The Agent MCP Gateway is a policy-based proxy that aggregates multiple MCP servers and provides on-demand tool discovery with access control, reducing context window usage by 90%+.
Core Capabilities:
list_servers- Discover available downstream servers based on your permissionsget_server_tools- Retrieve filtered tool definitions from specific servers (supports wildcard patterns likeget_*,*_user, and token budget limits)execute_tool- Run tools on downstream servers with transparent proxying and configurable timeoutsget_gateway_status- Monitor gateway health, configuration state, and diagnostics (debug mode only)
Key Features:
Policy-Based Access Control: Per-agent permissions using deny-before-allow precedence
Multi-Server Aggregation: Proxy to multiple downstream MCP servers (stdio and HTTP transports)
Session Isolation: Concurrent requests handled safely without interference
OAuth Support: Automatic authentication handling for OAuth-protected servers
Hot Configuration Reload: Update rules and servers without restarting
Audit Logging & Metrics: Track all operations with performance monitoring
Typical Workflow: Call list_servers to discover accessible servers → use get_server_tools to view available tools → execute tools via execute_tool with required arguments.
Provides web search capabilities through Brave Search API, allowing agents to perform web and local searches.
Enables interaction with GitHub APIs using Personal Access Token authentication for repository and project management.
Provides integration with Laravel applications through laravel-boost server, offering tools for database queries, file operations, and Laravel-specific functionality.
Provides access to Notion workspaces with OAuth authentication support for managing Notion content.
Enables PostgreSQL database access and query execution, allowing agents to interact with database tables and schemas.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Agent MCP Gatewaylist available servers I can access"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Agent MCP Gateway
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) gateway that aggregates multiple MCP servers and provides policy-based access control for agents and subagents. Solves Claude Code's MCP context window waste by enabling on-demand tool discovery instead of loading all tool definitions upfront.
Status
✅ M0: Foundation - Configuration, policy engine, audit logging,
list_serverstool✅ M1: Core - Proxy infrastructure,
get_server_tools,execute_tool, middleware, metrics, hot reload, OAuth support🚧 M2: Production - HTTP transport, health checks (planned)
🚧 M3: DX - Single-agent mode, config validation CLI, Docker (planned)
