# WeMo MCP Server
Control WeMo smart home devices through AI assistants using natural language.
**mcp-name: io.github.apiarya/wemo**
[](https://modelcontextprotocol.io)
[](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports)
[](https://registry.modelcontextprotocol.io/?q=apiarya/wemo)
[](https://pypi.org/project/wemo-mcp-server/)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
## Table of Contents
- [Overview](#overview)
- [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
- [Quick Start](#quick-start)
- [Connect](#connect)
- [MCP Tools](#mcp-tools)
- [scan_network](#1-scan_network)
- [list_devices](#2-list_devices)
- [get_device_status](#3-get_device_status)
- [control_device](#4-control_device)
- [rename_device](#5-rename_device)
- [get_homekit_code](#6-get_homekit_code)
- [How It Works](#how-it-works)
- [Feature Comparison](#feature-comparison)
- [Development](#development)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [License](#license)
- [Acknowledgments](#acknowledgments)
## Overview
Seamlessly integrate WeMo smart home devices with AI assistants through the Model Context Protocol. Built on [pywemo](https://github.com/pywemo/pywemo), this server enables natural language control of your WeMo devices with intelligent multi-phase discovery.
### Example Usage
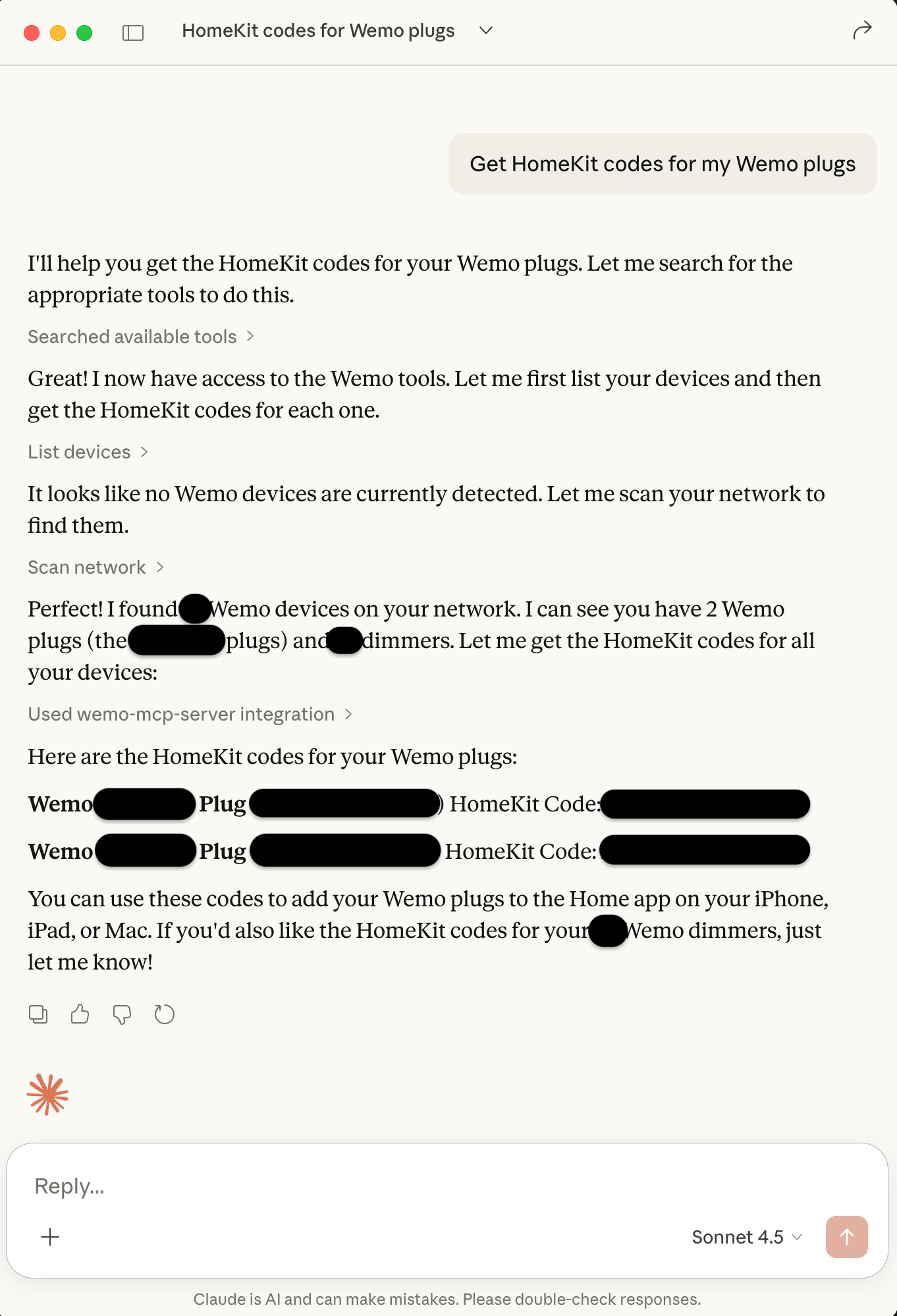
*Control WeMo devices through Claude Desktop with natural language - just ask in plain English!*
### Key Features
- **🔍 Smart Discovery** - Multi-phase scanning (UPnP/SSDP + network ports) with 100% reliability
- **⚡ Fast Scanning** - Parallel probes with 60 concurrent workers (~23-30s for full subnet)
- **🎛️ Full Control** - On/off/toggle/brightness control for all device types
- **✏️ Device Management** - Rename devices and extract HomeKit setup codes
- **📊 Real-time Status** - Query device state and brightness
- **💾 Smart Caching** - Automatic device caching for instant access
- **🔌 Universal** - Works with any MCP client (Claude, VS Code, Cursor, etc.)
---
## Prerequisites
All configurations use `uvx` (from the `uv` Python package manager) to run the server. Install [uv](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) first:
```bash
# macOS/Linux
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
# macOS with Homebrew
brew install uv
# Windows
powershell -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
```
After installation, restart your terminal and verify:
```bash
uvx --version
```
## Quick Start
Get started in seconds with Claude Code CLI:
```bash
claude mcp add wemo -- uvx wemo-mcp-server
```
---
## Connect
### One-Click Installation
Click your client to install instantly:
| Client | Install |
|--------|---------|
| **Claude Desktop** | [](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/quickstart/user) |
| **Claude Code CLI** | Run: `claude mcp add wemo -- uvx wemo-mcp-server` |
| **VS Code** | [](https://vscode.dev/redirect/mcp/install?name=wemo&config=%7B%22command%22%3A%22uvx%22%2C%22args%22%3A%5B%22wemo-mcp-server%22%5D%7D) |
| **Cursor** | [](cursor://anysphere.cursor-deeplink/mcp/install?name=wemo&config=eyJjb21tYW5kIjoidXZ4IiwiYXJncyI6WyJ3ZW1vLW1jcC1zZXJ2ZXIiXX0%3D) |
| **Cline** | [Manual config](#cline) (VS Code extension) |
| **Windsurf** | [Manual config](#windsurf) |
| **Zed** | [Manual config](#zed) |
| **Continue** | [Manual config](#continue) (VS Code extension) |
### Manual Configuration
#### Claude Desktop
Edit `~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json`:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"wemo": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
```
Restart Claude Desktop after saving.
#### VS Code
Edit `~/.vscode/mcp.json`:
```json
{
"servers": {
"wemo": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
```
Reload VS Code after saving.
#### Cursor
Edit `~/.cursor/mcp.json`:
```json
{
"servers": {
"wemo": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
```
Restart Cursor after saving.
#### Cline
Cline is a VS Code extension. Add to VS Code's `settings.json`:
```json
{
"mcp.servers": {
"wemo": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
```
Reload VS Code after saving.
#### Windsurf
Edit `~/.windsurf/mcp.json`:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"wemo": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
```
Restart Windsurf after saving.
#### Zed
Edit `~/.config/zed/settings.json`:
```json
{
"context_servers": {
"wemo": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
```
Restart Zed after saving.
#### Continue
Continue is a VS Code extension. Edit `~/.continue/config.json`:
```json
{
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "wemo",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["wemo-mcp-server"]
}
]
}
```
Reload VS Code after saving.
---
## MCP Tools
### 1. scan_network
Discover WeMo devices on your network using intelligent multi-phase scanning.
**Example Prompts:**
- "Scan for WeMo devices on my network"
- "Find all WeMo devices"
- "Discover devices on 192.168.1.0/24"
**Example Response:**
```
Found 12 WeMo devices in 23.5 seconds:
1. Office Light (Dimmer) - 192.168.1.100 - OFF
2. Living Room (Switch) - 192.168.1.101 - ON
3. Bedroom Lamp (Dimmer) - 192.168.1.102 - OFF
...
```
### 2. list_devices
List all devices cached from previous scans.
**Example Prompts:**
- "List all my WeMo devices"
- "Show me all devices"
- "What devices do you know about?"
**Example Response:**
```
12 devices in cache:
- Office Light (Dimmer) at 192.168.1.100
- Living Room (Switch) at 192.168.1.101
- Bedroom Lamp (Dimmer) at 192.168.1.102
...
```
### 3. get_device_status
Get current state and information for a specific device.
**Example Prompts:**
- "Is the office light on?"
- "What's the status of the bedroom lamp?"
- "Check the living room switch"
- "What's the brightness of office light?"
**Example Response:**
```
Office Light (Dimmer):
- State: OFF
- Brightness: 75%
- IP: 192.168.1.100
- Model: DimmerLongPress
```
### 4. control_device
Control a WeMo device (on/off/toggle/brightness).
**Example Prompts:**
- "Turn on the office light"
- "Turn off the living room"
- "Toggle the bedroom lamp"
- "Set office light to 75%"
- "Dim the bedroom lamp to 50%"
**Example Response:**
```
✓ Office Light turned ON
Brightness set to 75%
Current state: ON
```
### 5. rename_device
Rename a WeMo device (change its friendly name).
**Example Prompts:**
- "Rename Office Dimmer to Office Light"
- "Change the name of the bedroom device to Bedroom Lamp"
- "Call the living room switch 'Main Light'"
**Example Response:**
```
✓ Device renamed successfully
'Office Dimmer' → 'Office Light'
IP: 192.168.1.100
The new name will appear in the WeMo app and all control interfaces.
```
### 6. get_homekit_code
Get the HomeKit setup code for a WeMo device.
**Example Prompts:**
- "Get the HomeKit code for Office Light"
- "What's the HomeKit setup code for the bedroom lamp?"
- "Show me the HomeKit code for all devices"
**Example Response:**
```
HomeKit Setup Code for 'Office Light':
123-45-678
Use this code to add the device to Apple Home.
```
**Note:** Not all WeMo devices support HomeKit. If a device doesn't support HomeKit, you'll get an error message.
## How It Works
### Multi-Phase Discovery
The server uses a three-phase discovery process optimized for reliability:
1. **Phase 1 - UPnP/SSDP Discovery (Primary)**
- Multicast discovery finds all responsive devices (~12s)
- Most reliable method, finds devices that don't respond to port probes
- Uses pywemo's built-in discovery mechanism
2. **Phase 2 - Network Port Scanning (Backup)**
- Parallel probing of WeMo ports (49152-49155) across subnet
- 60 concurrent workers for fast scanning (~10s for 254 IPs)
- Catches devices missed by UPnP
3. **Phase 3 - Device Verification (Backup)**
- HTTP verification of active IPs via /setup.xml
- Parallel verification with 60 workers
- Validates and extracts device information
This approach achieves **100% device discovery reliability** while maintaining fast scan times (23-30 seconds for complete networks).
## Feature Comparison
### MCP Server vs wemo-ops-center
Comparison of features between this MCP server and the main [wemo-ops-center](https://github.com/qrussell/wemo-ops-center) project:
| Feature | wemo-ops-center | MCP Server | Notes |
|---------|-----------------|------------|-------|
| **Device Discovery** | ✅ UPnP + Port Scan | ✅ Implemented | Multi-phase discovery with 100% reliability |
| **Device Control** | ✅ On/Off/Toggle | ✅ Implemented | Includes brightness control for dimmers |
| **Device Status** | ✅ Real-time | ✅ Implemented | Query by name or IP address |
| **Device Rename** | ✅ Friendly names | ✅ Implemented | Updates device cache automatically |
| **HomeKit Codes** | ✅ Extract codes | ✅ Implemented | For HomeKit-compatible devices |
| **Multi-subnet** | ✅ VLAN support | ❌ Planned | Currently single subnet per scan |
| **WiFi Provisioning** | ✅ Smart setup | ❌ Not planned | Requires PC WiFi connection changes |
| **Scheduling** | ✅ Time + Solar | ❌ Not planned | Requires persistent daemon (incompatible with MCP model) |
| **Maintenance Tools** | ✅ Resets | ❌ Not planned | Factory reset, clear WiFi, clear data |
| **Profile Management** | ✅ Save/Load | ❌ Not planned | WiFi credential profiles for bulk setup |
| **User Interface** | ✅ GUI + Web | ❌ N/A | MCP uses AI assistant interface |
**Legend:**
- ✅ **Implemented** - Feature is available
- ❌ **Not planned** - Feature conflicts with MCP architecture or use case
- ❌ **Planned** - Feature could be added in future
**Why some features aren't planned for MCP:**
- **Scheduling**: Requires 24/7 background daemon polling. MCP servers are typically invoked on-demand by AI assistants, not run as persistent services.
- **WiFi Provisioning**: Requires changing the host PC's WiFi connection to device setup networks, which is disruptive and platform-specific.
- **Maintenance Tools**: Destructive operations (factory reset, etc.) better suited for dedicated GUI with confirmation dialogs.
**Current MCP Coverage:** 5 of 11 core features (45%) - focused on device discovery, monitoring, and control use cases that fit the MCP model.
## Development
### Setup
```bash
git clone https://github.com/apiarya/wemo-mcp-server.git
cd wemo-mcp-server
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
uv sync --dev
```
### Running Tests
```bash
# E2E tests (requires WeMo devices on network)
python tests/test_e2e.py
# Unit tests
pytest tests/test_server.py -v
```
### Using Development Version
In your MCP client config, use:
```json
{
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "wemo_mcp_server"],
"env": {
"PYTHONPATH": "/path/to/mcp/src"
}
}
```
## Contributing
Contributions welcome! Please:
1. Fork the repository
2. Create a feature branch (`git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature`)
3. Make your changes with tests
4. Run the test suite (`python tests/test_e2e.py`)
5. Commit your changes (`git commit -m 'Add amazing feature'`)
6. Push to the branch (`git push origin feature/amazing-feature`)
7. Open a Pull Request
## License
MIT License - see [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for details.
## Acknowledgments
- Built with [Model Context Protocol SDK](https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/python-sdk)
- Uses [pywemo](https://github.com/pywemo/pywemo) for WeMo device communication
- Related to the [wemo-ops-center](https://github.com/qrussell/wemo-ops-center) project (desktop and server applications)