Integrates with Git workflows to automatically capture and store memories during events like commits, tracking bug fixes, architecture decisions, and version releases.
Supports integration with JetBrains IDEs via MCP-compliant extensions to provide persistent memory capabilities directly within the developer's workspace.
Offers support for Neo4j as a graph database backend, enabling the storage and retrieval of complex relational paths and temporal markers.
Uses SQLite as a default, zero-configuration backend for lightweight and local persistent storage of memory nodes and relationships.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@MemoryGraphRecall the solution for the React hydration error from our last session."
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Quick Start
Claude Code CLI (30 seconds)
Verify it works:
Then in your coding agent you can ask it to remember important items: "Remember this for later: Use pytest for Python testing"
Other MCP clients? See Supported Clients below.
Need pipx?
pip install --user pipx && pipx ensurepathCommand not found? Run
pipx ensurepathand restart your terminal.
Important: MemoryGraph provides memory tools, but your coding agent won't use them automatically. You need to prompt or configure it to store memories. See Memory Best Practices below.
Quick setup: Add this to your ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md or AGENTS.md to enable automatic memory storage:
See CLAUDE.md Examples for more configuration templates.
Supported MCP Clients
MemoryGraph works with any MCP-compliant AI coding tool:
Client | Type | Quick Start |
Claude Code | CLI/IDE | |
Claude Desktop | Desktop App | |
ChatGPT Desktop | Desktop App | |
Cursor AI | IDE | |
Windsurf | IDE | |
VS Code + Copilot | IDE (1.102+) | |
Continue.dev | VS Code/JetBrains | |
Cline | VS Code | |
Gemini CLI | CLI |
See CONFIGURATION.md for detailed compatibility info.
Why MemoryGraph?
Graph Relationships Make the Difference
Research shows that naive vector search degrades on long-horizon and temporal tasks. Benchmarks such as Deep Memory Retrieval (DMR) and LongMemEval were introduced precisely because graph-based systems excel at temporal queries ("what did the user decide last week"), cross-session reasoning, and multi-hop questions requiring explicit relational paths.
Graph memory captures entities, relationships, and temporal markers that traditional vector stores miss. For example: Alice COMPLETED authentication_service, Bob BLOCKED_BY schema_conflicts with timeline information about when events occurred.
Flat storage (CLAUDE.md, vector stores):
No connection between these - search finds them separately. Best for static rules and prime directives.
Graph storage (MemoryGraph):
Query: "What happened with retry logic?" → Returns the full causal chain.
When to Use What
Use CLAUDE.md For | Use MemoryGraph For |
"Always use 2-space indentation" | "Last time we used 4-space, it broke the linter" |
"Run tests before committing" | "The auth tests failed because of X, fixed by Y" |
Static rules, prime directives | Dynamic learnings with relationships |
Relationship Types
MemoryGraph tracks 7 categories of relationships:
Causal: CAUSES, TRIGGERS, LEADS_TO, PREVENTS
Solution: SOLVES, ADDRESSES, ALTERNATIVE_TO, IMPROVES
Context: OCCURS_IN, APPLIES_TO, WORKS_WITH, REQUIRES
Learning: BUILDS_ON, CONTRADICTS, CONFIRMS
Similarity: SIMILAR_TO, VARIANT_OF, RELATED_TO
Workflow: FOLLOWS, DEPENDS_ON, ENABLES, BLOCKS
Quality: EFFECTIVE_FOR, PREFERRED_OVER, DEPRECATED_BY
Choose Your Mode
Feature | Core (Default) | Extended |
Memory Storage | 9 tools | 12 tools |
Relationships | Yes | Yes |
Session Briefings | Yes | Yes |
Database Stats | - | Yes |
Complex Queries | - | Yes |
Contextual Search | - | Yes |
Backend | SQLite | SQLite |
Setup Time | 30 sec | 30 sec |
Core Mode (Default)
Provides all essential tools for daily use. Store memories, create relationships, search with fuzzy matching, and get session briefings. This is all most users need.