Current Version: M1-Core Complete (with OAuth)
Table of Contents
Overview
The Problem
When multiple MCP servers are configured in development environments (Claude Code, Cursor, VS Code), all tool definitions from all servers load into every agent's and subagent's context window at startup:
5,000-50,000+ tokens consumed upfront
80-95% of loaded tools never used by individual agents
Context needed for actual work gets wasted on unused tool definitions
The Solution
The Agent MCP Gateway acts as a single MCP server that proxies to multiple downstream MCP servers based on configurable per-agent rules:
3 gateway tools load at startup (~2k tokens)
Agents discover and request specific tools on-demand
90%+ context reduction
Policy-based access control per agent/subagent
How It Works
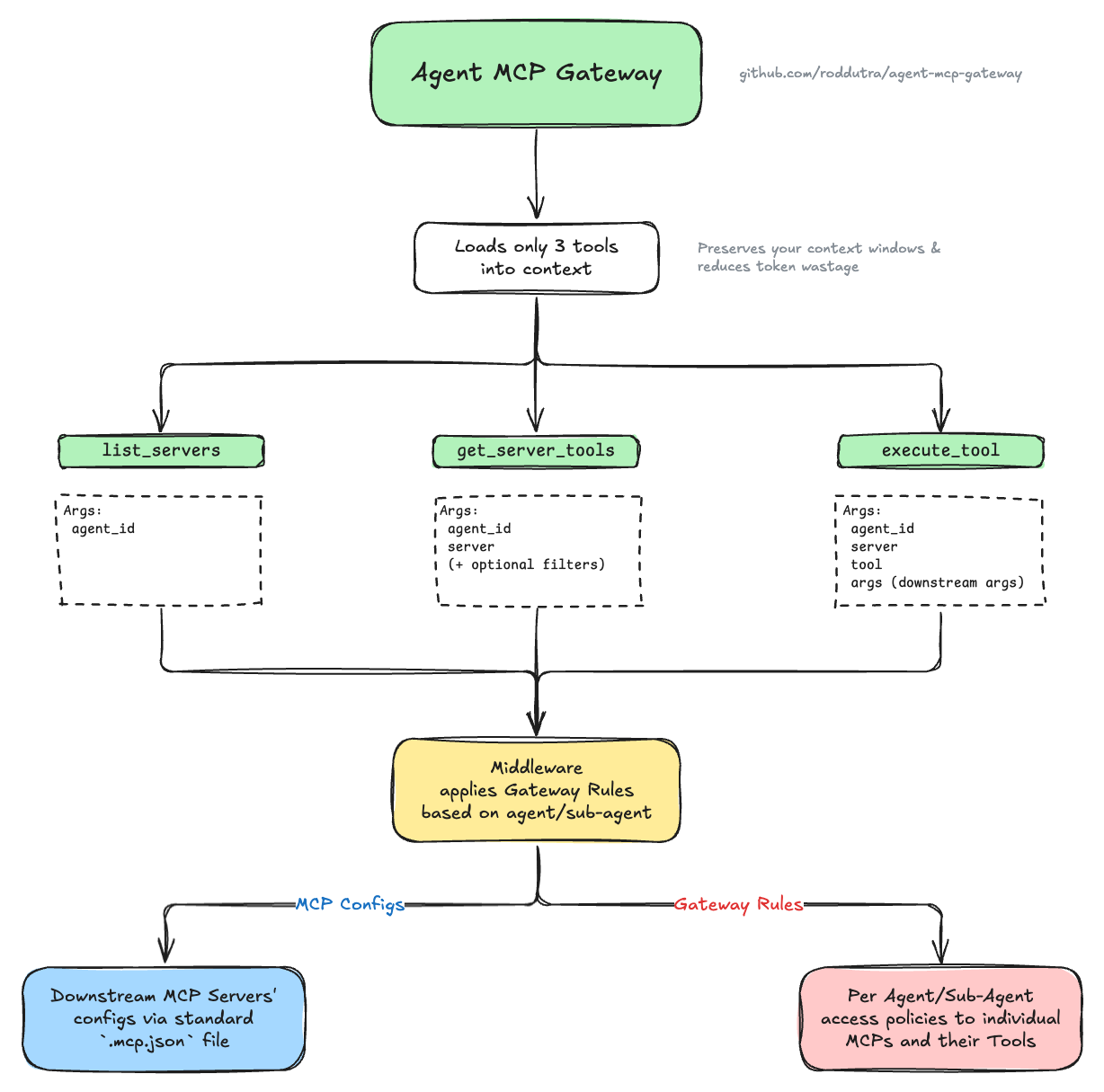
The gateway sits between agents and downstream MCP servers, exposing only 3 lightweight tools. When an agent needs specific functionality, it discovers available servers and tools through the gateway, which filters visibility based on policy rules - agents only see servers and tools they have access to. This reduces each agent's context window to only relevant tools, while the gateway handles proxying authorized requests to downstream servers.
View detailed diagram with examples → (includes downstream servers, tools, and gateway rules examples)
Key Features
✅ On-Demand Tool Discovery - Load tool definitions only when needed
✅ Per-Agent Access Control - Configure which servers/tools each agent can access
✅ Easy Agent Integration - Simple template to add gateway support to any agent (see guide)
✅ Deny-Before-Allow Policies - Explicit deny rules take precedence
✅ Wildcard Support - Pattern matching for tool names (
get_*,*_user)✅ Session Isolation - Concurrent requests don't interfere
✅ Transparent Proxying - Downstream servers unaware of gateway
✅ Audit Logging - All operations logged for monitoring
✅ Performance Metrics - Track latency and error rates per agent/operation
✅ Hot Configuration Reload - Update rules/servers without restart
✅ Thread-Safe Operations - Safe concurrent access during reloads
✅ Diagnostic Tools - Health monitoring via
get_gateway_status(debug mode only)
Installation
This generates two template files ready to customize:
mcp.json- Your downstream MCP servers (Brave, Postgres, etc.)mcp-gateway-rules.json- Per-agent access policies (who can use which servers/tools)
For local development: See Development section.
Quick Start
1. Configure Gateway Files
After running uvx agent-mcp-gateway --init (see Installation), edit the generated template files:
See Configuration section for detailed examples and Configuration File Discovery for alternative file locations.
