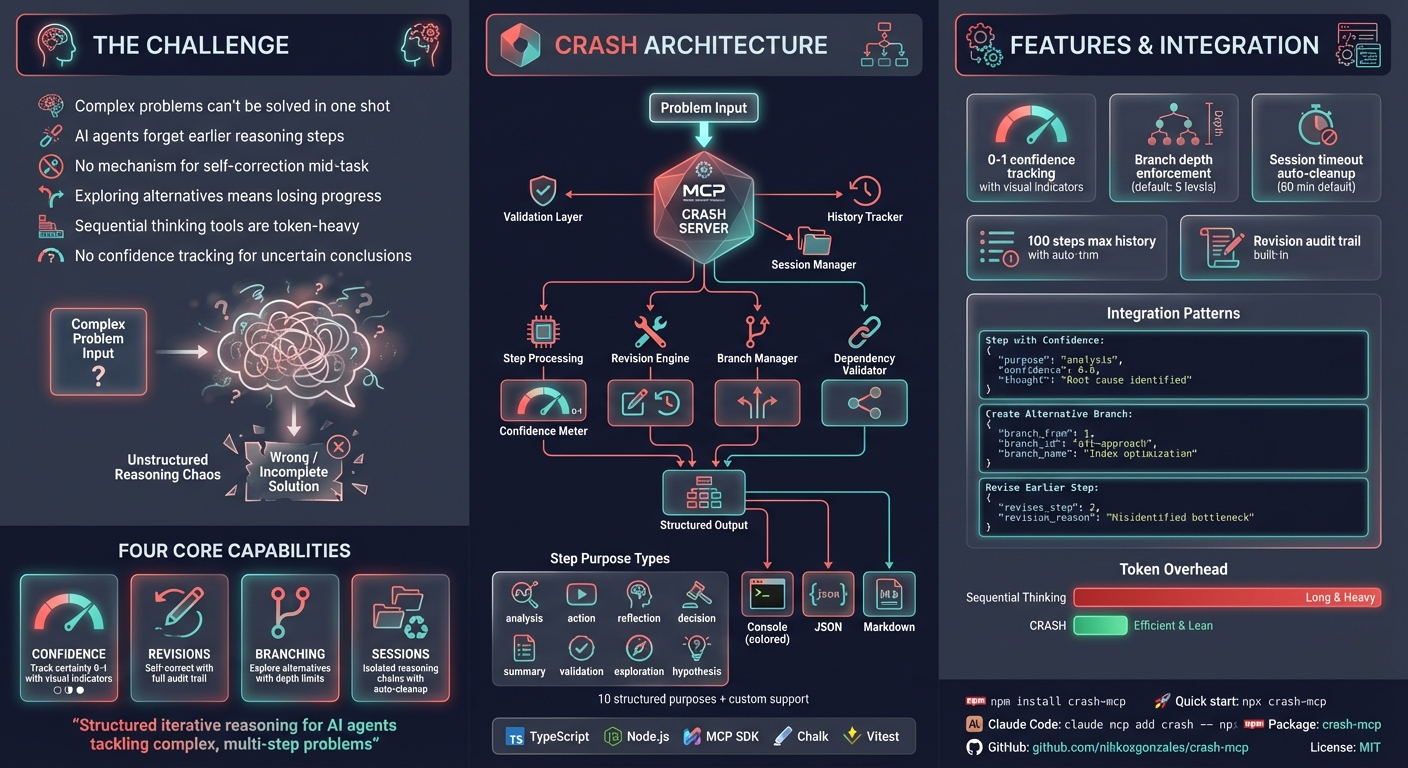
The CRASH server enables structured, iterative reasoning for complex problem-solving and analysis by breaking down tasks into sequential steps with defined purposes (analysis, action, validation, planning, etc.). Key capabilities include:
• Confidence tracking with 0-1 scale uncertainty measurement and doubt documentation • Revision mechanism to correct and improve previous steps with documented rationale • Branching support for exploring multiple solution paths concurrently using unique IDs • Tool integration with structured actions, parameters, and expected outputs • Session management for handling multiple concurrent reasoning chains • Flexible output formats (console, JSON, Markdown) with configurable settings • Context awareness to track completed steps and avoid redundancy • Custom purposes beyond standard step types for extended functionality
Ideal for code analysis, system design, debugging, research, decision-making, and comprehensive solution exploration.
