Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Smart Coding MCPfind where we handle user authentication in the codebase"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Smart Coding MCP
An extensible Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides intelligent semantic code search for AI assistants. Built with local AI models using Matryoshka Representation Learning (MRL) for flexible embedding dimensions (64-768d).
What This Does
AI coding assistants work better when they can find relevant code quickly. Traditional keyword search falls short - if you ask "where do we handle authentication?" but your code uses "login" and "session", keyword search misses it.
This MCP server solves that by indexing your codebase with AI embeddings. Your AI assistant can search by meaning instead of exact keywords, finding relevant code even when the terminology differs.
Available Tools
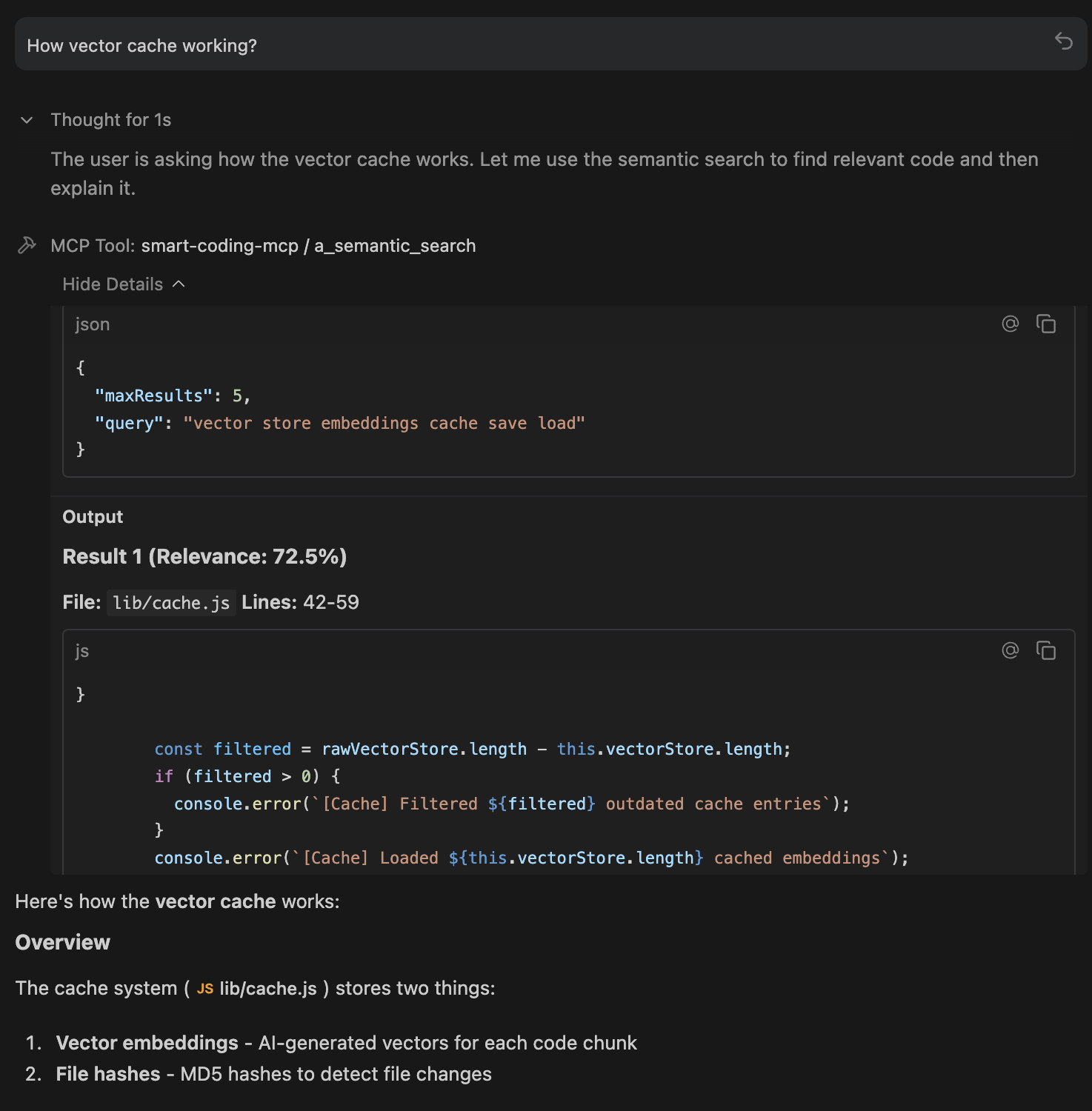
🔍 a_semantic_search - Find Code by Meaning
The primary tool for codebase exploration. Uses AI embeddings to understand what you're looking for, not just match keywords.
How it works: Converts your natural language query into a vector, then finds code chunks with similar meaning using cosine similarity + exact match boosting.
