This server enables AI assistants to convert text to speech using VOICEVOX Engine with multi-character conversations and advanced playback control.
Core Capabilities:
Text-to-Speech Playback - Convert and play text with multi-line support, per-line speaker assignment (e.g., "1:Hello\n2:World"), configurable speed, queue management, and synchronous/asynchronous playback options
Speaker Management - List available speakers, get detailed speaker information by UUID, and configure default speakers with per-project overrides
Audio File Generation - Create and save audio files from text to specified paths
Playback Control - Stop current audio and clear queue, with immediate or queued playback modes
Voice Synthesis Query Generation - Generate intermediate query objects for advanced synthesis use cases
Health Check - Verify VOICEVOX Engine connectivity and status
Key Features:
Cross-platform compatibility (Windows, macOS, Linux, WSL)
Streaming playback with ffplay for low latency
HTTP mode for remote connections
Configurable defaults via environment variables, command-line arguments, and custom HTTP headers in
mcp.jsonTool management with ability to disable specific tools and restrict options
Click on "Install Server".
Wait a few minutes for the server to deploy. Once ready, it will show a "Started" state.
In the chat, type
@followed by the MCP server name and your instructions, e.g., "@VOICEVOX TTS MCPSay 'Welcome to the stream!' using speaker 3"
That's it! The server will respond to your query, and you can continue using it as needed.
Here is a step-by-step guide with screenshots.
VOICEVOX TTS MCP
English | 日本語
A text-to-speech MCP server using VOICEVOX
🎮 Try the Browser Demo — Test VoicevoxClient directly in your browser
What You Can Do
Make your AI assistant speak — Text-to-speech from MCP clients like Claude Desktop
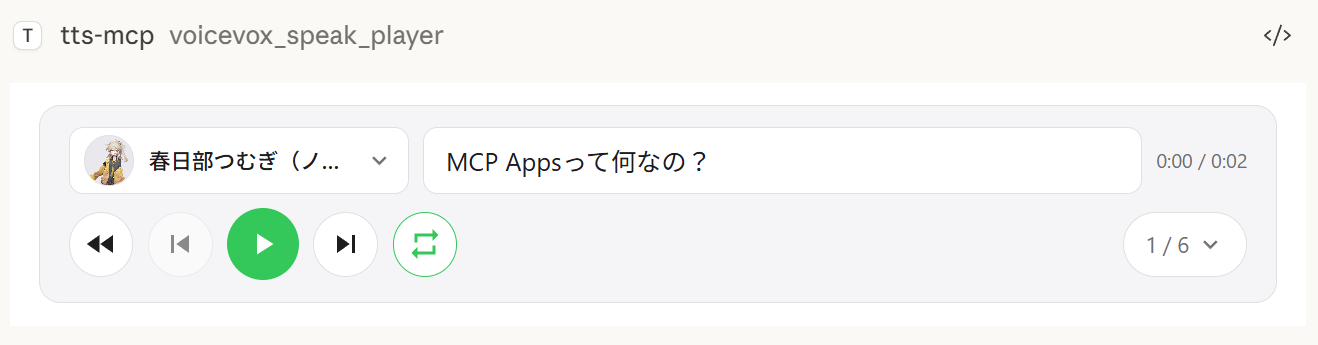
UI Audio Player (MCP Apps) — Play audio directly in the chat with an interactive player (ChatGPT / Claude Desktop / Claude Web etc.)
Multi-character conversations — Switch speakers per segment in a single call
Smooth playback — Queue management, immediate playback, prefetching, streaming
Cross-platform — Works on Windows, macOS, Linux (including WSL)
UI Audio Player (MCP Apps)

The voicevox_speak_player tool uses MCP Apps to render an interactive audio player directly inside the chat. Unlike the standard voicevox_speak tool which plays audio on the server, audio is played on the client side (in the browser/app) — no audio device needed on the server.
Features
Client-side playback — Audio plays in Claude Desktop's chat, not on the server. Works even over remote connections.