2. Add Gateway to Your MCP Client
Claude Code CLI:
Manual configuration:
Note: The env variables are optional if using default config locations. See Environment Variables Reference for all options.
3. Configure Your Agents
The gateway's tool descriptions are self-documenting, but for proper access control you should configure how your agents identify themselves. Choose the approach that fits your use case:
Approach 1: Multi-Agent Mode (Recommended)
For different agents with different permissions, configure each agent to pass its identity.
Add this to your agent's system prompt (e.g., CLAUDE.md, .claude/agents/agent-name.md):
Replace YOUR_AGENT_NAME with your agent's identifier (e.g., "researcher", "backend", "admin").
Examples: See .claude/agents/researcher.md and .claude/agents/mcp-developer.md for complete configuration examples.
Approach 2: Single-Agent Mode
For simpler setups where all agents should have the same permissions, or when using MCP clients without system prompt configuration (e.g., Claude Desktop), configure a default agent using either method:
Option A: Environment Variable
Note: The agent specified (e.g., "developer") must exist in your .mcp-gateway-rules.json file with appropriate permissions.
Option B: "default" Agent in Rules
Note: Allowing all servers ("servers": ["*"]) without specifying tool restrictions grants access to all tools on all servers.
With either approach, agents can omit agent_id in tool calls - the gateway uses your configured default agent automatically.
Command-Line Options
Configuration File Discovery
The gateway searches for configuration files in this order:
MCP Server Config (.mcp.json)
GATEWAY_MCP_CONFIGenvironment variable (if set).mcp.jsonin current directory~/.config/agent-mcp-gateway/.mcp.json(home directory)./config/.mcp.json(fallback)
Gateway Rules (.mcp-gateway-rules.json)
GATEWAY_RULESenvironment variable (if set).mcp-gateway-rules.jsonin current directory~/.config/agent-mcp-gateway/.mcp-gateway-rules.json(home directory)./config/.mcp-gateway-rules.json(fallback)
Tip: Use agent-mcp-gateway --init to create the home directory configs on first run.
Configuration
The gateway requires two configuration files:
1. MCP Servers Configuration
File: mcp.json (searched in multiple locations)
Defines the downstream MCP servers the gateway will proxy to. Uses the standard MCP config format compatible with Claude Code and other coding agents:
Server Descriptions (Recommended):
Adding a description field to each server helps AI agents understand what each server provides and when to use it. Descriptions are always returned by list_servers, enabling agents to make informed decisions about which servers to query for tools. While optional, descriptions significantly improve agent tool discovery and decision-making.
Supported Transports:
stdio- Local servers via npx/uvx (specified withcommand+args)http- Remote HTTP servers (specified withurl)
Environment Variables:
Use
${VAR_NAME}syntax for environment variable substitutionSet variables before running:
export BRAVE_API_KEY=your-key
Important - GUI Applications (Claude Desktop, etc.):
If you use ${VAR_NAME} syntax in .mcp.json, note that macOS GUI applications run in isolated environments without access to your shell's environment variables. For Claude Desktop and similar apps, add API keys to the gateway's env object in your MCP client configuration:
(If you hardcode values directly in .mcp.json without ${VAR_NAME} syntax, this is not necessary.)