Best for:
Exploring unfamiliar codebases:
"How does authentication work?"Finding related code:
"Where do we validate user input?"Conceptual searches:
"error handling patterns"Works even with typos:
"embeding modle initializashun"still finds embedding code
Example queries:
📦 d_check_last_version - Package Version Lookup
Fetches the latest version of any package from its official registry. Supports 20+ ecosystems.
How it works: Queries official package registries (npm, PyPI, Crates.io, etc.) in real-time. No guessing, no stale training data.
Supported ecosystems: npm, PyPI, Crates.io, Maven, Go, RubyGems, NuGet, Packagist, Hex, pub.dev, Homebrew, Conda, and more.
Best for:
Before adding dependencies:
"express"→4.18.2Checking for updates:
"pip:requests"→2.31.0Multi-ecosystem projects:
"npm:react","go:github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
Example usage:
🔄 b_index_codebase - Manual Reindexing
Triggers a full reindex of your codebase. Normally not needed since indexing is automatic and incremental.
How it works: Scans all files, generates new embeddings, and updates the SQLite cache. Uses progressive indexing so you can search while it runs.
When to use:
After major refactoring or branch switches
After pulling large changes from remote
If search results seem stale or incomplete
After changing embedding configuration (dimension, model)
🗑️ c_clear_cache - Reset Everything
Deletes the embeddings cache entirely, forcing a complete reindex on next search.
How it works: Removes the .smart-coding-cache/ directory. Next search or index operation starts fresh.
When to use:
Cache corruption (rare, but possible)
Switching embedding models or dimensions
Starting fresh after major codebase restructure
Troubleshooting search issues
📂 e_set_workspace - Switch Projects
Changes the workspace path at runtime without restarting the server.
How it works: Updates the internal workspace reference, creates cache folder for new path, and optionally triggers reindexing.
When to use:
Working on multiple projects in one session
Monorepo navigation between packages
Switching between related repositories
ℹ️ f_get_status - Server Health Check
Returns comprehensive status information about the MCP server.
What it shows:
Server version and uptime
Workspace path and cache location
Indexing status (ready, indexing, percentage complete)
Files indexed and chunk count
Model configuration (name, dimension, device)
Cache size and type
When to use:
Start of session to verify everything is working
Debugging connection or indexing issues
Checking indexing progress on large codebases
Installation
To update:
IDE Integration
Detailed setup instructions for your preferred environment:
IDE / App | Setup Guide |
|
VS Code | ✅ Yes | |
Cursor | ✅ Yes | |
Windsurf | ❌ Absolute paths only | |
Claude Desktop | ❌ Absolute paths only | |
OpenCode | ❌ Absolute paths only | |
Raycast | ❌ Absolute paths only | |
Antigravity | ❌ Absolute paths only |
Quick Setup
Add to your MCP config file:
Config File Locations
IDE | OS | Path |
Claude Desktop | macOS |
|
Claude Desktop | Windows |
|
OpenCode | Global |
|
OpenCode | Project |
|
Windsurf | macOS |
|
Windsurf | Windows |
|
Multi-Project Setup
Environment Variables
Customize behavior via environment variables:
Variable | Default | Description |
|
| Enable detailed logging |
|
| Max search results returned |
|
| Files to process in parallel |
|
| Max file size in bytes (1MB) |
|
| Lines of code per chunk |
|
| MRL dimension (64, 128, 256, 512, 768) |
|
| AI embedding model |
|
| Inference device ( |
|
| Weight for semantic vs exact matching |
|
| Boost multiplier for exact text matches |
|
| Max CPU usage during indexing (10-100%) |
|
| Code chunking ( |
|
| Auto-reindex on file changes |
|
| Delay before background indexing (ms), |
Example with env vars:
Performance
Progressive Indexing - Search works immediately while indexing continues in the background. No waiting for large codebases.
Resource Throttling - CPU limited to 50% by default. Your machine stays responsive during indexing.
SQLite Cache - 5-10x faster than JSON. Automatic migration from older JSON caches.
Incremental Updates - Only changed files are re-indexed. Saves every 5 batches, so no data loss if interrupted.
Optimized Defaults - 128d embeddings (2x faster than 256d with minimal quality loss), smart batch sizing, parallel processing.
How It Works
Tech Stack
Component | Technology |
Protocol | Model Context Protocol (JSON-RPC) |
AI Model | nomic-embed-text-v1.5 (MRL) |
Inference | transformers.js + ONNX Runtime |
Chunking | Smart regex / Tree-sitter AST |
Search | Cosine similarity + exact match boost |
Cache | SQLite with WAL mode |
Privacy
Everything runs 100% locally:
AI model runs on your machine (no API calls)
Code never leaves your system
No telemetry or analytics
Cache stored in
.smart-coding-cache/
Research Background
This project builds on research from Cursor showing that semantic search improves AI coding agent performance by 12.5% on average. The key insight: AI assistants benefit more from relevant context than from large amounts of context.
License
MIT License - Copyright (c) 2025 Omar Haris
See LICENSE for full text.