Play/Pause controls — Full playback controls embedded in the conversation
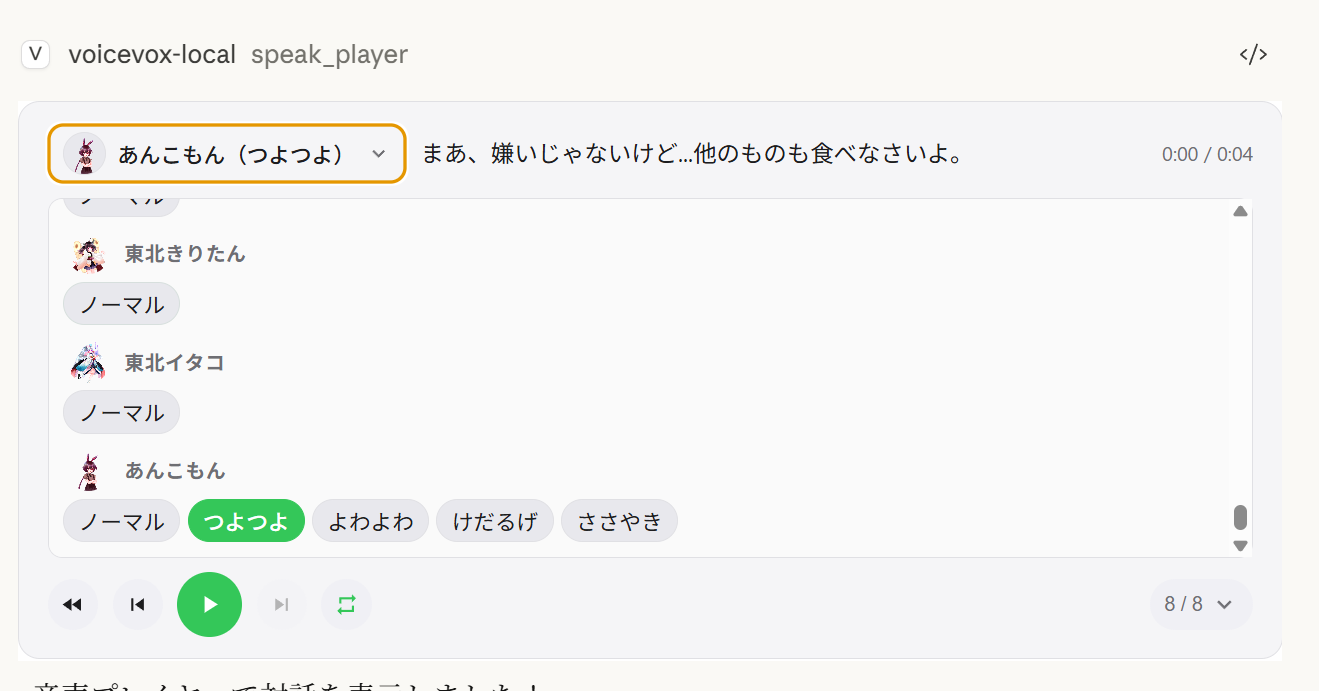
Multi-speaker dialogue — Sequential playback of multiple speakers in one player with track navigation
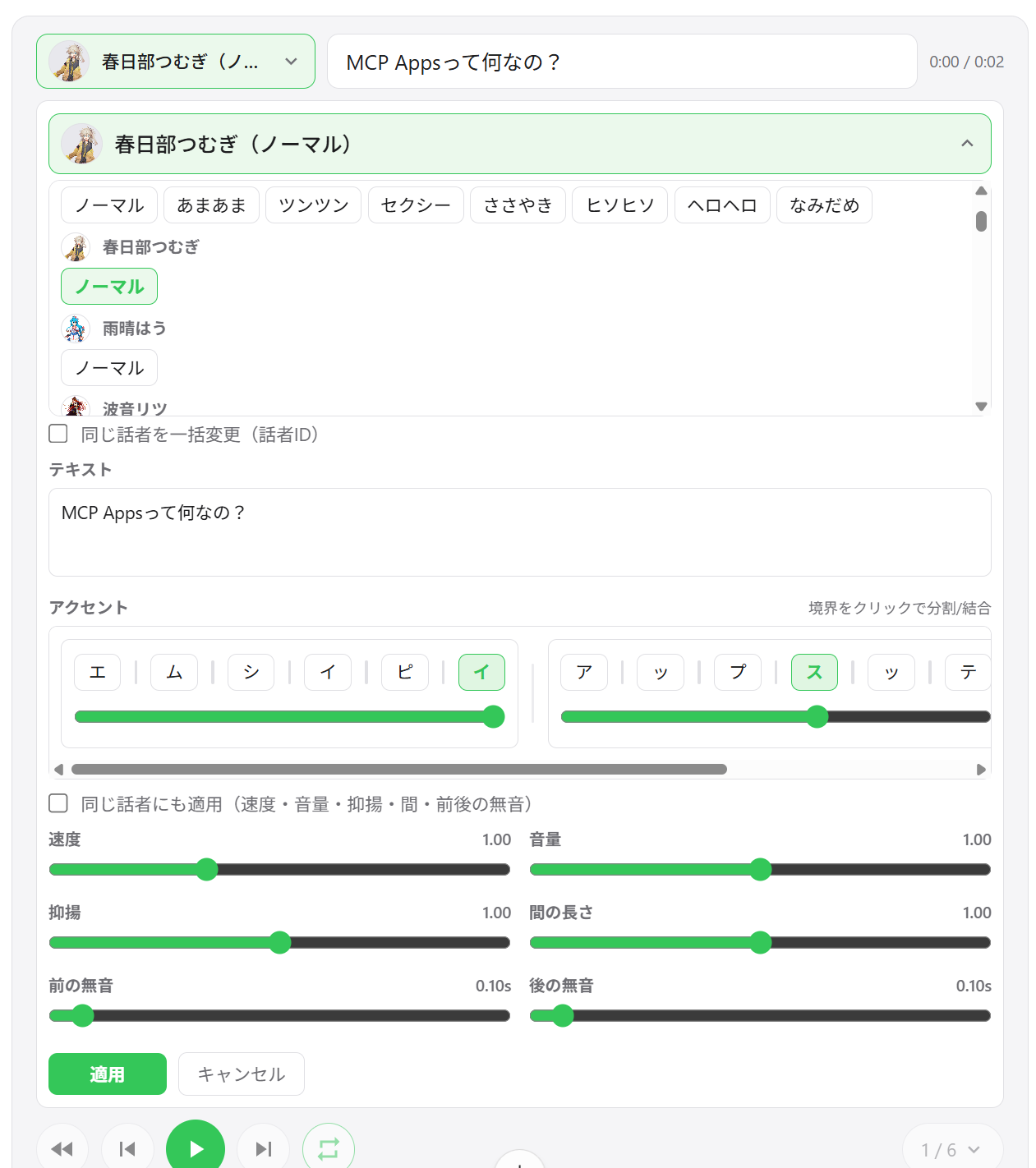
Speaker switching — Change the voice of any segment directly from the player UI
Segment editing — Adjust speed, volume, intonation, pause length, and pre/post silence per segment
Accent phrase editing — Edit accent positions and mora pitch directly in the UI
Add / delete / reorder segments — Drag-and-drop track reordering; add new segments inline
WAV export — Save all tracks as numbered WAV files and open the output folder automatically
User dictionary manager — Add, edit, and delete VOICEVOX user dictionary words with preview playback
Cross-session state restore — Player state is persisted on the server; reopening the chat restores previous tracks
Export behavior by environment:
Save and openalways exports WAV files. If opening the file explorer is not supported, export still succeeds and the save path is shown in the UI.Choose output folderuses a native directory picker on Windows/macOS. On unsupported environments, this action falls back to the default export directory.