2. Gateway Rules Configuration
File: mcp-gateway-rules.json (searched in multiple locations)
Defines per-agent access policies using deny-before-allow precedence:
Agent Examples Explained:
researcher - Demonstrates implicit grant + explicit allow:
brave-search: ONLYbrave_web_searchtool (explicit allow narrows access)context7: ALL tools (implicit grant - server allowed, no tool rules specified)
backend - Demonstrates wildcard allows with deny-before-allow precedence:
postgres: ONLYquery,list_tables,list_schemas(explicit allows); deny rules serve as safety netlaravel-boost: Wildcard allows (get_*,list_*,read_*,database_*,search_*) grant broad access, BUTdatabase_queryexplicitly denied despite matchingdatabase_*wildcard (deny wins), andtinkerblocked as safety measure
admin - Demonstrates server wildcard + mixed access patterns:
notion: DENIED (server-level deny overrides wildcard server allow)brave-search: ONLYbrave_web_search(explicit restriction on one server)playwright: ALL tools EXCEPTbrowser_type(implicit grant with explicit deny)All other servers: ALL tools (implicit grant - no tool rules specified)
claude-desktop - Demonstrates implicit grant with multiple deny types:
context7,brave-search,notion: ALL tools (implicit grant)playwright: ALL tools EXCEPTbrowser_type,browser_close_all, and tools matchinglaunch_*(implicit grant with explicit + wildcard denies)
default - Principle of least privilege:
Used as fallback when
agent_idnot provided anddeny_on_missing_agentisfalseDenies all servers by default; use
GATEWAY_DEFAULT_AGENTenvironment variable to specify a different default agent
Policy Precedence Order:
Explicit deny rules (highest priority)
Wildcard deny rules
Explicit allow rules
Wildcard allow rules
Implicit grant (if server allowed but no tool rules specified)
Default policy (deny)
Implicit Grant Behavior:
If agent has server access and no
allow.tools.{server}entry, all tools from that server are implicitly grantedallow.tools.{server}entries narrow access to specified tools onlydeny.tools.{server}entries filter out specific tools (evaluated in steps 1-2)Rules are server-specific and don't affect other servers
Configuration Flexibility:
Rules can reference servers not currently in
.mcp.jsonUndefined server references treated as warnings (not errors)
Allows keeping rules for temporarily removed servers
Hot reload applies changes immediately without restart
Wildcard Patterns:
*- Matches everythingget_*- Matches tools starting with "get_"*_user- Matches tools ending with "_user"
Agent Naming:
Use hierarchical names:
team.role(e.g.,backend.database,frontend.ui)Alphanumeric characters, hyphens, underscores, and dots allowed
Configure your agents to pass their identity: See Configure Your Agents
Configuration Validation
The gateway validates configurations at startup and during hot reload. Example output:
Validation Behavior:
Structural errors (invalid JSON, missing required fields) → Fail startup/reload
Undefined server references → Log warnings, continue with valid rules
Policy conflicts → Deny-before-allow precedence resolves automatically
3. OAuth Support for Downstream Servers
OAuth-protected downstream servers (Notion, GitHub) are automatically supported via auto-detection when servers return HTTP 401. The gateway uses FastMCP's OAuth support to handle authentication flows transparently - browser opens once for initial authentication, then tokens are cached for future use. See OAuth User Guide for detailed setup and troubleshooting.
OAuth Limitations:
The gateway supports OAuth servers that implement Dynamic Client Registration (RFC 7591).
✅ Supported: OAuth with auto-detection (e.g., Notion MCP)
❌ Not Supported: OAuth with pre-registered apps (e.g., GitHub OAuth flow)
💡 For GitHub MCP: Use Personal Access Token instead
GitHub MCP with PAT Example:
For detailed OAuth setup and troubleshooting, see OAuth User Guide.
4. Environment Variables Reference
Variable | Description | Default | Example |
| Path to MCP servers configuration file |
|
|
| Path to gateway rules configuration file |
|
|
| Default agent identity when | None |
|
| Enable debug mode to expose |
|
|
| Path to audit log file |
|
|
| Transport protocol (stdio or http) |
|
|
| Initialization strategy (eager or lazy) |
|
|
Note on GUI Applications: macOS GUI applications (Claude Desktop, etc.) run in isolated environments without access to shell environment variables. If using ${VAR_NAME} syntax in .mcp.json, add required API keys to the gateway's env object in your MCP client configuration.
Usage
The gateway runs automatically when your MCP client starts. See Quick Start for adding it to your MCP client configuration.
Custom configuration paths can be specified via environment variables in your MCP client config:
See Environment Variables Reference for all available options.
Startup Output
Gateway Tools
The gateway exposes exactly 3 tools to agents. All tools accept an optional agent_id parameter for access control. When agent_id is not provided, the gateway uses a fallback chain to determine agent identity (see Agent Identity Modes).
For Agent Developers: To configure your agents to properly use these gateway tools with access control, see Configure Your Agents.
1. list_servers
Lists MCP servers available to the calling agent based on policy rules.
Parameters:
agent_id(string, optional) - Identifier of the agent making the request (see Agent Identity Modes)include_metadata(boolean, optional) - Include technical details like transport, command, and url (default: false)
Returns:
With
Note: Server descriptions are always included (when configured in .mcp.json) to help agents understand what each server provides. The include_metadata flag only controls whether technical details (transport, command, url) are included.