When to Use Extended Mode
Switch to extended mode when you need:
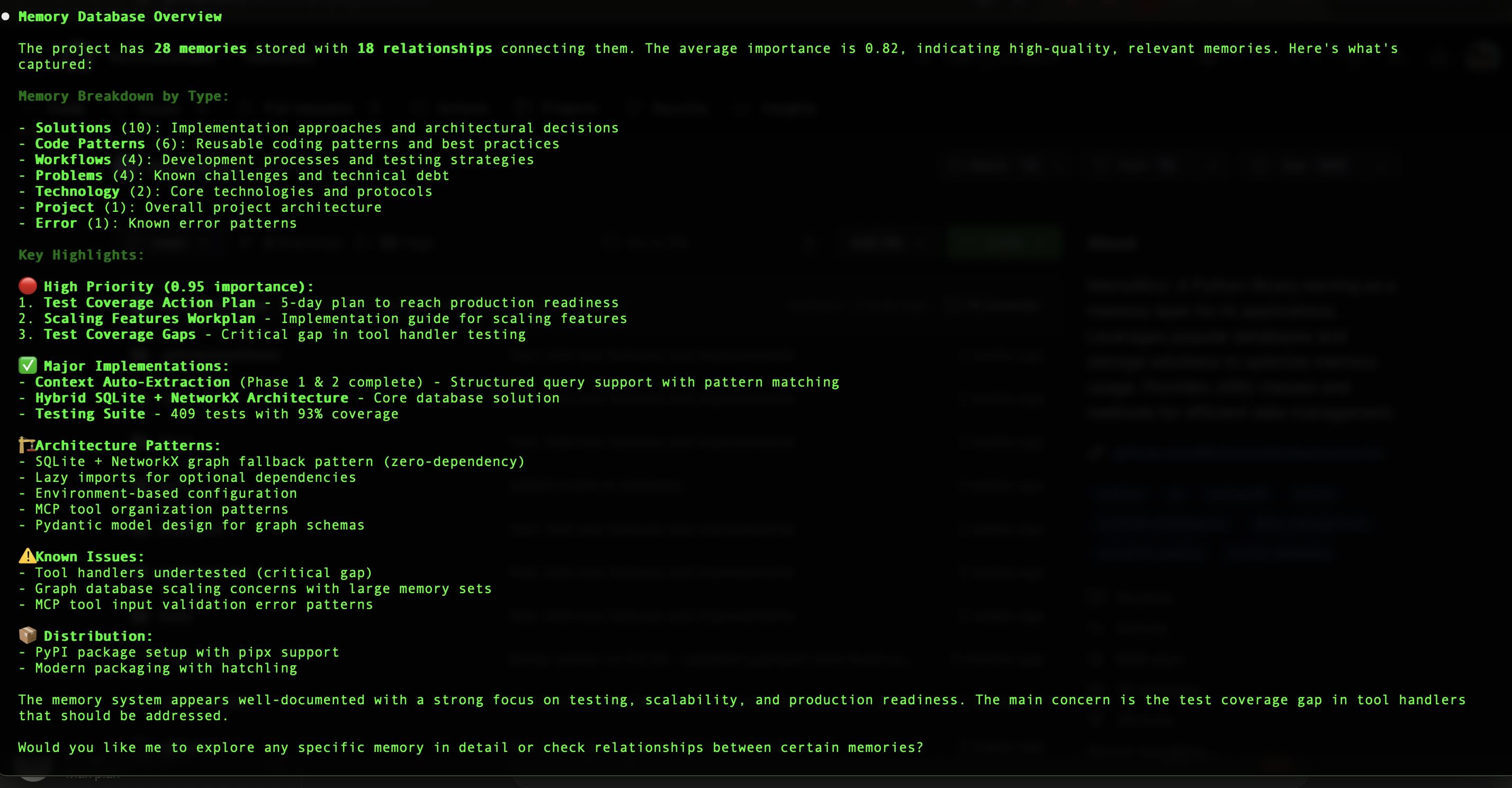
Database statistics (
get_memory_statistics) - See total memories, breakdown by type, average importance scores, and graph metrics. Useful for understanding how your knowledge base is growing.Complex relationship queries (
search_relationships_by_context) - Search relationships by structured context fields like scope, conditions, and evidence. Example: "Find all partial implementations" or "Show relationships with experimental evidence."
Common extended mode scenarios:
Auditing your memory graph before a major refactor
Analyzing patterns across hundreds of memories
Finding all conditionally-applied solutions
Generating reports on project knowledge coverage
See TOOL_PROFILES.md for complete tool list and details.
Installation Options
pipx (Recommended)
pip
Docker
uvx (Quick Test)
Method | Best For | Persistence |
pipx | Most users | Yes |
pip | PATH already configured | Yes |
Docker | Teams, production | Yes |
uvx | Quick testing | No |
See CONFIGURATION.md for detailed options.
Claude Code Web Support
MemoryGraph works in Claude Code Web (remote) environments via project hooks.
Quick Setup
Copy the hook files to your project:
When you open this project in Claude Code Web, MemoryGraph installs automatically.