Multi-speaker playback | Track list | Segment editing |
|
|
|
Speaker selection | Dictionary manager | WAV export |
|
|
|
Supported Clients
Client | Connection | Notes |
ChatGPT | HTTP (remote) | Requires |
Claude Desktop | stdio (local) | Works out of the box |
Claude Desktop | HTTP (via mcp-remote) | Do not set |
Note:
speak_playerrequires a host that supports MCP Apps. In hosts without MCP Apps support, the tool is not available andspeak(server-side playback) can be used instead.
Player MCP Tools
Tool | Description |
| Create a new player session and display the UI. Returns |
| Update all segments for an existing player (new |
| Read the current player state (paginated) for AI tuning. |
| Open the user dictionary manager UI. |
Quick Start
Requirements
Node.js 18.0.0 or higher (or Bun) or Docker
VOICEVOX Engine (must be running; included in Docker Compose)
ffplay (optional, recommended — not needed with Docker)
Installing FFplay
ffplay is a lightweight player included with FFmpeg that supports playback from stdin. When available, it automatically enables low-latency streaming playback.
💡 FFplay is optional. Without it, playback falls back to temp file-based playback (Windows: PowerShell, macOS: afplay, Linux: aplay, etc.).
Easy setup: One-liner installation for each OS (see steps below)
Required:
ffplaymust be in PATH (restart terminal/apps after installation)
Installation examples:
Windows (any of these)
Winget:
winget install --id=Gyan.FFmpeg -eChocolatey:
choco install ffmpegScoop:
scoop install ffmpegOfficial builds: Download from https://www.gyan.dev/ffmpeg/builds/ or https://github.com/BtbN/FFmpeg-Builds and add the
binfolder to PATH
macOS
Homebrew:
brew install ffmpeg
Linux
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y ffmpegFedora:
sudo dnf install -y ffmpegArch:
sudo pacman -S ffmpeg
PATH Setup:
Windows: Add
...\ffmpeg\binto environment variables, then restart PowerShell/terminal and editor (Claude/VS Code, etc.)Verify:
powershell -c "$env:Path"should include the ffmpeg path
macOS/Linux: Usually auto-detected. Check with
echo $PATHif needed, restart shell.MCP clients (Claude Desktop/Code): Restart the app to reload PATH.
Verification:
ffplay -versionIf version info is displayed, installation is complete. CLI/MCP will automatically detect ffplay and use stdin streaming playback.
3 Steps to Get Started
1. Start VOICEVOX Engine
2. Add to Claude Desktop config file
Config file location:
Windows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.jsonmacOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"tts-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox"]
}
}
}💡 If using Bun, just replace
npxwithbunx:"command": "bunx", "args": ["@kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox"]
3. Restart Claude Desktop
That's it! Ask Claude to "say hello" and it will speak!
Quick Start with Docker
You can run both the MCP server and VOICEVOX Engine with a single command using Docker Compose. No Node.js or VOICEVOX installation required.
1. Start the containers
docker compose up -dThis starts the VOICEVOX Engine and the MCP server (HTTP mode on port 3000).
2. Add to Claude Desktop config file (using mcp-remote)
{
"mcpServers": {
"tts-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "mcp-remote", "http://localhost:3000/mcp"]
}
}
}3. Restart Claude Desktop
Limitations (Docker): The Docker container has no audio device, so the
voicevox_speaktool (server-side playback) is disabled by default. Usevoicevox_speak_playerinstead — it plays audio on the client side (in Claude Desktop) and works without any audio device on the server. See UI Audio Player for details.
MCP Tools
voicevox_speak — Text-to-Speech
The main feature callable from Claude.