Provides Markdown output formatting for human-readable documentation of reasoning processes and analysis workflows
Distributed as an npm package for easy installation and integration into Node.js-based MCP server environments
Built with TypeScript for type-safe development and enhanced tooling support in the reasoning server implementation
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@CRASH - Cascaded Reasoning with Adaptive Step Handlinganalyze why our API response times are slow and propose solutions"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
CRASH
Cascaded Reasoning with Adaptive Step Handling
An MCP (Model Context Protocol) server for structured, iterative reasoning. CRASH helps AI assistants break down complex problems into trackable steps with confidence tracking, revision support, and branching for exploring alternatives.
Inspired by MCP Sequential Thinking Server
Related MCP server: Sequential Thinking MCP Server
Why CRASH?
I created this because typing "use sequential_thinking" was cumbersome. Now I can simply say "use crash" instead.
CRASH is more token-efficient than sequential thinking - it doesn't include code in thoughts and has streamlined prompting. It's my go-to solution when an agent can't solve an issue in one shot or when plan mode falls short.
Claude Code's Assessment
CRASH helped significantly for this specific task:
Where CRASH helped:
- Systematic analysis: Forced me to break down the issue methodically
- Solution exploration: Explored multiple approaches before settling on the best one
- Planning validation: Each step built on the previous one logically
The key difference:
CRASH forced me to be more thorough in the analysis phase. Without it, I might have
rushed to implement the first solution rather than exploring cleaner approaches.
Verdict: CRASH adds value for complex problems requiring systematic analysis of
multiple solution paths. For simpler tasks, internal planning is sufficient and faster.Features
Structured reasoning steps - Track thought process, outcomes, and next actions
Confidence tracking - Express uncertainty with 0-1 scores, get warnings on low confidence
Revision mechanism - Correct previous steps, with original steps marked as revised
Branching support - Explore multiple solution paths with depth limits
Dependency validation - Declare and validate step dependencies
Session management - Group related reasoning chains with automatic timeout cleanup
Multiple output formats - Console (colored), JSON, or Markdown
Flexible validation - Strict mode for rigid rules, flexible mode for natural language
Installation
npm install crash-mcpOr use directly with npx:
npx crash-mcpQuick Setup
Most MCP clients use this JSON configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"crash": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "crash-mcp"]
}
}
}Configuration by Client
Client | Setup Method |
Claude Code |
|
Cursor | Add to |
VS Code | Add to settings JSON under |
Claude Desktop | Add to |
Windsurf | Add to MCP config file |
JetBrains | Settings > Tools > AI Assistant > MCP |
Others | Use standard MCP JSON config above |
Use the cmd wrapper:
{
"mcpServers": {
"crash": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": ["/c", "npx", "-y", "crash-mcp"]
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"crash": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "crash-mcp"],
"env": {
"CRASH_STRICT_MODE": "false",
"MAX_HISTORY_SIZE": "100",
"CRASH_OUTPUT_FORMAT": "console",
"CRASH_SESSION_TIMEOUT": "60",
"CRASH_MAX_BRANCH_DEPTH": "5"
}
}
}
}FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /app
RUN npm install -g crash-mcp
CMD ["crash-mcp"]{
"mcpServers": {
"crash": {
"command": "docker",
"args": ["run", "-i", "--rm", "crash-mcp"]
}
}
}Bun:
{ "command": "bunx", "args": ["-y", "crash-mcp"] }Deno:
{
"command": "deno",
"args": ["run", "--allow-env", "--allow-net", "npm:crash-mcp"]
}Configuration
Variable | Default | Description |
|
| Enable strict validation (requires specific prefixes) |
|
| Maximum steps to retain in history |
|
| Output format: |
|
| Disable colored console output |
|
| Session timeout in minutes |