Persistent Storage (Optional)
Remote environments are ephemeral. For persistent memories, configure cloud storage in your Claude Code Web environment variables:
Variable | Description |
| API key from memorygraph.dev (coming soon) |
| Your Turso database URL |
| Your Turso auth token |
See Claude Code Web Setup for detailed instructions.
Configuration
Claude Code CLI
Get your API key: Sign up at memorygraph.dev to get your free API key.
Other MCP Clients
See CONFIGURATION.md for all options.
Recommended: Add to CLAUDE.md
For best results, add this to your CLAUDE.md or project instructions:
This helps Claude use the optimal tool for memory recall.
Usage
Store Memories
Recall Memories (Recommended)
Returns fuzzy-matched results with relationship context and match quality hints.
Search Memories (Advanced)
Use when you need exact matching or advanced filtering.
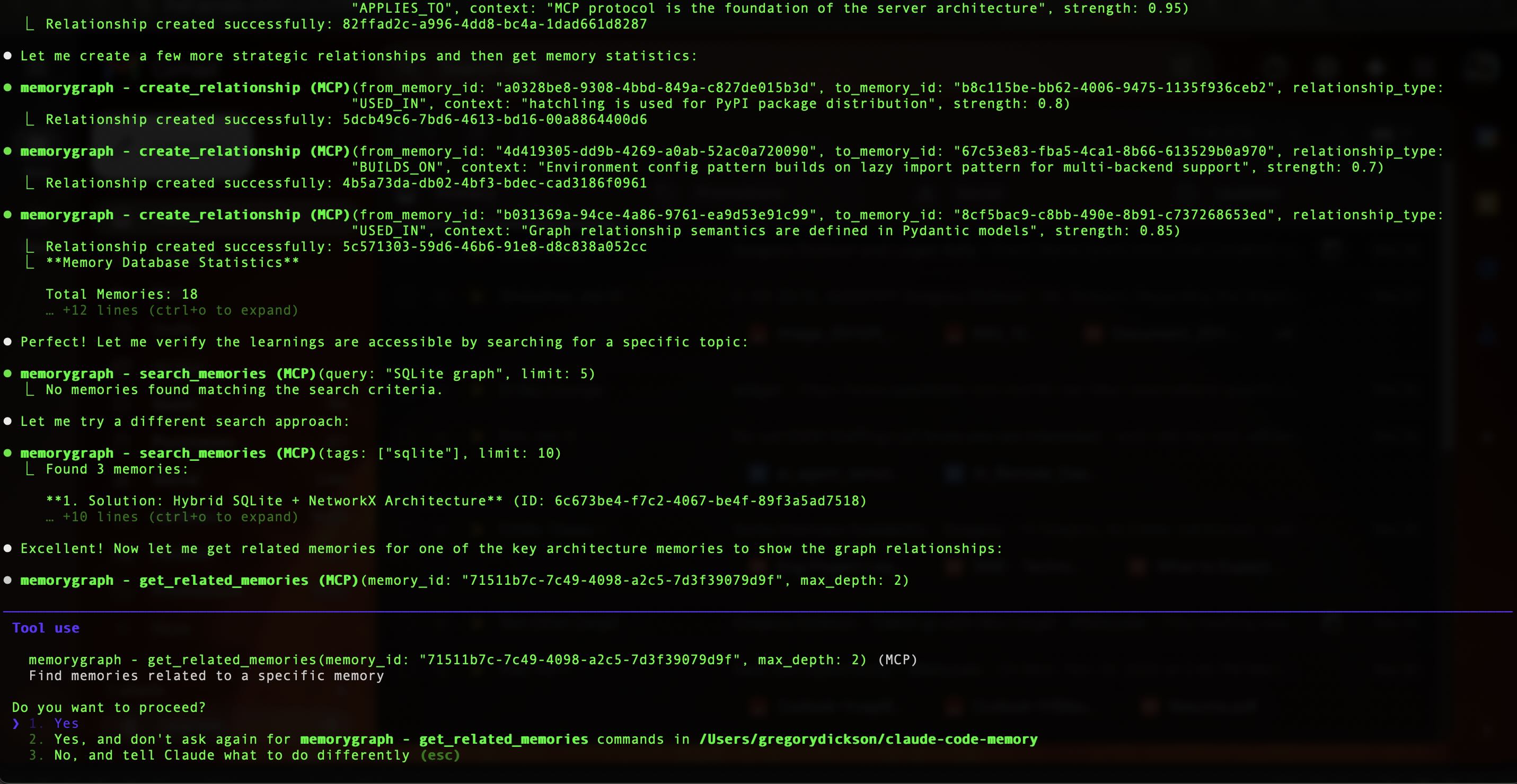
Create Relationships
See docs/examples/ for more use cases.