Parameter | Description | Default |
| Text to speak (multiple segments separated by newlines) | Required |
| Speaker ID | 1 |
| Playback speed | 1.0 |
| Immediate playback (clears queue) | true |
| Wait for playback completion | false |
Examples:
// Simple text
{ "text": "Hello" }
// Specify speaker
{ "text": "Hello", "speaker": 3 }
// Different speakers per segment
{ "text": "1:Hello\n3:Nice weather today" }
// Wait for completion (synchronous processing)
{ "text": "Wait for this to finish before continuing", "waitForEnd": true }Tool | Description |
| Speak with UI audio player (disable with |
| Check VOICEVOX Engine connection |
| Get list of available speakers |
| Stop playback and clear queue |
| Generate audio file |
Configuration
VOICEVOX Settings
Variable | Description | Default |
| Engine URL |
|
| Default speaker ID |
|
| Playback speed |
|
Playback Options
Variable | Description | Default |
| Streaming playback (requires |
|
| Immediate playback |
|
| Wait for playback start |
|
| Wait for playback end |
|
Restriction Settings
Restrict AI from specifying certain options.
Variable | Description |
| Restrict |
| Restrict |
| Restrict |
Disable Tools
# Disable unnecessary tools
export VOICEVOX_DISABLED_TOOLS=speak_player,synthesize_fileUI Player Settings
Variable | Description | Default |
| Widget domain for UI player (required for ChatGPT, e.g. | (unset) |
| Auto-play audio in UI player |
|
| Enable track export(download) from UI player ( |
|
| Default output directory for exported tracks (also used as fallback when folder picker is unavailable) |
|
| Directory for player cache files ( |
|
| Enable persistent audio cache on disk ( |
|
| Audio cache retention in days ( |
|
| Audio cache size cap in MB ( |
|
| Path of persisted player state JSON |
|
Server Settings
Variable | Description | Default |
| Enable HTTP mode |
|
| HTTP port |
|
| HTTP host |
|
| Allowed hosts (comma-separated) |
|
| Allowed origins (comma-separated) |
|
| Required API key for | (unset) |
Command line arguments take priority over environment variables.
# Basic settings
npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox --url http://192.168.1.100:50021 --speaker 3 --speed 1.2
# HTTP mode
npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox --http --port 8080
# With restrictions
npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox --restrict-immediate --restrict-wait-for-end
# Disable tools
npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox --disable-tools speak_player,synthesize_fileArgument | Description |
| Show help |
| Show version |
| VOICEVOX Engine URL |
| Default speaker ID |
| Playback speed |
| Streaming playback |
| Immediate playback |
| Wait for start |
| Wait for end |
| Restrict immediate |
| Restrict waitForStart |
| Restrict waitForEnd |
| Disable tools |
| Auto-play in UI player |
| Enable/disable track export(download) in UI player |
| Default output directory for exported tracks |
| Player cache directory |
| Persisted player state file path |
| Enable/disable disk audio cache for player |
| Audio cache retention days ( |
| Audio cache size cap in MB ( |
| HTTP mode |
| HTTP port |
| HTTP host |
| Allowed hosts (comma-separated) |
| Allowed origins (comma-separated) |
| Required API key for |
For remote connections:
Start Server:
# Linux/macOS
MCP_HTTP_MODE=true MCP_HTTP_PORT=3000 npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox
# Windows PowerShell
$env:MCP_HTTP_MODE='true'; $env:MCP_HTTP_PORT='3000'; npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevoxClaude Desktop Config (using mcp-remote):
{
"mcpServers": {
"tts-mcp-proxy": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "mcp-remote", "http://localhost:3000/mcp"]
}
}
}Per-Project Speaker Settings
With Claude Code, you can configure different default speakers per project using custom headers in .mcp.json:
Header | Description |
| Default speaker ID for this project |
| API key when |
Example
{
"mcpServers": {
"tts": {
"type": "http",
"url": "http://localhost:3000/mcp",
"headers": {
"X-Voicevox-Speaker": "113",
"X-API-Key": "your-api-key"
}
}
}
}This allows each project to use a different voice character automatically.
