DBHub
by bytebase
postgres-mcp-server-review-mcp-toolbox.mdx•12.4 kB
---
title: "Postgres MCP Server Review - MCP Toolbox for Databases"
description: "A deep-dive review of Google's MCP Toolbox for Databases, examining its token efficiency, authentication capabilities, and PostgreSQL support in a multi-database MCP server that supports 40+ data sources."
---
_Last updated: Dec 20, 2025_
This is the first in a series of deep-dive reviews examining popular Postgres MCP servers. We begin with [MCP Toolbox for Databases](https://github.com/googleapis/genai-toolbox),
an open-source MCP server developed by Google that supports a wide range of databases and data platforms including PostgreSQL, MySQL, BigQuery, MongoDB, and many others.
- **GitHub Stars**
[](https://www.star-history.com/#googleapis/genai-toolbox&type=date&legend=top-left)
- **License:** Apache-2.0
- **Language:** Go
## Installation
<Note>I am testing on a Mac (Apple Silicon)</Note>
Download the binary:
```bash
export VERSION=0.24.0
curl -L -o toolbox https://storage.googleapis.com/genai-toolbox/v$VERSION/darwin/arm64/toolbox
chmod +x toolbox
```
Create a YAML configuration file defining your database sources and tools:
```yaml tools.yaml
sources:
local-pg:
kind: postgres
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5432
database: employee
user: postgres
password: testpwd1
tools:
current_managers:
kind: postgres-sql
source: local-pg
description: List all current department managers
statement: |
SELECT e.emp_no, e.first_name, e.last_name, d.dept_name, dm.from_date
FROM dept_manager dm
JOIN employee e ON dm.emp_no = e.emp_no
JOIN department d ON dm.dept_no = d.dept_no
ORDER BY d.dept_name
```
Start the server with your configuration file:
```bash
./toolbox --tools-file "tools.yaml"
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443076-08:00 INFO "Initialized 1 sources: local-pg"
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443379-08:00 INFO "Initialized 0 authServices: "
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443488-08:00 INFO "Initialized 1 tools: current_managers"
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443512-08:00 INFO "Initialized 1 toolsets: default"
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443517-08:00 INFO "Initialized 0 prompts: "
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443524-08:00 INFO "Initialized 1 promptsets: default"
2025-12-19T08:10:47.443665-08:00 WARN "wildcard (`*`) allows all origin to access the resource and is not secure. Use it with cautious for public, non-sensitive data, or during local development. Recommended to use `--allowed-origins` flag to prevent DNS rebinding attacks"
2025-12-19T08:10:47.444054-08:00 INFO "Server ready to serve!"
```
The server runs on `http://127.0.0.1:5000/mcp` by default. The endpoint isn't shown in the startup logs—you'll need to check the documentation for that.
## Transports and GUI
MCP Toolbox supports multiple transport mechanisms:
- **Streamable HTTP** (default): Runs on `http://127.0.0.1:5000/mcp`
- **stdio**: Use `--stdio` flag for standard input/output communication