Memory Best Practices
Why Memories Aren't Automatic
MemoryGraph is an MCP tool provider, not an autonomous agent. This means:
Claude needs to be prompted to use the memory tools
You control what gets stored - nothing is saved without explicit instruction
Configuration is key - Add memory protocols to your CLAUDE.md for consistent behavior
This design gives you full control over your memory graph, but requires setup to work effectively.
How to Encourage Memory Creation
1. Configure CLAUDE.md (Recommended)
Add a memory protocol to ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md for persistent behavior across all sessions:
2. Use Trigger Phrases
Claude responds well to explicit memory-related requests:
For storing:
"Store this for later..."
"Remember that..."
"Save this pattern..."
"Record this decision..."
"Create a memory about..."
For recalling:
"What do you remember about...?"
"Have we solved this before?"
"Recall any patterns for..."
"What did we decide about...?"
For session management:
"Summarize and store what we accomplished today"
"Store a summary of this session"
"Catch me up on this project" (uses stored memories)
3. Establish Workflow Habits
Start of session:
During work:
End of session:
4. Project-Specific Configuration
For team projects or specific repositories, add .claude/CLAUDE.md to the project:
Memory Types Guide
Choose the right type for better organization:
Type | Use For | Example |
solution | Working fixes and implementations | "Fixed N+1 query with eager loading" |
problem | Issues encountered | "Database deadlock under high concurrency" |
code_pattern | Reusable patterns | "Repository pattern for database access" |
decision | Architecture choices | "Chose PostgreSQL over MongoDB for transactions" |
task | Work completed | "Implemented user authentication" |
technology | Tool/framework knowledge | "FastAPI dependency injection best practices" |
error | Specific errors | "ImportError: module not found" |
fix | Error resolutions | "Added missing import statement" |
Relationship Types Guide
Common relationship patterns:
Example Workflows
Debugging workflow:
Feature development workflow:
Optimization workflow:
More Examples and Templates
For comprehensive CLAUDE.md configuration examples including:
Domain-specific setups (web dev, ML, DevOps)
Team collaboration protocols
Migration strategies from other systems
See: CLAUDE.md Configuration Examples
Backends
MemoryGraph supports 8 backend options to fit your deployment needs:
Backend | Type | Config | Native Graph | Zero-Config | Best For |
sqlite | Embedded | File path | No (simulated) | ✅ | Default, simple use |
falkordblite | Embedded | File path | ✅ Cypher | ✅ | Graph queries without server |
ladybugdb | Embedded | File path | ✅ Cypher | ✅ | Graph queries without server |
falkordb | Client-server | Host:port | ✅ Cypher | ❌ | High-performance production |
neo4j | Client-server | URI | ✅ Cypher | ❌ | Enterprise features |
memgraph | Client-server | Host:port | ✅ Cypher | ❌ | Real-time analytics |
turso | Cloud | URL + Token | No (simulated) | ❌ | Distributed SQLite, edge deployments |
cloud | Cloud | API Key | ✅ Cypher | ❌ | MemoryGraph Cloud (production ready) |
New: FalkorDB Options
FalkorDBLite: Zero-config embedded database with native Cypher support, perfect upgrade from SQLite
LadybugDB: Leading columnar embedded graph database with Cypher support
FalkorDB: Redis-based graph DB with 500x faster p99 than Neo4j (docs)
New: Cloud Backend
Multi-device sync: Access your memories from anywhere
Team collaboration: Share memories with your team
Automatic backups: Never lose your knowledge graph
Zero maintenance: No database setup required
See CONFIGURATION.md for setup details and Cloud Backend Guide for cloud-specific configuration.
Multi-Tenancy (v0.10.0+)
MemoryGraph now supports optional multi-tenancy for team memory sharing and organizational deployments. Phase 1 provides the foundational schema with 100% backward compatibility.
Key Features:
Optional: Disabled by default, zero impact on existing single-tenant deployments
Tenant Isolation: Scope memories to specific organizations/teams
Visibility Levels: Control access with
private,project,team, orpublicvisibilityMigration Support: Migrate existing databases with built-in CLI command
Performance Optimized: Conditional indexes only created when multi-tenant mode is enabled
Quick Start:
Use Cases:
Team collaboration and shared memory
Multi-team organizations
Department-specific knowledge bases
Enterprise deployments
See MULTI_TENANCY.md for complete guide including architecture, migration steps, and usage patterns.
