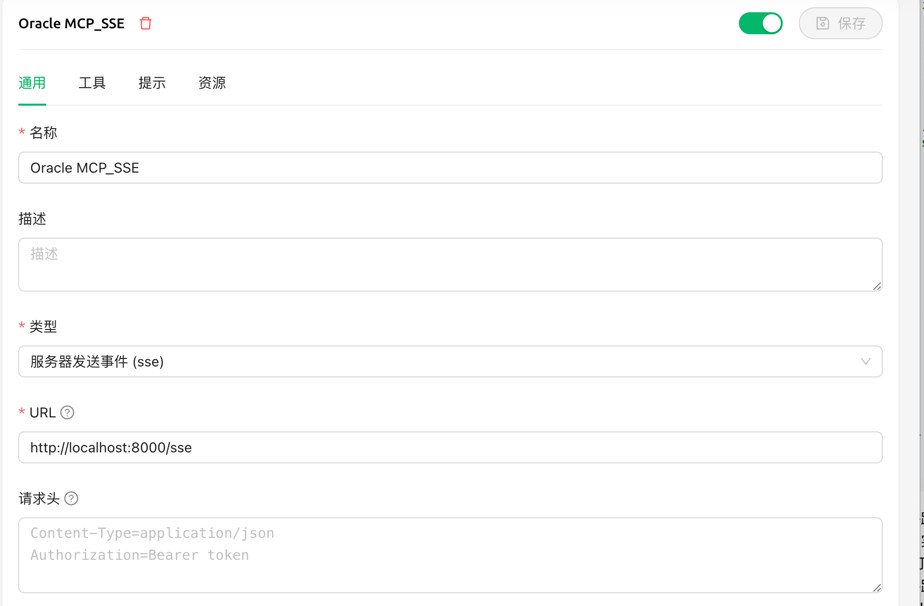
Starting the Server locally
To run the MCP server directly:
For development and testing:
Available Tools
When connected to an AI assistant like GitHub Copilot in VSCode Insiders or Claude, the following tools will be available:
get_table_schema
Get detailed schema information for a specific table including columns, data types, nullability, and relationships. Example:
get_tables_schema
Get schema information for multiple tables at once. More efficient than calling get_table_schema multiple times. Example:
search_tables_schema
Search for tables by name pattern and retrieve their schemas. Example:
rebuild_schema_cache
Force a rebuild of the schema cache. Use sparingly as this is resource-intensive. Example:
get_database_vendor_info
Get information about the connected Oracle database version and schema. Example:
search_columns
Search for tables containing columns that match a specific term. Useful when you know what data you need but aren't sure which tables contain it. Example:
get_pl_sql_objects
Get information about PL/SQL objects like procedures, functions, packages, triggers, etc. Example:
get_object_source
Retrieve the source code for a PL/SQL object. Useful for debugging and understanding database logic. Example:
get_table_constraints
Get all constraints (primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, check constraints) for a table. Example:
get_table_indexes
Get all indexes defined on a table, helpful for query optimization. Example:
get_dependent_objects
Find all objects that depend on a specified database object. Example:
get_user_defined_types
Get information about user-defined types in the database. Example:
get_related_tables
Get all tables that are related to a specified table through foreign keys, showing both incoming and outgoing relationships. Example:
read_query
执行SELECT查询 示例:
exec_ddl_sql
执行CREATE/ALTER/DROP操作 示例:
exec_dml_sql
执行INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE操作 示例:
exec_pro_sql
执行PL/SQL代码块
Architecture
This MCP server employs a three-layer architecture optimized for large-scale Oracle databases:
DatabaseConnector Layer
Manages Oracle database connections and query execution
Implements connection pooling and retry logic
Handles raw SQL operations
SchemaManager Layer
Implements intelligent schema caching
Provides optimized schema lookup and search
Manages the persistent cache on disk
DatabaseContext Layer
Exposes high-level MCP tools and interfaces
Handles authorization and access control
Provides schema optimization for AI consumption
Connection Modes
The database connector supports two connection modes:
Thin Mode (Default)
By default, the connector uses Oracle's thin mode, which is a pure Python implementation. This mode is:
Easier to set up and deploy
Sufficient for most basic database operations
More portable across different environments
Thick Mode
For scenarios requiring advanced Oracle features or better performance, you can enable thick mode:
When using Docker (recommended): Set
THICK_MODE=1in the Docker environment variablesWhen using local installation: Export
THICK_MODE=1environment variable and ensure Oracle Client libraries, compatible with your system architecture and database version, are installed
You can specify a custom location for the Oracle Client libraries using the ORACLE_CLIENT_LIB_DIR environment variable. This is particularly useful when:
You have Oracle Client libraries installed in non-standard locations
You need to work with multiple Oracle Client versions on the same system
You don't have administrative privileges to install Oracle Client in standard locations
You need specific Oracle Client versions for compatibility with certain database features
Note: When using Docker, you don't need to worry about installing Oracle Client libraries as they are included in the container (Oracle Instant Client v23.7). The container supports Oracle databases versions 19c up to 23ai in both linux/arm64 and linux/amd64 architectures.
System Requirements
Python: Version 3.12 or higher (required for optimal performance)
Memory: 4GB+ available RAM for large databases (10,000+ tables)
Disk: Minimum 500MB free space for schema cache
Oracle: Compatible with Oracle Database 11g and higher
Network: Stable connection to Oracle database server
Performance Considerations
Initial cache building may take 5-10 minutes for very large databases
Subsequent startups typically take less than 30 seconds
Schema lookups are generally sub-second after caching
Memory usage scales with active schema size
Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guidelines for details.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Support
For issues and questions:
Create an issue in this GitHub repository