Additionally, you can launch with `--ui` flag to access a web-based console for viewing and testing tools:
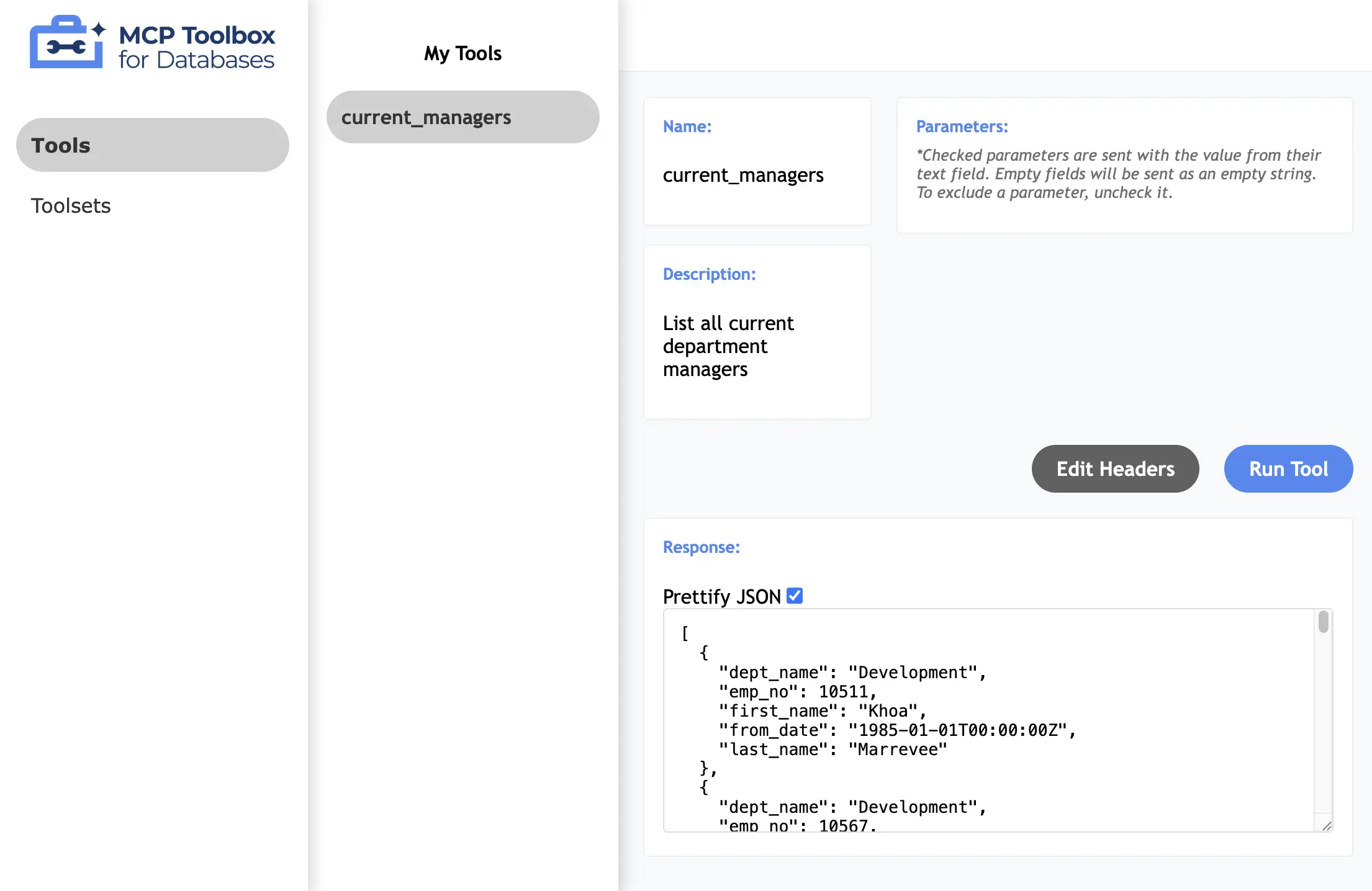
## Tools
MCP Toolbox distinguishes between custom tools and prebuilt tools:
**Custom Tools** are user-defined operations configured in the YAML file. These include:
- **Database tools** (e.g., `postgres-sql`) for executing SQL queries with parameterized statements
- **HTTP tools** for calling external APIs with configurable methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), headers, query parameters, and request bodies
Each tool specifies a `source` (which connection to use), `description` (guidance for AI agents), and operation details with optional typed parameters (string, integer, float, boolean, arrays, maps).
**Toolsets** organize related tools into logical collections that can be loaded by name through client SDKs.
**Prebuilt Tools** are ready-to-use tool collections for 40+ database systems and services, including open source databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, Neo4j), cloud databases (BigQuery, Spanner, AlloyDB), analytics platforms (Looker, Elasticsearch), and specialized services.
## Token Efficiency
### Using Prebuilt Tools
To get started quickly, you might be tempted to use the prebuilt PostgreSQL tools. This requires setting environment variables and launching with the `--prebuilt postgres` flag:
```bash
export POSTGRES_HOST=127.0.0.1
export POSTGRES_PORT=5432
export POSTGRES_DATABASE=employee
export POSTGRES_USER=postgres
export POSTGRES_PASSWORD=testpwd1
./toolbox --prebuilt postgres
```
The prebuilt PostgreSQL toolset loads 28 tools:
```bash
│ Tools for mcp-toolbox (28 tools) │
│ │
│ ❯ 1. list_memory_configurations │
│ 2. list_autovacuum_configurations │
│ 3. database_overview │
│ 4. get_query_plan │
│ ↓ 5. list_triggers
```
For token-conscious users, the upfront cost of 19.0k tokens is far from efficient:
```bash
> /context
⎿
Context Usage
⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929 · 86k/200k tokens (43%)
⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛀ ⛁
⛀ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ System prompt: 2.7k tokens (1.3%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ System tools: 15.9k tokens (7.9%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ MCP tools: 19.0k tokens (9.5%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ Custom agents: 247 tokens (0.1%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ Memory files: 2.4k tokens (1.2%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛁ Messages: 1.2k tokens (0.6%)
⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛶ Free space: 114k (56.8%)
⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ Autocompact buffer: 45.0k tokens (22.5%)
```
### Picking Specific Tools
A wiser choice is to specify exact tools via the configuration file. For example, you can specify just the [`postgres-execute-sql`](https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/resources/tools/postgres/postgres-execute-sql/) tool:
```yaml
tools:
execute_sql_tool:
kind: postgres-execute-sql
source: local-pg
description: Use this tool to execute sql statement.