Priority order:
Explicit
speakerparameter in tool call (highest)Project default from
X-Voicevox-SpeakerheaderGlobal
VOICEVOX_DEFAULT_SPEAKERsetting (lowest)
Connecting from WSL to an MCP server running on Windows:
1. Get Windows Host IP from WSL
# Method 1: From default gateway
ip route show | grep -oP 'default via \K[\d.]+'
# Usually in the format 172.x.x.1
# Method 2: From /etc/resolv.conf (WSL2)
cat /etc/resolv.conf | grep nameserver | awk '{print $2}'2. Start Server on Windows
Add the WSL gateway IP to MCP_ALLOWED_HOSTS to allow access from WSL:
$env:MCP_HTTP_MODE='true'
$env:MCP_ALLOWED_HOSTS='localhost,127.0.0.1,172.29.176.1'
npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevoxOr with CLI arguments:
npx @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox --http --allowed-hosts "localhost,127.0.0.1,172.29.176.1"3. WSL Configuration (.mcp.json)
{
"mcpServers": {
"tts": {
"type": "http",
"url": "http://172.29.176.1:3000/mcp"
}
}
}⚠️ Within WSL,
localhostrefers to WSL itself. Use the WSL gateway IP to access the Windows host.
To use with ChatGPT, deploy the MCP server in HTTP mode to the cloud with access to a VOICEVOX Engine.
1. Deploy to the Cloud
Deploy with Docker to Render, Railway, etc. (Dockerfile included).
2. Set Up VOICEVOX Engine
Run VOICEVOX Engine locally and expose it via ngrok, or deploy it alongside the MCP server.
3. Configure Environment Variables
Variable | Example | Description |
|
| VOICEVOX Engine URL |
|
| Enable HTTP mode |
|
| Deployed hostname |
|
| Widget domain for UI player (required for ChatGPT) |
|
| Disable server-side playback (no audio device) |
|
| Disable export feature (files cannot be downloaded from cloud) |
4. Add Connector in ChatGPT
Go to ChatGPT Settings → Connectors → Add MCP server URL (https://your-app.onrender.com/mcp).
The basic steps are the same as ChatGPT, but the VOICEVOX_PLAYER_DOMAIN value is different.
Claude Web requires ui.domain to be a hash-based dedicated domain. Compute it with the following command:
node -e "console.log(require('crypto').createHash('sha256').update('Your MCP server URL').digest('hex').slice(0,32)+'.claudemcpcontent.com')"Example: If your MCP server URL is https://your-app.onrender.com/mcp:
node -e "console.log(require('crypto').createHash('sha256').update('https://your-app.onrender.com/mcp').digest('hex').slice(0,32)+'.claudemcpcontent.com')"
# Example output: 48fb73a6...claudemcpcontent.comSet this output value as VOICEVOX_PLAYER_DOMAIN.
Note: Since ChatGPT and Claude Web require different
VOICEVOX_PLAYER_DOMAINvalues, a single instance cannot serve both clients simultaneously. Deploy separate instances for each, or switch the environment variable depending on your target client.
Troubleshooting
1. Check if VOICEVOX Engine is running
curl http://localhost:50021/speakers2. Check platform-specific playback tools
OS | Required Tool |
Linux | One of |
macOS |
|
Windows | PowerShell (pre-installed) |
Check package installation:
npm list -g @kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevoxVerify JSON syntax in config file
Restart the client
Package Structure
Package | Description |
| MCP server |
General-purpose VOICEVOX client library (can be used independently) | |
| React-based audio player UI for browser playback |
Setup
git clone https://github.com/kajidog/mcp-tts-voicevox.git
cd mcp-tts-voicevox
pnpm installCommands
Command | Description |
| Build all packages |
| Run tests |
| Run lint |
| Start dev server |
| Dev with stdio mode |
| Start dev server with Bun |
| Start HTTP dev server with Bun |
License
ISC