The Daytona MCP Python Interpreter enables AI assistants to execute code in secure, ephemeral sandboxed workspaces. With this server, you can:
Execute Python code and shell commands
Upload and download files with smart size management
Clone Git repositories (with branch selection and LFS support)
Generate web preview URLs for running servers
Integrate with AI assistants like Claude for code execution
All operations occur in isolated environments that are automatically cleaned up after use.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Daytona MCP Python Interpreterrun a Python script to calculate the average of these numbers: [5, 10, 15, 20, 25]"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
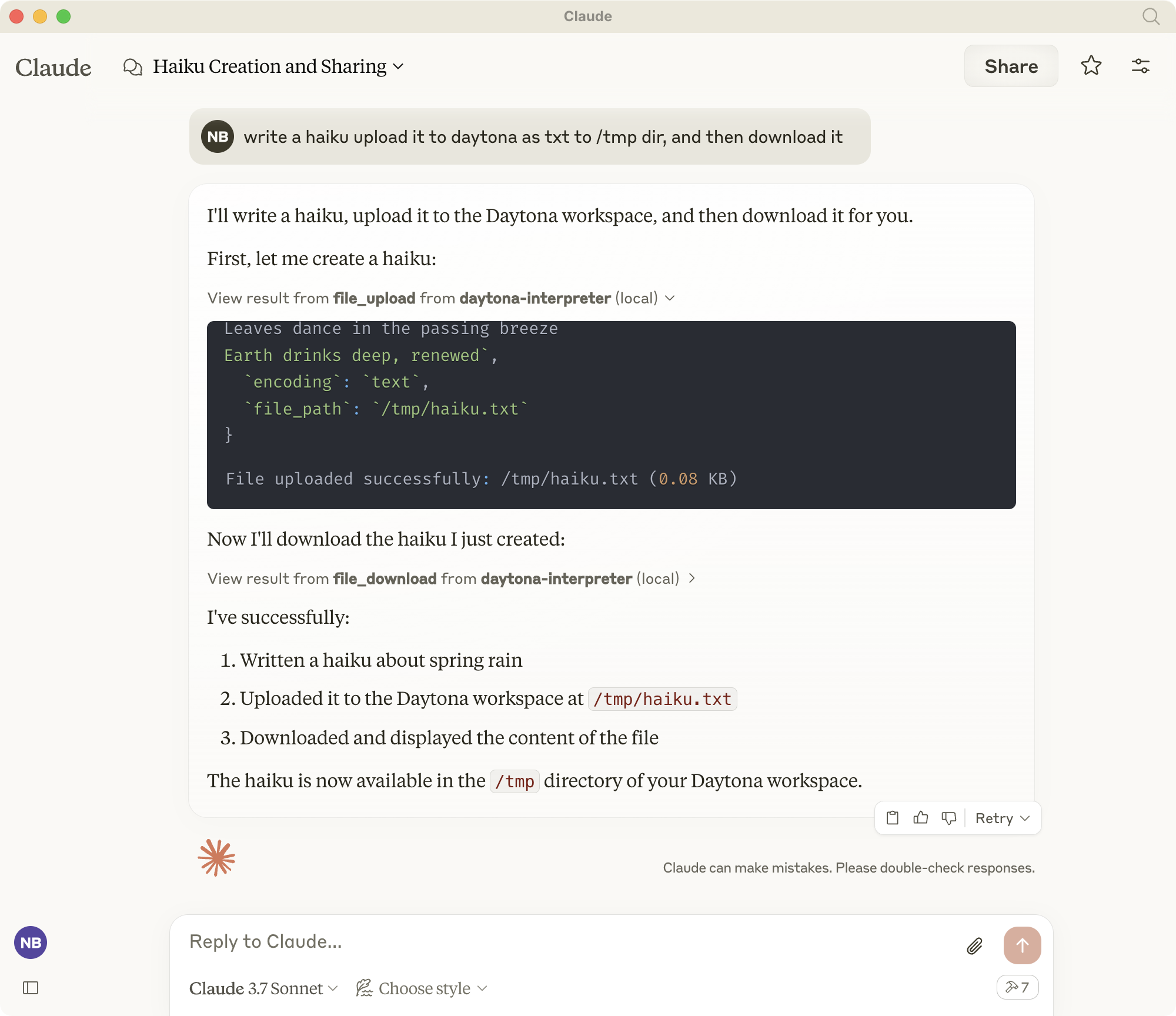
Daytona MCP Interpreter
A Model Context Protocol server that provides Python code execution capabilities in ephemeral Daytona sandboxes.
Overview
Daytona MCP Interpreter enables AI assistants like Claude to execute Python code and shell commands in secure, isolated environments. It implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP) standard to provide tools for:
Python code execution in sandboxed environments
Shell command execution
File management (upload/download)
Git repository cloning
Web preview generation for running servers
All execution happens in ephemeral Daytona workspaces that are automatically cleaned up after use.
Related MCP server: MCP Python Toolbox
Installation
Install uv if you haven't already:
Create and activate virtual environment.
If you have an existing env, deactivate and remove it first:
Create and activate a new virtual environment:
(On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate)
Install dependencies:
Note: This project requires daytona-sdk version 0.10.5 or higher. Earlier versions have incompatible FileSystem API.
Environment Variables
Configure these environment variables for proper operation:
MCP_DAYTONA_API_KEY: Required API key for Daytona authenticationMCP_DAYTONA_SERVER_URL: Server URL (default: https://app.daytona.io/api)MCP_DAYTONA_TIMEOUT: Request timeout in seconds (default: 180.0)MCP_DAYTONA_TARGET: Target region (default: eu)MCP_VERIFY_SSL: Enable SSL verification (default: false)
Development
Run the server directly:
Or if uv is not in your path:
Use MCP Inspector to test the server:
View logs:
Integration with Claude Desktop

Configure in Claude Desktop (or other MCP-compatible clients):
On MacOS, edit: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
On Windows, edit: %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
Restart Claude Desktop
The Daytona Python interpreter tools will be available in Claude
Available Tools
Shell Exec
Executes shell commands in the Daytona workspace.
File Download
Downloads files from the Daytona workspace with smart handling for large files.
Basic Usage:
Advanced Usage:
File Upload
Uploads files to the Daytona workspace. Supports both text and binary files.
Basic Usage:
Advanced Usage:
Git Clone
Clones a Git repository into the Daytona workspace for analysis and code execution.
Basic Usage:
Advanced Usage:
Web Preview
Generates a preview URL for web servers running inside the Daytona workspace.
Basic Usage:
Advanced Usage:
Example: