The Elasticsearch MCP Server enables natural language interaction with Elasticsearch clusters through MCP Clients, providing these capabilities:
Cluster Management: Check cluster health status with optional index-level details
Index Operations: List indices (with regex filtering), create indices with custom settings/mappings, and reindex data between indices
Mapping Management: Retrieve, create, or update field mappings for specific indices
Search & Data Operations: Perform searches using Elasticsearch Query DSL and bulk import data into indices
Template Management: Create, retrieve, or delete index templates, with support for versioning and priority
Connects to Elasticsearch clusters allowing interaction with indices through natural language, including listing indices, retrieving mappings, performing searches, managing index templates, bulk operations, reindexing data, and monitoring cluster health.
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@Elasticsearch MCP Servershow me the health status of my Elasticsearch cluster"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
Elasticsearch MCP Server
MCP Server for connecting to your Elasticsearch cluster directly from any MCP Client (like Claude Desktop, Cursor).
This server connects agents to your Elasticsearch data using the Model Context Protocol. It allows you to interact with your Elasticsearch indices through natural language conversations.
Demo
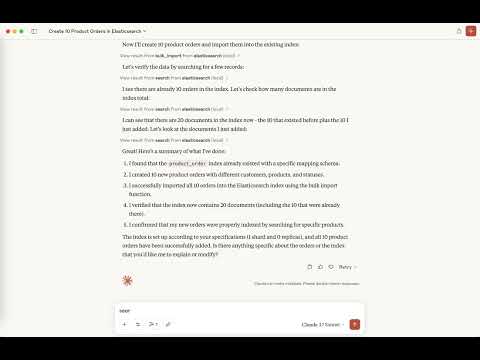
Related MCP server: Elasticsearch MCP Server
Feature Overview
Available Features
Cluster Management
elasticsearch_health: Get Elasticsearch cluster health status, optionally including index-level details
Index Operations
list_indices: List available Elasticsearch indices, support regexcreate_index: Create Elasticsearch index with optional settings and mappingsreindex: Reindex data from a source index to a target index with optional query and script
Mapping Management
get_mappings: Get field mappings for a specific Elasticsearch indexcreate_mapping: Create or update mapping structure for an Elasticsearch index
Search & Data Operations
search: Perform an Elasticsearch search with the provided query DSLbulk: Bulk data into an Elasticsearch index
Template Management
create_index_template: Create or update an index templateget_index_template: Get information about index templatesdelete_index_template: Delete an index template
How It Works
The MCP Client analyzes your request and determines which Elasticsearch operations are needed.
The MCP server carries out these operations (listing indices, fetching mappings, performing searches).
The MCP Client processes the results and presents them in a user-friendly format.
Getting Started
Prerequisites
An Elasticsearch instance
Elasticsearch authentication credentials (API key or username/password)
MCP Client (e.g. Claude Desktop, Cursor)
Installation & Setup
Using the Published NPM Package
The easiest way to use Elasticsearch MCP Server is through the published npm package.
Configure MCP Client
Open your MCP Client. See the list of MCP Clients, here we are configuring Claude Desktop.
Go to Settings > Developer > MCP Servers
Click
Edit Configand add a new MCP Server with the following configuration:
{ "mcpServers": { "elasticsearch-mcp": { "command": "npx", "args": [ "-y", "@awesome-ai/elasticsearch-mcp" ], "env": { "ES_HOST": "your-elasticsearch-host", "ES_API_KEY": "your-api-key" } } } }Start a Conversation
Open a new conversation in your MCP Client.
The MCP server should connect automatically.
You can now ask questions about your Elasticsearch data.
Configuration Options
The Elasticsearch MCP Server supports configuration options to connect to your Elasticsearch:
You must provide either an API key or both username and password for authentication.
Environment Variable | Description | Required |
| Your Elasticsearch instance URL(s) - supports single URL or comma-separated multiple URLs (also supports legacy | Yes |
| Elasticsearch API key for authentication (also supports legacy | No |
| Elasticsearch username for basic authentication (also supports legacy | No |
| Elasticsearch password for basic authentication (also supports legacy | No |
| Path to custom CA certificate for Elasticsearch SSL/TLS (also supports legacy | No |
Multiple URLs Configuration
You can configure multiple Elasticsearch nodes for high availability and load balancing:
{
"mcpServers": {
"elasticsearch-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@awesome-ai/elasticsearch-mcp"
],
"env": {
"ES_HOST": "https://es-node1:9200,https://es-node2:9200,https://es-node3:9200",
"ES_API_KEY": "your-api-key"
}
}
}
}The client will automatically handle failover and load balancing between the configured nodes.
Local Development
If you want to modify or extend the MCP Server, follow these local development steps.
Use the correct Node.js version
nvm useInstall Dependencies
npm installBuild the Project
npm run buildRun locally in Claude Desktop App
Open Claude Desktop App
Go to Settings > Developer > MCP Servers
Click
Edit Configand add a new MCP Server with the following configuration:
{ "mcpServers": { "elasticsearch-mcp": { "command": "node", "args": [ "/path/to/your/project/dist/index.js" ], "env": { "ES_HOST": "your-elasticsearch-host", "ES_API_KEY": "your-api-key" } } } }Run locally in Cursor Editor
Open Cursor Editor
Go to Cursor Settings > MCP
Click
Add new global MCP Serverand add a new MCP Server with the following configuration:
{ "mcpServers": { "elasticsearch-mcp": { "command": "node", "args": [ "/path/to/your/project/dist/index.js" ], "env": { "ES_HOST": "your-elasticsearch-host", "ES_API_KEY": "your-api-key" } } } }Debugging with MCP Inspector
ES_HOST=your-elasticsearch-url ES_API_KEY=your-api-key npm run inspectorThis will start the MCP Inspector, allowing you to debug and analyze requests. You should see:
Starting MCP inspector... ⚙️ Proxy server listening on port 6277 🔍 MCP Inspector is up and running at http://127.0.0.1:6274 🚀
Example Queries
Here are some natural language queries you can try with your MCP Client.
Cluster Management
"What is the health status of my Elasticsearch cluster?"
"How many active nodes are in my cluster?"
Index Operations
"What indices do I have in my Elasticsearch cluster?"
"Create a new index called 'users' with 3 shards and 1 replica."
"Reindex data from 'old_index' to 'new_index'."
Mapping Management
"Show me the field mappings for the 'products' index."
"Add a keyword type field called 'tags' to the 'products' index."
Search & Data Operations
"Find all orders over $500 from last month."
"Which products received the most 5-star reviews?"
"Bulk import these customer records into the 'customers' index."
Template Management
"Create an index template for logs with pattern 'logs-*'."
"Show me all my index templates."
"Delete the 'outdated_template' index template."
If you encounter issues, feel free to open an issue on the GitHub repository.
Appeared in Searches
- Using an AI Agent for Structured Search and Traversal in a Neo4j Database
- Tools and Components for Visual AI Code Editing and Chat Interfaces
- Servers for Cloud Architecture (AWS) and Platform Engineering with Oauth Integration for Documentation Access
- Natural Language to SQL Conversion and Executing MySQL Queries to Retrieve Data
- How to query a MySQL database