```
With this approach, only that tool is loaded, consuming just 579 tokens—a 30x reduction:
```bash
> /context
⎿
Context Usage
⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛁ ⛀ claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929 · 68k/200k tokens (34%)
⛀ ⛁ ⛀ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ System prompt: 2.6k tokens (1.3%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ System tools: 15.9k tokens (7.9%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ MCP tools: 579 tokens (0.3%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ Custom agents: 247 tokens (0.1%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛁ Memory files: 2.4k tokens (1.2%)
⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛶ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛁ Messages: 1.3k tokens (0.6%)
⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛶ Free space: 132k (66.0%)
⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ ⛝ Autocompact buffer: 45.0k tokens (22.5%)
```
<Note>
The built-in `postgres-execute-sql` tool does not provide safety guardrails such as read-only enforcement, row limits, connection timeouts, or query timeouts. In contrast, [`spanner-execute-sql`](https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/resources/tools/spanner/spanner-execute-sql/) does support a `readOnly` parameter.
</Note>
## Auth & Security
MCP Toolbox has built-in authentication and authorization through [AuthServices](https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/resources/authservices/). Two main security mechanisms:
### OIDC Token Authentication
The `authRequired` field enforces OIDC token validation before tool execution:
```yaml
authServices:
my-google-auth:
kind: google
clientId: ${GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID}
tools:
list_sensitive_data:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-instance
statement: SELECT * FROM confidential_table
authRequired:
- my-google-auth
```
When a tool specifies `authRequired`, the server validates OIDC tokens against the configured authentication service. Invalid or missing tokens get rejected.
### Row-Level Security (RLS)
MCP Toolbox can extract user information from OIDC token claims to enforce row-level security. The `authServices` field auto-populates parameters from the authenticated user's token:
```yaml
tools:
get_user_orders:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-instance
statement: SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_id = $1
parameters:
- name: user_id
type: string
description: Auto-populated from authenticated user
authServices:
- name: my-google-auth
field: sub # OIDC subject claim (user ID)
```
This prevents users from accessing data belonging to others—the `user_id` parameter is automatically populated from the authenticated user's token, not from user input.
<Note>
Currently, only **Google Sign-In** (OAuth 2.0 / OIDC) is supported. Other OIDC providers such as [Keycloak](https://github.com/googleapis/genai-toolbox/issues/1072) and [Microsoft Entra ID](https://github.com/googleapis/genai-toolbox/issues/482) are pending discussion.
</Note>
## Telemetry
MCP Toolbox supports [structured JSON logging](https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/concepts/telemetry/) to stdout/stderr (for streaming to SIEM systems like Splunk or Elastic) and exports metrics and traces to any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend. As a Google product, it has built-in integration with Google Cloud.
## Summary
**MCP Toolbox for Databases** isn't really a PostgreSQL MCP server. It's not even just a general-purpose database MCP server as its name suggests. With HTTP tools baked in, you can connect to basically anything with an HTTP endpoint. This "cast a wide net" approach seems to be working—it has the most GitHub stars among all database-related MCP servers.
### The Good
- YAML-based configuration lets you cherry-pick tools for token efficiency. Instead of loading all 28 prebuilt PostgreSQL tools (19k tokens), specify just `postgres-execute-sql` for 579 tokens—a 30x reduction.
- Built-in auth (OIDC with row-level security) and telemetry (OpenTelemetry) are solid production features most database MCP servers lack. Auto-populating query parameters from authenticated tokens is useful for multi-tenant scenarios.
- Supports 40+ data sources—PostgreSQL, BigQuery, MongoDB, and anything with an HTTP endpoint. If you need that versatility, nothing else comes close.
### The Bad
- The `postgres-execute-sql` tool lacks common guardrails like read-only mode, row limits, and timeouts. Compare that to `spanner-execute-sql` which does have a `readOnly` parameter—you can see where Google's priorities lie.
- Everything tilts toward the Google ecosystem. Auth only works with Google Sign-In (Keycloak and Microsoft Entra ID are still "pending discussion"). Telemetry has native Google Cloud integration. Fine if you're in GCP, limiting otherwise.
- The documentation is struggling. Search is broken, and the content feels out of control as they add more sources.
### Should You Use It?
If you're in the Google ecosystem and need to connect AI agents to multiple data sources, MCP Toolbox is your best bet. The configuration flexibility and production features are real advantages.
But if you need a dedicated PostgreSQL server with proper safety guardrails, auth providers beyond Google, or documentation that doesn't make you ~hurt~hunt, look elsewhere.
Latest Blog Posts
- Federated Learning with MCP: Building Privacy-Preserving Agents Across Distributed EdgesBy Om-Shree-0709 on .SecuremcpLearning
- MCP Moves to the Linux Foundation: Neutral Stewardship for Agentic InfrastructureBy Om-Shree-0709 on .mcpanthropicLinux Foundation
MCP directory API
We provide all the information about MCP servers via our MCP API.
curl -X GET 'https://glama.ai/api/mcp/v1/servers/bytebase/dbhub'
If you have feedback or need assistance with the MCP directory API, please join our Discord server