|
| Maximum branch nesting depth |
|
| Enable session management |
Usage
Required Parameters
Parameter | Type | Description |
| integer | Sequential step number (starts at 1) |
| integer | Estimated total steps (adjustable) |
| string | Step category: analysis, action, validation, exploration, hypothesis, correction, planning, or custom |
| string | What's already known to avoid redundancy |
| string | Current reasoning process |
| string | Expected or actual result |
| string/object | Next action (simple string or structured with tool details) |
| string | Why this next action was chosen |
Optional Parameters
Parameter | Type | Description |
| boolean | Mark as final step to complete reasoning |
| number | Confidence level 0-1 (warnings below 0.5) |
| string | Describe doubts or assumptions |
| integer | Step number being corrected |
| string | Why revision is needed |
| integer | Step to branch from |
| string | Unique branch identifier |
| string | Human-readable branch name |
| integer[] | Step numbers this depends on |
| string | Group related reasoning chains |
| string[] | Tools used in this step |
| object | External data relevant to step |
Examples
Basic Usage
{
"step_number": 1,
"estimated_total": 3,
"purpose": "analysis",
"context": "User requested optimization of database queries",
"thought": "I need to first understand the current query patterns before proposing changes",
"outcome": "Identified slow queries for optimization",
"next_action": "analyze query execution plans",
"rationale": "Understanding execution plans will reveal bottlenecks"
}With Confidence and Final Step
{
"step_number": 3,
"estimated_total": 3,
"purpose": "summary",
"context": "Analyzed queries and tested index optimizations",
"thought": "The index on user_id reduced query time from 2s to 50ms",
"outcome": "Performance issue resolved with new index",
"next_action": "document the change",
"rationale": "Team should know about the optimization",
"confidence": 0.9,
"is_final_step": true
}Revision Example
{
"step_number": 4,
"estimated_total": 5,
"purpose": "correction",
"context": "Previous analysis missed a critical join condition",
"thought": "The join was causing a cartesian product, not the index",
"outcome": "Corrected root cause identification",
"next_action": "fix the join condition",
"rationale": "This is the actual performance issue",
"revises_step": 2,
"revision_reason": "Overlooked critical join in initial analysis"
}Branching Example
{
"step_number": 3,
"estimated_total": 6,
"purpose": "exploration",
"context": "Two optimization approaches identified",
"thought": "Exploring the indexing approach first as it's lower risk",
"outcome": "Branch created for index optimization testing",
"next_action": "test index performance",
"rationale": "This approach has lower risk than query rewrite",
"branch_from": 2,
"branch_id": "index-optimization",
"branch_name": "Index-based optimization"
}When to Use CRASH
Good fit:
Complex multi-step problem solving
Code analysis and optimization
System design with multiple considerations
Debugging requiring systematic investigation
Exploring multiple solution paths
Tasks where you need to track confidence
Not needed:
Simple, single-step tasks
Pure information retrieval
Deterministic procedures with no uncertainty
Development
npm install # Install dependencies
npm run build # Build TypeScript
npm run dev # Run with MCP inspector
npm start # Start built serverTroubleshooting
Try using bunx instead of npx:
{ "command": "bunx", "args": ["-y", "crash-mcp"] }Try the experimental VM modules flag:
{ "args": ["-y", "--node-options=--experimental-vm-modules", "crash-mcp"] }Credits
MCP Sequential Thinking Server - Primary inspiration
Author
Nikko Gonzales - nikkoxgonzales
License
MIT
Appeared in Searches
- MCP servers for curated context in Cursor IDE to plan, debug, and iterate on features
- Interaction or Feedback Enhancement to Increase Frequency/Attempts
- AWS DevOps automation tool with documentation retrieval and configuration analysis
- A server for finding information about sequential thinking
- Slow thinking, distributed thinking, and reasoning abilities research