Provides Docker container deployment options for running the DBHub server with configurable database connections and transport options.
Supports connecting to DuckDB databases to explore tables, access schema information, and perform read-only SQL queries with safety measures.
Provides access to MySQL databases for browsing tables, viewing schema information, and executing read-only SQL queries with safety protections.
Allows querying PostgreSQL databases, browsing tables, viewing schema information, and running read-only SQL queries with safety checks.
Enables connection to SQLite databases to browse available tables, view schema information, and run protected read-only SQL queries.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@DBHubshow me the top 10 customers by total order amount"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Brought to you by Bytebase, open-source database DevSecOps platform.
DBHub is a zero-dependency, token efficient MCP server implementing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server interface. This lightweight gateway allows MCP-compatible clients to connect to and explore different databases:
Local Development First: Zero dependency, token efficient with just two MCP tools to maximize context window
Multi-Database: PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, and SQLite through a single interface
Multi-Connection: Connect to multiple databases simultaneously with TOML configuration
Guardrails: Read-only mode, row limiting, and query timeout to prevent runaway operations
Secure Access: SSH tunneling and SSL/TLS encryption
Supported Databases
PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, and SQLite.
Related MCP server: Supabase MCP Server
MCP Tools
DBHub implements MCP tools for database operations:
execute_sql: Execute SQL queries with transaction support and safety controls
search_objects: Search and explore database schemas, tables, columns, indexes, and procedures with progressive disclosure
Custom Tools: Define reusable, parameterized SQL operations in your
dbhub.tomlconfiguration file
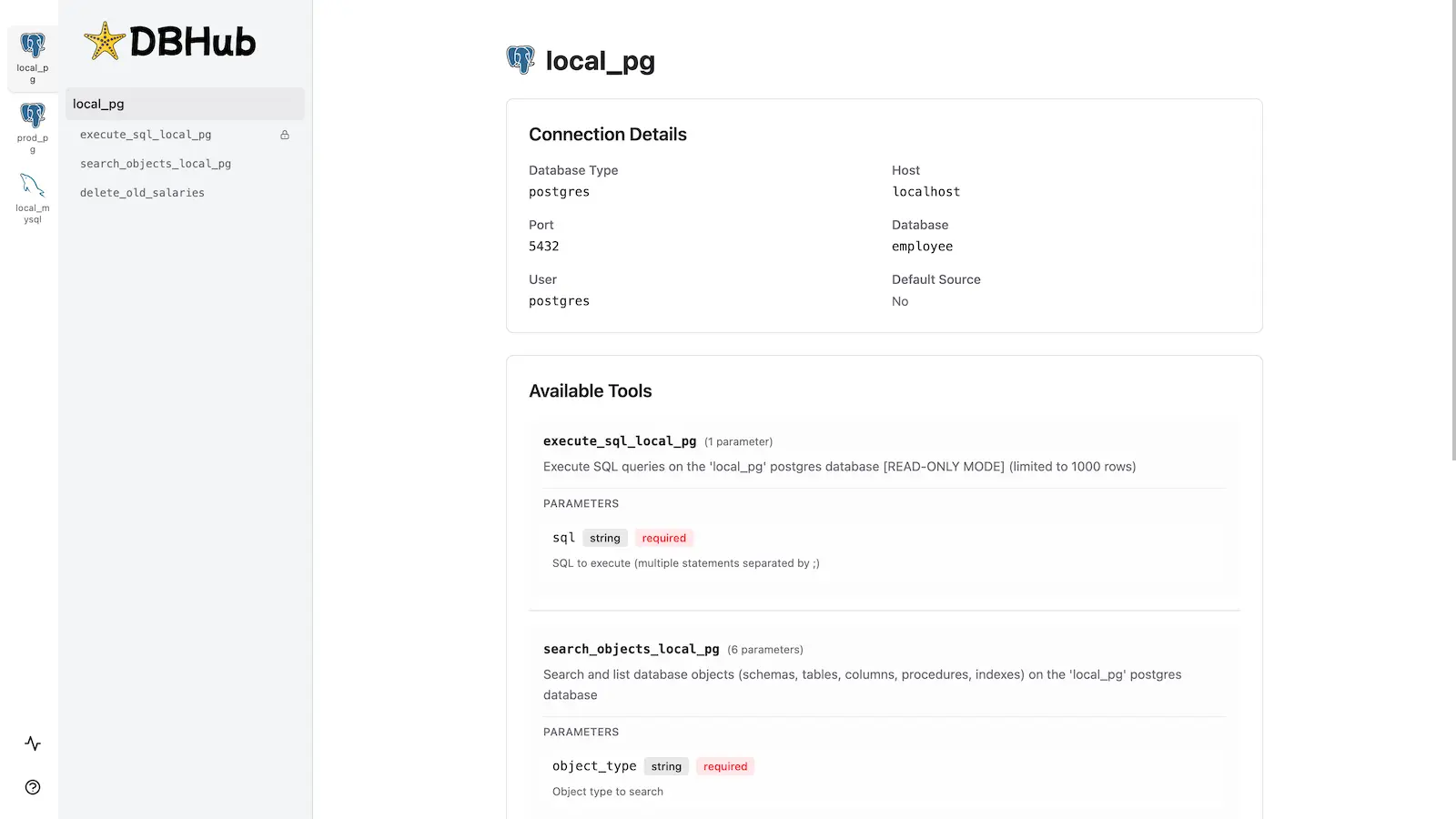
Workbench
DBHub includes a built-in web interface for interacting with your database tools. It provides a visual way to execute queries, run custom tools, and view request traces without requiring an MCP client.
Installation
See the full Installation Guide for detailed instructions.
Quick Start
Docker:
NPM:
Demo Mode:
See Command-Line Options for all available parameters.
Multi-Database Setup
Connect to multiple databases simultaneously using TOML configuration files. Perfect for managing production, staging, and development databases from a single DBHub instance.
See Multi-Database Configuration for complete setup instructions.