Example:
2. get_server_tools
Retrieves tool definitions from a specific MCP server, filtered by agent permissions.
Parameters:
agent_id(string, optional) - Identifier of the agent (see Agent Identity Modes)server(string, required) - Name of the downstream MCP servernames(string, optional) - Comma-separated list of tool names (e.g.,"tool1,tool2,tool3") or single tool namepattern(string, optional) - Wildcard pattern for tool names (e.g.,"get_*")max_schema_tokens(integer, optional) - Token budget limit for schemas
Returns:
Example:
3. execute_tool
Executes a tool on a downstream MCP server with transparent result forwarding.
Parameters:
agent_id(string, optional) - Identifier of the agent (see Agent Identity Modes)server(string, required) - Name of the downstream MCP servertool(string, required) - Name of the tool to executeargs(object, required) - Arguments to pass to the tooltimeout_ms(integer, optional) - Timeout in milliseconds
Returns:
Example:
4. get_gateway_status (Debug Mode Only)
Returns comprehensive gateway health and diagnostics information.
Important: This tool is only available when debug mode is enabled (via GATEWAY_DEBUG=true environment variable or --debug CLI flag). See Security Considerations for details.
Parameters:
agent_id(string, optional) - Identifier of the agent (see Agent Identity Modes)
Returns:
Example:
Error Handling
All tools return structured errors with clear messages:
Error Codes:
DENIED_BY_POLICY- Agent lacks permissionSERVER_UNAVAILABLE- Downstream server unreachableTOOL_NOT_FOUND- Requested tool doesn't existTIMEOUT- Operation exceeded time limitINVALID_AGENT_ID- Missing or unknown agent identifierFALLBACK_AGENT_NOT_IN_RULES- Configured fallback agent not found in gateway rulesNO_FALLBACK_CONFIGURED- No agent_id provided and no fallback agent configured
Complete Workflow Example
Here's a minimal working example showing the typical gateway workflow:
This workflow demonstrates on-demand tool discovery - load definitions only when needed, not upfront.
Agent Identity Modes
The gateway supports two deployment modes for handling agent identity:
Multi-Agent Mode (Recommended)
Use when different agents need different permissions (production, multi-agent systems):
Configure each agent to pass their identity (see Configure Your Agents).
Single-Agent Mode
Use when all agents should have the same permissions (development, personal use, single-agent deployments):
Or define a "default" agent in rules:
Agents can omit agent_id in tool calls - the gateway automatically uses the configured default.
When agent_id is not provided, the gateway uses this fallback chain:
GATEWAY_DEFAULT_AGENTenvironment variable (highest priority)Agent named "default" in
.mcp-gateway-rules.jsonError if neither configured
The deny_on_missing_agent setting controls this behavior:
true: Require explicitagent_id(bypass fallback chain)false: Use fallback chain whenagent_idomitted
Security Note: The fallback mechanism follows the principle of least privilege - it never grants implicit "allow all" access, only the explicitly configured agent's permissions.
Security Considerations
Rules File Location: Store .mcp-gateway-rules.json in-project for context optimization only. For production access control, store outside project directory (e.g., ~/.claude/mcp-gateway-rules.json) to prevent agents from reading/modifying permissions.
Debug Mode: The get_gateway_status tool exposes gateway internals and is only available when GATEWAY_DEBUG=true. Disable in production environments.
For comprehensive security guidance: See Security Guide for detailed information on rules file security, debug mode considerations, agent impersonation risks, and production best practices.
Troubleshooting
Gateway Won't Start
Symptom: Error on startup or gateway fails to initialize
Solutions:
Check configuration files exist: Verify
.mcp.jsonand.mcp-gateway-rules.jsonare in the expected locationValidate JSON syntax: Use
python -m json.tool < .mcp.jsonto check for syntax errorsCheck Python version: Ensure Python 3.12+ is installed (
python --version)Verify dependencies: Run
uv syncto ensure all packages are installed
Can't Connect to Downstream Server
Symptom: SERVER_UNAVAILABLE error when calling tools
Solutions:
Verify server configuration: Check server is properly defined in
.mcp.jsonTest stdio servers: Ensure command is available (
npx --version,uvx --version)Check environment variables: Verify API keys and credentials are set
Test HTTP servers: Try accessing server URL directly in browser
Review startup logs: Look for server initialization errors in gateway output
Permission Denied Errors
Symptom: DENIED_BY_POLICY when agent tries to use a tool
Solutions:
Verify agent_id: Ensure agent is passing correct identity (check audit logs)
Check agent rules: Confirm agent exists in
.mcp-gateway-rules.jsonReview policy precedence: Remember deny rules take precedence over allow rules
Test with wildcard: Try
"tools": {"server-name": ["*"]}to grant broad access temporarilyEnable debug mode: Use
GATEWAY_DEBUG=trueand callget_gateway_statusto inspect policy state
OAuth Authentication Issues
Symptom: Browser doesn't open or OAuth flow fails
See detailed troubleshooting in OAuth User Guide.
