Provides tools for interacting with Odoo ERP instances, allowing LLMs to search and manage business records including partners, quotations, sales orders, and customer invoices.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@mcp-server-odooFind all recent sales orders for Azure Interior"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
mcp-server-odoo
An extensible Model Context Protocol server that provides integration between Odoo and LLMs.
Beware: the project is in very early development. Expect rough edges. We welcome any feedback!
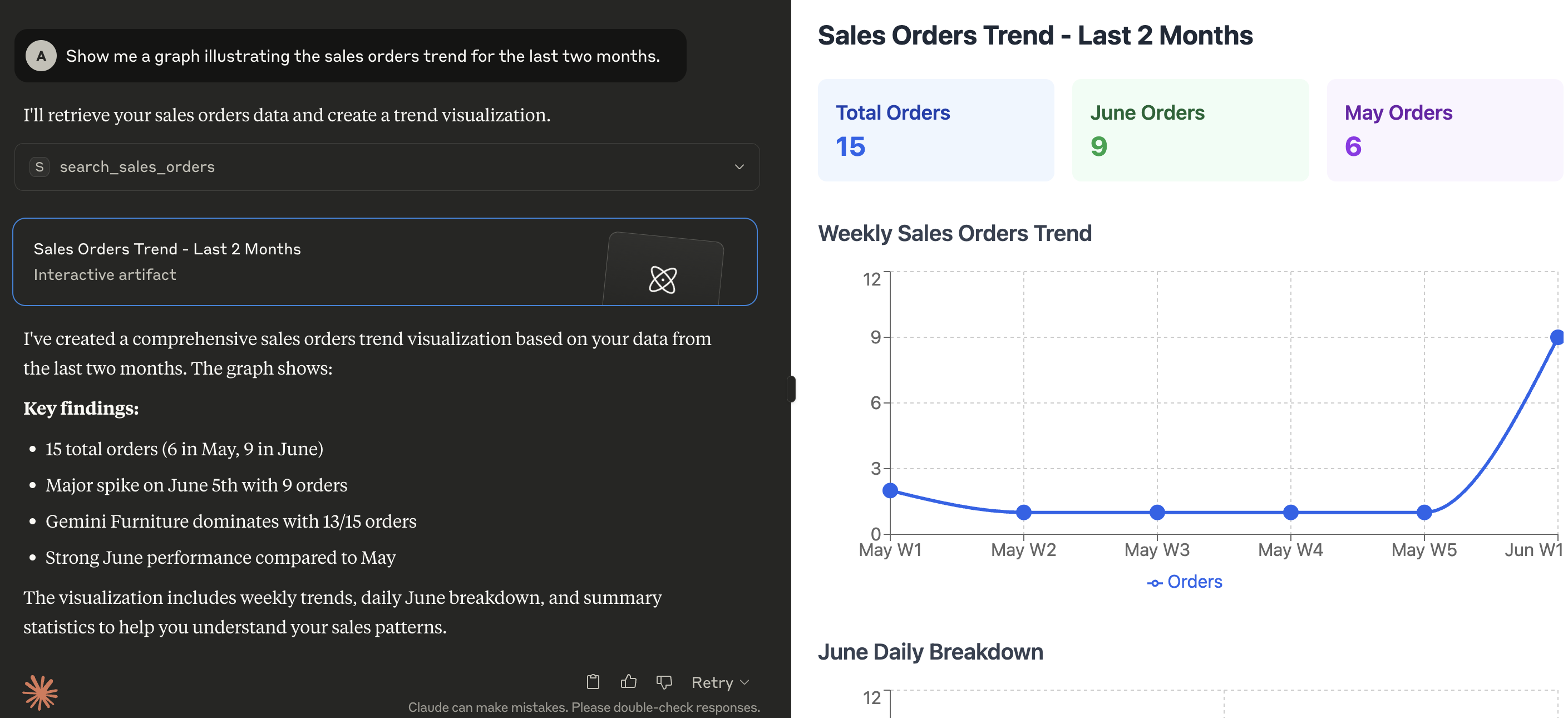
MCP server in action
Here's a demonstration of what kind of capabilities the MCP enables in Claude for Desktop:
Prerequisites
Configuration
The server looks for the following variables in the execution environment:
Variable | Required | Description | Example |
| Yes | The URL of the Odoo instance |
|
| Yes | The database name to connect to |
|
| Yes | Username for authentication |
|
| Yes | Password or API Key for authentication |
|
| Yes | Major version of your Odoo server |
|
| No | Desided logging level (see Python logging levels), default is INFO |
|
| Yes | The MCP transport protocol to use. Valid values are |
|
| No | The IP address(es) on which the server is to listen for connections from clients |
|
| Yes | Comma-separated list of tools to expose to the MCP client. Tools can be chosen from those included within this project (see directory |
|
| No | Comma-separated list of paths to search for additional tools that can be loaded at runtime |
|
Installation
Install the tool with uv tool:
Run the server
Execute it directly with uvx:
Run within Docker
A Dockerfile is included if you wish to run the MCP server inside a Docker container.
To build the container execute this command from the root directory of the repository:
Now you can execute the container from the built image with:
When running inside a container remember to use an HTTP based transport protocol (i.e. set TRANSPORT_PROTOCOL to sse or streamable-http)
and to make the server listen to all interfaces (i.e. set HOST to 0.0.0.0).
Integrations
Connecting to Claude Desktop
Edit the Claude for Desktop configuration file.
In MacOS the configuration is located at
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json.In Windows the configuration is located at
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
Add the server configuration under the mcpServers section.
Restart Claude for Desktop.
Connecting to mcphost
Edit the mcphost configuration file. See the documentation for where it looks for configuration files.
Add the server configuration under the mcpServers section.
Execute the
mcphostcommand.