Roadmap:
✅ Phase 1 (v0.10.0): Schema enhancement with optional tenant fields
Phase 2 (v0.11.0): Query filtering and visibility enforcement
Phase 3 (v1.0.0): Authentication integration (JWT, OAuth2)
Phase 4 (v1.1.0): Advanced RBAC and audit logging
Architecture
Memory Types
Task - Development tasks and patterns
CodePattern - Reusable solutions
Problem - Issues encountered
Solution - How problems were resolved
Project - Codebase context
Technology - Framework/tool knowledge
Project Structure
See schema.md for complete data model.
Troubleshooting
Command not found?
MCP connection failed?
Multiple version conflict?
See TROUBLESHOOTING.md for more solutions.
Development
What's New in v0.11.0
Python SDK for Agent Frameworks
NEW: memorygraphsdk - Native integrations for popular AI frameworks!
Framework | Integration | Description |
LlamaIndex |
| Chat memory + RAG retrieval |
LangChain |
| BaseMemory with session support |
CrewAI |
| Multi-agent persistent memory |
AutoGen |
| Conversation history |
See SDK Documentation for full integration guides.
What's New in v0.10.0
Context Budget Optimization (60-70% token savings)
Leaner tool profiles - Removed 29 unimplemented tools, keeping only production-ready features
9 core tools / 12 extended - Focused toolset that fits in any context window
~40k tokens saved - More room for your actual work
ADR-017 - Context budget as architectural constraint (docs/adr/017-context-budget-constraint.md)
Cloud Backend (Production Ready)
Multi-device sync - Access memories from anywhere
Circuit breaker pattern - Resilient to network failures with automatic recovery
Zero setup - Just add your API key from memorygraph.dev
Team collaboration ready - Share knowledge graphs with your team
Bi-Temporal Memory Tracking
Time-travel queries - Query what was known at any point in time
Knowledge evolution - Track how solutions and understanding changed
Four temporal fields -
valid_from,valid_until,recorded_at,invalidated_byMigration support - Upgrade existing databases with
migrate_to_bitemporal()Inspired by Graphiti - Learned from Zep AI's proven temporal model
Semantic Navigation
Contextual search - LLM-powered graph traversal without embeddings
Graph-first approach - Validated by Cipher's shift away from vector search
Scoped queries - Search within related memory contexts
See temporal-memory.md for comprehensive temporal tracking guide and CLOUD_BACKEND.md for cloud setup.
What's New in v0.9.5
Cloud Backend & Turso Support
MemoryGraph Cloud - REST API client with circuit breaker for resilience (coming soon)
Turso Backend - Distributed SQLite with embedded replica support for edge deployments
8 total backends - sqlite, neo4j, memgraph, falkordb, falkordblite, ladybugdb, turso, cloud
Backend Migration
memorygraph migrate- Migrate data between any two backends5-phase validation - Pre-flight checks, export, validate, import, verify
Dry-run mode - Test migrations without writing data
Rollback support - Automatic cleanup on failure
Universal Export/Import
Works with ALL backends - Export from any backend, import to any backend
Progress reporting - Track long-running operations
Format v2.0 - Enhanced metadata with backend info and counts
Architecture Improvements
Circuit breaker - Prevents cascading failures in cloud backend
Thread-safe backend creation - Safe for concurrent migrations
Async correctness - All Turso operations properly non-blocking
What's New in v0.9.0
Pagination & Cycle Detection
Result pagination for large datasets with
limitandoffsetparametersCycle detection prevents circular relationships by default
Health Check CLI
Quick diagnostics with
memorygraph --healthJSON output with
--health-jsonfor scripting
Roadmap
Current (v0.11.0) ✅
Python SDK -
memorygraphsdkwith LlamaIndex, LangChain, CrewAI, AutoGen integrationsCloud Backend - Multi-device sync via memorygraph.dev
Bi-temporal tracking - Track knowledge evolution over time
Semantic navigation - LLM-powered contextual search
8 backend options (SQLite, Neo4j, Memgraph, FalkorDB, FalkorDBLite, LadybugDB, Turso, Cloud)
1,200+ tests passing
Two PyPI packages:
memorygraphMCP+memorygraphsdk
Planned (v1.0+)
Real-time team sync
Multi-tenancy features
Enhanced SDK documentation
See PRODUCT_ROADMAP.md for details.
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
License
MIT License - see LICENSE.
Links
Made for the Claude Code community
Start simple. Upgrade when needed. Never lose context again.