Quick fixes:
Clear token cache:
rm -rf ~/.fastmcp/oauth-mcp-client-cache/Test browser:
python -m webbrowser https://example.comCheck server URL: Verify correct OAuth server URL in
.mcp.json
Hot Reload Not Working
Symptom: Changes to config files don't take effect
Solutions:
Check file watch: Ensure config files are in expected locations
Review logs: Look for reload errors in gateway output
Manual reload: Send SIGHUP signal or restart gateway
Debug mode: Use
get_gateway_statusto check last reload timestamps
For additional help: See Security Guide, OAuth User Guide, or open a GitHub issue.
Testing
Testing with MCP Inspector
The MCP Inspector is an interactive tool for testing MCP servers.
Inspector features:
View all gateway tools with schemas
Test tools with custom inputs
Inspect request/response messages
Monitor logs and notifications
Testing Gateway Tools in Inspector
1. Test
Expected: List of servers the "researcher" agent can access.
2. Test
Expected: Tool definitions from brave-search server.
3. Test
Expected: Search results from Brave (if server configured and running).
Troubleshooting:
Check Logs pane for errors
Verify
agent_idexists in rules fileConfirm downstream servers configured
Review Message pane for policy denials
Development
Local Installation
Clone and install in development mode:
Add Local Gateway to MCP Client
Note: The --directory flag tells uv run to change to the project directory before running, ensuring it finds pyproject.toml and the gateway configuration files.
Project Structure
Running in Development
Testing
Testing with MCP Inspector:
Manual testing with FastMCP Client:
Adding a New Feature
Update specs: Document in relevant milestone file
Write tests first: Create test file in
tests/Implement feature: Add code in
src/Run tests:
uv run pytestCheck coverage:
uv run pytest --cov=srcUpdate docs: Document in README and relevant files
Commit: Follow commit message format
Code Style
Follow existing patterns in M0/M1 code
Use type hints throughout
Write docstrings for all public functions
Keep functions focused and testable
Add tests for all new functionality
Architecture
Component Diagram
Request Flow
Agent sends request to gateway tool with
agent_idMiddleware intercepts: Extracts and validates
agent_idTool validates: Checks PolicyEngine for server/tool access
Proxy forwards: ProxyManager routes to downstream server
Session isolated: Each request gets fresh connection
Result returns: Transparently forwarded to agent
Audit logged: Operation recorded with metrics
Performance Characteristics
Context reduction: 90%+ (2k tokens vs 5,000-50,000+)
Added latency: <100ms (P95)
Gateway overhead: <30ms per operation
Session isolation: Automatic per-request
Concurrent requests: Fully supported
Future Features
M2: Production (Planned)
🚧 Status: Not yet implemented
Features:
HTTP transport for gateway server
Health check endpoints
Enhanced error handling
Metrics export API
Connection pooling optimization
Rate limiting
When available:
M3: Developer Experience (Planned)
🚧 Status: Not yet implemented
Features:
Single-agent mode (bypass agent_id requirement)
Config validation CLI tool
Docker container with examples
Interactive setup wizard
VS Code extension
When available:
Documentation
Contributing
Contributions welcome! Please:
Read the PRD and relevant milestone specs
Follow the existing code style and patterns
Write tests for all new functionality
Ensure all tests pass:
uv run pytestUpdate documentation as needed
Submit a pull request with clear description
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Support
For issues and questions:
GitHub Issues: Create an issue
Documentation: docs/
MCP Specification: https://modelcontextprotocol.io
Acknowledgments
Built with:
FastMCP - MCP server framework
Model Context Protocol - Protocol specification